Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council
The Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC), a post-Cold War NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. States meet to cooperate and go to the range of political and security issues. It was formed on May 29, 1997 in the ministers meeting of Sintra, Portugal, as the successor to the North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC), which was created in 1991. It works alongside the Partnership for Peace (PfP), created in 1994.
Members
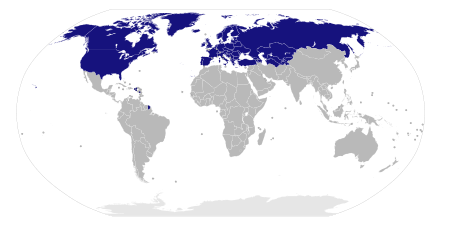
There are 50 members, the 29 NATO member countries and 21 partner countries. The partner countries are:
- 6 countries that (though militarily neutral) possessed capitalistic market economies during the Cold War:
- 12 former Soviet republics:
- 3 of the Former Yugoslav nations on neither side of the Iron Curtain during the Cold War:
The USSR at the North Atlantic Cooperation Council
On 20 December 1991, the first meeting of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council, hosted a meeting between NATO, Eastern European nations and the USSR. Near the end of the meeting, the Soviet Ambassador received a message that concurrently to the meeting, the Soviet Union was dissolving and would cease to exist the following day. The Soviet Ambassador noted that as of then, he was only representing the Russian Federation and no longer the Soviet Union.[2]
See also
- Individual Partnership Action Plan
- Foreign relations of NATO
- Partnership for Peace
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
- International Security Assistance Force
- United Nations
References
- ↑ EAPC partner state as the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
- ↑ "NATO Declassified - Dissolution of the Soviet Union announced at NATO meeting". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
External links
- Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council
- History of NATO – the Atlantic Alliance - UK Government site
- EAPC Security Forum 2007 in Ohrid, Macedonia
