North Ossetia-Alania
| Republic of North Ossetia-Alania Республика Северная Осетия-Алания (Russian) Республикӕ Цӕгат Ирыстон-Алани (Ossetic) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — Republic — | |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
| Political status | |||||
| Country | Russia | ||||
| Federal district | North Caucasian[2] | ||||
| Economic region | North Caucasus[3] | ||||
| Established | December 5, 1936[4] | ||||
| Capital | Vladikavkaz | ||||
| Government (as of October 2015) | |||||
| • Head[5] | Vyacheslav Bitarov (acting)[6] | ||||
| • Legislature | Parliament[5] | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Area (as of the 2002 Census)[7] | |||||
| • Total | 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) | ||||
| Area rank | 79th | ||||
| Population (2010 Census)[8] | |||||
| • Total | 712,980 | ||||
| • Rank | 64th | ||||
| • Density[9] | 89.12/km2 (230.8/sq mi) | ||||
| • Urban | 63.8% | ||||
| • Rural | 36.2% | ||||
| Population (January 2015 est.) | |||||
| • Total | 705,270[10] | ||||
| Time zone(s) | MSK (UTC+03:00)[11] | ||||
| ISO 3166-2 | RU-SE | ||||
| License plates | 15 | ||||
| Official languages | Russian;[12] Ossetian[13] | ||||
| Official website | |||||
The Republic of North Ossetia-Alania (Russian: Республика Северная Осетия-Алания, tr. Respublika Severnaya Osetiya-Alaniya; IPA: [rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə ˈsʲevʲɪrnəjə ɐˈsʲetʲɪjə ɐˈlanʲɪjə]; Ossetian: Республикӕ Цӕгат Ирыстон-Алани, Respublikæ Cægat Iryston-Alani, Ossetic pronunciation: [resˈpublikə t͡səˈgat irɨˈʃton-aˈlani] ![]() listen ) is a federal subject of Russia (a republic). Its population according to the 2010 Census was 712,980.[8] Its capital is the city of Vladikavkaz.
listen ) is a federal subject of Russia (a republic). Its population according to the 2010 Census was 712,980.[8] Its capital is the city of Vladikavkaz.
Name
In the last years of the Soviet Union, as nationalist movements swept throughout the Caucasus, many intellectuals in the North Ossetian ASSR called for the revival of the name of Alania, a medieval kingdom of the Alans. The term of "Alania" quickly became popular in Ossetian daily life through the names of various enterprises, a TV channel, political and civic organizations, publishing house, football team, etc. In November 1994, the name of "Alania" was officially added to the republican title (Republic of North Ossetia-Alania).[14]
Geography

The republic is located in the North Caucasus. The northern part of the republic is situated in the Stavropol Plain. 22% of the republic's territory is covered by forests.
- Area: 8,000 square kilometers (3,100 sq mi)
- Borders:
- internal: Kabardino-Balkar Republic (W/NW/N), Stavropol Krai (N), Chechen Republic (NE/E), Republic of Ingushetia (E/SE)
- international: Georgia (including South Ossetia) (SE/S/SW)
- Highest point: Mount Kazbek (5,033 meters (16,512 ft))
- Maximum north-south distance: 130 kilometers (81 mi)
- Maximum east-west distance: 120 kilometers (75 mi)
Rivers
All of the republic's rivers belong to the drainage basin of the Terek River. Major rivers include:
- Terek River (~600 km)
- Urukh River (104 km)
- Ardon River (101 km)
- Kambileyevka River (99 km)
- Gizeldon River (81 km)
- Fiagdon River
- Sunzha River (278 km)
Mountains
All of the mountains located on the territory of the republic are a part of the Caucasus. Mount Kazbek is the highest point (5,033 m), with Mount Dzhimara being the second highest (4,780 m).
Natural resources
Natural resources include minerals (copper, silver, zinc), timber, mineral waters, hydroelectric power, and untapped reserves of oil and gas.
Climate
Climate is moderately continental.
- Average January temperature: −5 °C (23 °F)
- Average July temperature: +24 °C (75 °F)
- Average annual precipitation: 400–700 millimeters (16–28 in) in the plains; over 1,000 millimeters (39 in) in the mountains.
History

Early history
The territory of North Ossetia was first inhabited by Caucasian tribes. Some Nomadic Alans settled in the region in the 7th century, forming the kingdom of Alania. It was eventually converted to Christianity by missionaries from Byzantium. Alania greatly profited from the Silk Road which passed through its territory.
After the Middle Ages, the Mongols' and Tartars' repeated invasions decimated the population, now known as the Ossetians. Islam was introduced to the region in the 17th century by Kabardians. Conflicts between the Khanate of Crimea and the Ottoman Empire eventually pushed Ossetia into an alliance with Imperial Russia in the 18th century. Soon, Russia established a military base in the capital, Vladikavkaz, making it the first Russian-controlled area in the northern Caucasus. By 1806, Ossetia was under complete Russian control.
Russian/Soviet rule
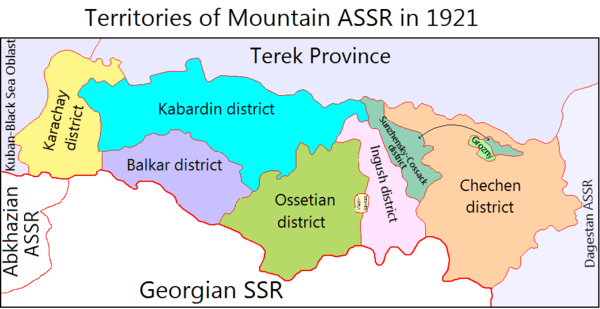
The Russians' rule led to rapid development of industry and railways which overcame its isolation. The first books from the area came during the late 18th century, and became part of the Terskaya Region of Russia in the mid-19th century.
The Russian Revolution of 1917 resulted in North Ossetia being merged into the Soviet Mountain Republic in 1921. It then became the North Ossetian Autonomous Oblast on 7 July 1924, then merged into the North Ossetian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic on 5 December 1936. In World War II, it was subject to a number of attacks by Nazi German invaders unsuccessfully trying to seize Vladikavkaz in 1942.
The North Ossetian SSR declared itself the autonomous republic of the Soviet Union on June 20, 1990. Its name was changed to Republic of North Ossetia-Alania in 1991.
The dissolution of the Soviet Union posed particular problems for the Ossetian people, who were divided between North Ossetia, which was part of the Russian SFSR, and South Ossetia, part of the Georgian SSR. In December 1990, the Supreme Soviet of Georgia abolished the autonomous Ossetian enclave amid the rising ethnic tensions in the region, which was further fanned by the Moscow; a lot of the conflict zone population, faced with the ethnic genocide, was forced to flee across the border to either North Ossetia or Georgia proper. Some 70,000 South Ossetian refugees were resettled in North Ossetia, sparking clashes with the predominantly Ingush population in the Prigorodny District, which sparked the Ossetian–Ingush conflict. As well as dealing with the effects of the conflict in South Ossetia, North Ossetia has had to deal with refugees and the occasional spillover of fighting from the wars around them. The so-called "peacekeeping mission" by the Moscow pretty much resulted in the territory being military reoccupied by the Russian Federation, which ignored international borders. Starting with the 2008 invasion Russian Federation military kept illegally moving borders further inside Georgia despite international pressure.
Administrative divisions
Economy

In recent years, North Ossetia-Alania's economic development has been successful; the indicators of the republic's social and economic development in 2005–2007 revealed a stable growth of all sectors of the economy and major social parameters. The nature and climatic conditions of the republic contribute to the successful development of various economic sectors, which is compounded by the abundance of natural resources. Gross regional product pro capita of the region in 2006 was 61,000 rubles ($2,596), and increased 30% in the 2005–2007 time period.[17] GRP pro capita in 2007 was 76 455 rubles.[18] In 2005–2007, the average monthly wage in North Ossetia-Alania doubled, with the actual cash earnings increased by 42.5 percent. In terms of the average monthly wage growth, the republic ranks first in the North Caucasus.[17]
The regional government's economic priorities include industrial growth, development of small enterprise, spas, and resorts, and strengthening the budgetary and tax discipline.[19]
Natural resources, agriculture, and industry
The most widespread resources are zinc- and lead-containing complex ores. There are deposits of limestone, dolomites, marble and touchstone. There is also a large availability of construction materials, such as clay, sand and gravel. The local oil deposit reserves are estimated at 10 million metric tons.[17]
Agricultural sector is varied and specializes in the cultivation of wheat, corn, and sunflowers; horticulture; viticulture; and cattle and sheep breeding.[20][21]
North Ossetia's industry is mainly concentrated in Vladikavkaz. Major companies located here include Elektrotsink, Gazoapparat, an instrument-making plant, Elektrokontraktor, a factory producing automotive electrical equipment, a large-panel construction complex, and companies in the food industry. The Sadonsky industrial center has grown around the mining and forest industries.[21]
Tourism
Despite the proximity to Chechnya, North Ossetia is making efforts to develop its tourist industry.[22] Projects under a program for spa, resort, and tourism development have been successfully implemented in the mountainous part of the republic, according to the head of the regional government.[19] There are nearly 3000 historical monuments in the republic and more than half of the its area is occupied bv Alania National Park, the North Ossetia National Preserve, and game preserves. There are more than 250 therapeutic, mineral, and freshwater springs in the republic with estimated daily reserves of 15,000 cubic meters. Besides providing the basis for health spas, these mineral waters also have the potential to be bottled and sold. North Ossetian mineral waters are known for their unique qualities, as well as special mineral composition.[21][22]
Infrastructure
In terms of its infrastructure, North Ossetia-Alania ranks second in the Southern Federal District and 10th in the nation.[17] The republic has some of the most extensive telecommunication networks in the North Caucasus region and in Russia. It ranks first in terms of its telecom network installations in the Southern Federal District.
The republic ranks fourth in Russia in terms of its paved roads, and its expanding transport and logistics complex provides communication networks between Russia and the South Caucasus, as well as Central Asia. The complex includes two federal highways (Georgian Military Road connects Vladikavkaz with Transcaucasia) running across the Greater Caucasus Range, two customs checkpoints for cars, a developed railway network, Vladikavkaz international airport, and well-equipped transport terminals.[17]
Demographics
Population: 712,980 (2010 Census);[8] 710,275 (2002 Census);[23] 634,009 (1989 Census).[24]
Number of Refugees: 12,570 [25]
Vital statistics
| Average population (1000s) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 554 | 9,731 | 3,964 | 5,767 | 17.6 | 7.2 | 10.4 | |
| 1975 | 575 | 10,368 | 4,664 | 5,704 | 18.0 | 8.1 | 9.9 | |
| 1980 | 598 | 10,135 | 5,821 | 4,314 | 16.9 | 9.7 | 7.2 | |
| 1985 | 617 | 11,598 | 6,047 | 5,551 | 18.8 | 9.8 | 9.0 | |
| 1990 | 649 | 10,967 | 6,166 | 4,801 | 16.9 | 9.5 | 7.4 | 2.23 |
| 1991 | 679 | 10,985 | 6,694 | 4,291 | 16.2 | 9.9 | 6.3 | 2.09 |
| 1992 | 683 | 10,048 | 7,125 | 2,923 | 14.7 | 10.4 | 4.3 | 1.89 |
| 1993 | 661 | 8,251 | 7,872 | 379 | 12.5 | 11.9 | 0.6 | 1.67 |
| 1994 | 666 | 8,806 | 8,329 | 477 | 13.2 | 12.5 | 0.7 | 1.79 |
| 1995 | 674 | 8,781 | 8,574 | 207 | 13.0 | 12.7 | 0.3 | 1.78 |
| 1996 | 680 | 8,043 | 8,514 | −471 | 11.8 | 12.5 | −0.7 | 1.62 |
| 1997 | 681 | 7,758 | 8,378 | −620 | 11.4 | 12.3 | −0.9 | 1.56 |
| 1998 | 683 | 7,767 | 8,188 | −421 | 11.4 | 12.0 | −0.6 | 1.56 |
| 1999 | 689 | 7,195 | 8,412 | −1,217 | 10.4 | 12.2 | −1.8 | 1.43 |
| 2000 | 699 | 7,179 | 8,626 | −1,447 | 10.3 | 12.3 | −2.0 | 1.39 |
| 2001 | 707 | 7,317 | 8,205 | −888 | 10.3 | 11.6 | −1.3 | 1.39 |
| 2002 | 709 | 7,874 | 8,753 | −879 | 11.1 | 12.3 | −1.2 | 1.47 |
| 2003 | 709 | 7,978 | 8,952 | −974 | 11.3 | 12.6 | −1.4 | 1.48 |
| 2004 | 707 | 7,893 | 8,663 | −770 | 11.2 | 12.2 | −1.1 | 1.46 |
| 2005 | 706 | 7,894 | 8,654 | −760 | 11.2 | 12.3 | −1.1 | 1.46 |
| 2006 | 706 | 8,308 | 8,138 | 170 | 11.8 | 11.5 | 0.2 | 1.53 |
| 2007 | 706 | 9,556 | 7,806 | 1,750 | 13.5 | 11.1 | 2.5 | 1.76 |
| 2008 | 708 | 9,981 | 7,975 | 2,006 | 14.1 | 11.3 | 2.8 | 1.83 |
| 2009 | 710 | 10,017 | 7,987 | 2,030 | 14.1 | 11.3 | 2.9 | 1.84 |
| 2010 | 712 | 10,303 | 7,748 | 2,555 | 14.5 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 1.88 |
| 2011 | 715 | 10,375 | 7,720 | 2,655 | 14.5 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 1.88 |
| 2012 | 708 | 10,801 | 7,525 | 3,276 | 15.3 | 10.6 | 4.7 | 1.96 |
| 2013 | 705 | 10,760 | 7,394 | 3,366 | 15.3 | 10.5 | 4.8 | 1.98 |
| 2014 | 705 | 10,798 | 7,554 | 3,244 | 15.3 | 10.7 | 4.6 | 2.01 |
| 2015 | 704 | 10,341 | 7,558 | 2,783 | 14.6 | 10.7 | 3.9 | 1.93 |
| 2016 | 704 | 9,916 | 7,296 | 2,620 | 14.1 | 10.3 | 3.8 | 1.89 (est.) |
Ethnic groups
The majority of the population of North Ossetia are Christians who belong to the Russian Orthodox Church, although there is also a Muslim minority who are of Ossetian speaking origin.
According to the 2010 Census,[8] Ossetians make up 65.1% of the republic's population. Other groups include Russians (20.8%), Ingush (4.0%), Armenians (2.3%), Kumyks (2.3%), Georgians (1.3%), Ukrainians (0.4%), Chechens (0.3%), Caucasus Greeks (0.2%).
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census1 | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Ossetians | 141,723 | 49.6% | 165,616 | 50.3% | 215,463 | 47.8% | 269,326 | 48.7% | 299,022 | 50.5% | 334,876 | 53.0% | 445,310 | 62.7% | 459,688 | 65.1% |
| Russians | 68,192 | 23.8% | 122,614 | 37.2% | 178,654 | 39.6% | 202,367 | 36.6% | 200,692 | 33.9% | 189,159 | 29.9% | 164,734 | 23.2% | 147,090 | 20.8% |
| Ingush | 23,851 | 8.3% | 6,106 | 1.9% | 6,071 | 1.3% | 18,387 | 3.3% | 23,663 | 4.0% | 32,783 | 5.2% | 21,442 | 3.0% | 28,336 | 4.0% |
| Armenians | 9,185 | 3.2% | 8,932 | 2.7% | 12,012 | 2.7% | 13,355 | 2.4% | 12,912 | 2.2% | 13,619 | 2.2% | 17,147 | 2.4% | 16,235 | 2.3% |
| Kumyks | 3,153 | 1.1% | 85 | 0.0% | 3,921 | 0.9% | 6,363 | 1.2% | 7,610 | 1.3% | 9,478 | 1.5% | 12,659 | 1.8% | 16,092 | 2.3% |
| Georgians | 6,057 | 2.1% | 6,312 | 1.9% | 8,160 | 1.8% | 10,323 | 1.9% | 11,347 | 1.9% | 12,284 | 1.9% | 10,803 | 1.5% | 9,095 | 1.3% |
| Ukrainians | 19,101 | 6.7% | 7,063 | 2.1% | 9,362 | 2.1% | 9,250 | 1.7% | 10,574 | 1.8% | 10,088 | 1.6% | 5,198 | 0.7% | 3,251 | 0.4% |
| Others | 14,690 | 5.1% | 12,477 | 3.8% | 16,938 | 3.8% | 23,210 | 4.2% | 26,182 | 4.4% | 30,141 | 4.8% | 32,982 | 4.6% | 26,636 | 3.8% |
| 1 The results of the 1926 census refer to the present territory, which is a combination of the North Ossetian AO, the city of Vladikavkaz and adjacent areas.[26]
2 6,557 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[27] | ||||||||||||||||
Languages
There are two official languages in North Ossetia – Russian, which is official on all of the Russia's territory, and Ossetian. Ossetian is an Indo-European language, belonging to the East Iranian group. Russian, acting as a lingua franca in the region, but also native to many, is an East Slavic language and as such also belongs to the Indo-European family, which means the two languages are related, albeit distantly.
Religion
According to a 2012 survey,[28] 49.2% of the population of North Ossetia-Alania adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 10% declare to be unaffiliated Christian believers, 2% are either Orthodox Christian believers who do not belong to churches or members of non-Russian Orthodox bodies. The second largest religion is Ossetian ethnic religion, generally called Uatsdin (Уацдин, "True Faith"), a Scythian religion organised into movements such as the Atsætæ Church, comprising 29% of the population. Muslims constitute 4% of the population, and Protestants the 1%. In addition, 1% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious" and 3% to be atheist.[28]
Politics
During the Soviet period, the high authority in the republic was shared between three people; the first secretary of the North Ossetia Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) Committee (who in reality had the biggest authority), the chairman of the oblast Soviet (legislative power), and the Chairman of the Republic Executive Committee (executive power). Since 1991, CPSU lost all the power, and the head of the Republic administration, and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside elected regional parliament.
The Charter of Republic of North Ossetia-Alania is the fundamental law of the region. The Parliament of North Ossetia-Alania is the republic's regional standing legislative (representative) body. The Legislative Assembly exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. The highest executive body is the Republic's Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters of the province. The Oblast administration supports the activities of the Governor who is the highest official and acts as guarantor of the observance of the krai Charter in accordance with the Constitution of Russia.
The head of government in the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania is the Head of the Republic. As of 2008, the head of the republic is Taymuraz Mamsurov. Mamsurov succeeded Alexander Dzasokhov, who voluntarily quit his post on May 31, 2005.[30]
Education
The most important facilities of higher education include North Caucasus State Technological University, North Ossetian State University, North Ossetian State Medical Academy, and Mountain State Agrarian University; all in Vladikavkaz.
Culture
There are six professional theaters in North Ossetia-Alania, as well as Ossetian State Philarmonia.
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Law #520A
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ North Ossetian ASSR, of which the modern Republic of North Ossetia-Alania is a direct successor, was established as a separate entity within the Russian SFSR upon the adoption of the 1936 Soviet Constitution
- 1 2 Constitution of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, Article 7
- ↑ Official website of the Head of the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania. Vyacheslav Zelimkhanovich Bitarov, Acting Head of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania (in Russian)
- ↑ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- 1 2 3 4 Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (2010 All-Russia Population Census) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ↑ The density value was calculated by dividing the population reported by the 2010 Census by the area shown in the "Area" field. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox is not necessarily reported for the same year as the population.
- ↑ Republic of North Ossetia-Alania Territorial Branch of the Federal State Statistics Service. Оценка численности постоянного населения Республики Северная Осетия-Алания по компонентам изменения на 1 января 2015 года (in Russian)
- ↑ Правительство Российской Федерации. Федеральный закон №107-ФЗ от 3 июня 2011 г. «Об исчислении времени», в ред. Федерального закона №271-ФЗ от 03 июля 2016 г. «О внесении изменений в Федеральный закон "Об исчислении времени"». Вступил в силу по истечении шестидесяти дней после дня официального опубликования (6 августа 2011 г.). Опубликован: "Российская газета", №120, 6 июня 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Federal Law #107-FZ of June 31, 2011 On Calculating Time, as amended by the Federal Law #271-FZ of July 03, 2016 On Amending Federal Law "On Calculating Time". Effective as of after sixty days following the day of the official publication.).
- ↑ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ↑ Constitution of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, Article 15
- ↑ Shnirelman, Victor (2006). The Politics of a Name: Between Consolidation and Separation in the Northern Caucasus. Acta Slavica Iaponica 23, pp. 37–49.
- ↑ https://s23.postimg.org/aze2tqr9n/2fec9d793e3d.jpg?noredir=1
- ↑ http://s50.radikal.ru/i129/1003/22/2fec9d793e3d.jpg
- 1 2 3 4 5 "North Ossetia–Alania: social and economic indicators looking up". Moscow News. 2008-09-18.
- ↑ Валовой региональный продукт на душу населения Федеральная служба государственной статистики
- 1 2 "Republic of North Ossetia–Alania: Introduction". Russia: All Regions Trade & Investment Guide. CTEC Publishing LLC. 2008. Archived from the original on July 15, 2011.
- ↑ "North Ossetia–Alania". Microsoft Encarta. Archived from the original on 2009-11-01. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- 1 2 3 "Republic of North Ossetia". Kommersant. 2004-03-11. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- 1 2 "Republic of North Ossetia". Russia Profile. 2008-08-25. Archived from the original on December 4, 2008. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек" [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian). Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ Demoscope Weekly (1989). "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров" [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ В 2008 году естественный прирост населения Северной Осетии составил более 2 тыс. человек – Новости России – ИА REGNUM. Regnum.ru (2009-02-26). Retrieved on 2012-08-18.
- ↑ население северной осетии. Ethno-kavkaz.narod.ru. Retrieved on 2012-08-18.
- ↑ Перепись-2010: русских становится больше. Perepis-2010.ru (2011-12-19). Retrieved on 2012-08-18.
- 1 2 3 Arena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia. Sreda.org
- ↑ 2012 Survey Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved September 24, 2012.
- ↑ "Regional government to quit over Beslan tragedy: president". ABC News.
Sources
- Парламент Республики Северная Осетия-Алания. Закон №520А от 24 ноября 1994 г. «О государственном гимне Республики Северная Осетия-Алания», в ред. Закона №44-РЗ от 31 июля 2006 г «О внесении изменений в Закон Республики Северная Осетия-Алания "О государственном гимне Республики Северная Осетия-Алания"». Опубликован: Газета "Северная Осетия". (Parliament of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania. Law #520A of November 24, 1994 On the State Anthem of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, as amended by the Law #44-RZ of July 31, 2006 On Amending the Law of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania "On the State Anthem of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania". ).
- Верховный Совет Республики Северная Осетия. 12 ноября 1994 г. «Республика Северная Осетия-Алания. Конституция.», в ред. Конституционного Закона №5-РКЗ от 4 декабря 2013 г. «О внесении изменений в Конституцию Республики Северная Осетия–Алания». Вступил в силу 7 декабря 1994 г. Опубликован: брошюрой "Конституция Республики Северная Осетия–Алания". (Supreme Council of the Republic of North Ossetia. November 12, 1994 Republic of North Ossetia–Alania. Constitution., as amended by the Constitutional Law #5-RKZ of December 4, 2013 On Amending the Constitution of the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania. Effective as of December 7, 1994.).
External links
General
- (in Russian) Official website of the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania
- (in Russian) Official website of the Parliament of the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania
- Russian News Agency Ria Novosty
- (in Russian) Official website of Alexander Dzasokhov
- (in Russian) Ossetia—History, culture, politics, news
- (in Esperanto) Pictures of North Ossetia–Alania
- (in English) (in Ossetic) (in Russian) Welcome to North Ossetia (by Toma Kulayeva)
- (in English) (in Ossetic) (in Russian) Ossetian history and culture
Education
- (in Russian) North Ossetian State University
- (in Russian) North Ossetian State Medical Academy
- (in Russian) Higher Institute of Management
- Institute of Civilization
Mass media
- (in Russian) Electronic version of the North Ossetia (Severnaya Osetiya) republican newspaper
- (in Russian) North Ossetian information portal 15th Region (15y Region)