Nok culture
Coordinates: 9°30′N 8°0′E / 9.500°N 8.000°E
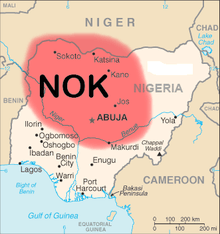 | |
| Geographical range | West Africa |
|---|---|
| Period | Iron Age |
| Dates | c. 1000 BC — c. 300 AD |
| Type site | Nok |
| Major sites | Samun Dukiya, Taruga, Jos |
| Followed by | Kwararafa |
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Northern Nigeria |
 |
|
Timeline
|
|
By ethnicity
|
|
By topic
|
|
By Province
|
The Nok culture is an early Iron Age population whose material remains are named after the Ham village of Nok in Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their famous terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok Culture appeared in northern Nigeria around 1000 BC and vanished under unknown circumstances around 500 AD, thus having lasted for approximately 1,500 years.[1]
Iron use, in smelting and forging for tools, appears in Nok culture by at least 550 BC and possibly earlier. Data from historical linguistics suggest that iron smelting was independently discovered in the region prior to 1000 BC.[2][3] Scientific field work began in 2005 to systematically investigate Nok archaeological sites, and to better understand Nok terracotta sculptures within their Iron Age archaeological context.[4][5][6]
Sculptures


48 cm tall
Age: 900 to 1,500 years

53 cm tall
Age: 1,400 to 2,000 years
The function of Nok terracotta sculptures is still unknown. For the most part, the terracotta is preserved in the form of scattered fragments. That is why Nok art is well known today only for the heads, both male and female, whose hairstyles are particularly detailed and refined. The statues are in fragments because the discoveries are usually made from alluvial mud, in terrain made by the erosion of water. The terracotta statues found there are hidden, rolled, polished, and broken. Rarely are works of great size conserved intact making them highly valued on the international art market.
The terracotta figures are hollow, coil built, nearly life sized human heads and bodies that are depicted with highly stylized features, abundant jewelry, and varied postures.
Little is known of the original function of the pieces, but theories include ancestor portrayal, grave markers, and charms to prevent crop failure, infertility, and illness. Also, based on the dome-shaped bases found on several figures, they could have been used as finials for the roofs of ancient structures.
Margaret Young-Sanchez, Associate Curator of Art of the Americas, Africa, and Oceania in The Cleveland Museum of Art, explains that most Nok ceramics were shaped by hand from coarse-grained clay and subtractively sculpted in a manner that suggests an influence from wood carving. After some drying, the sculptures were covered with slip and burnished to produce a smooth, glossy surface. The figures are hollow, with several openings to facilitate thorough drying and firing. The firing process most likely resembled that used today in Nigeria, in which the pieces are covered with grass, twigs, and leaves and burned for several hours.
As a result of natural erosion and deposition, Nok terracottas were scattered at various depths throughout the Sahel grasslands, causing difficulty in the dating and classification of the mysterious artifacts. Luckily, two archaeological sites, Samun Dukiya and Taruga, were found containing Nok art that had remained unmoved. Radiocarbon and thermo-luminescence tests narrowed the sculptures’ age down to between 2,000 and 2,500 years ago, making them some of the oldest in West Africa. Many further dates were retrieved in the course of new archaeological excavations, extending the beginnings of the Nok tradition even further back in time.[4]
Because of the similarities between the two sites, archaeologist Graham Connah believes that "Nok artwork represents a style that was adopted by a range of iron-using farming societies of varying cultures, rather than being the diagnostic feature of a particular human group as has often been claimed."
Discovery
The first Nok terracotta was discovered in 1928 by Colonel Dent Young, a co-owner of a mining partnership, near the village of Nok on the Jos Plateau in Nigeria.[7] The terracotta was accidentally unearthed at a level of 24 feet from an alluvial tin mine. Young presented the sculptures to the museum of the Department of Mines in Jos.[8]
Fifteen years later, in 1943 near the village of Nok, in the center of Nigeria, a new series of clay figurines were discovered by accident while mining tin. A clerk in charge of the mine had found a head and had taken it back to his home for use as a scarecrow, a role that it filled (successfully) for a year in a yam field. This scarecrow was eventually noticed by Bernard Fagg who at the time was an administrative officer who had studied archaeology at the University of Cambridge. Fagg noticed that the head on the scarecrow looked similar to the sculpture that Young had found. He traveled to Jos where Young showed Fagg other recently uncovered terracotta figures. Eventually it became clear that the tin mining in Nok and Jema'a areas were revealing and destroying archaeological material.[8]
Preliminary archaeology
Preliminary excavations at the beginning of January 1961 began near a remote valley named Taruga near the village of Takushara. The trial excavations took place during a period of eight days. The finds included objects of wrought iron, a quantity of iron slag, fragments of tuyere, pottery, figurine fragments, red ocher, quartz hammer-stones, and small concentrations of charcoal. The most famous finds at the site were the pottery graters which were shallow, flat-bottomed dishes which were deeply scored inside with diced patterns to produce a sharp abrasive surface. These pottery graters were probably used for food preparation. In the preliminary excavation a proton magnetometer survey was used to try and locate furnaces. The survey revealed a total of 61 magnetic anomalies which were mostly located in a flat, central area which probably indicated the limits of actual occupation. Twenty of the anomalies revealed concentrations of slag and nine of them contained in situ structures of furnace walls and bases. The most common type of artefact found was domestic pottery which can be divided into two different types. One type are bowls or shallow basins without lips and the other are globular pots which have averted lips. Because of this preliminary excavation, the Nok Culture would start being regarded as belonging to the Iron Age.[1]
Archaeology
In 1989, German scientists were working in northeastern Nigeria's Chad Basin as part of a cooperative project between the University of Maiduguri located in Borno State, Nigeria, and archaeologists of Goethe University Frankfurt. This project examined the beginnings of sedentary farming societies in the Chad Basin. Questions arose about whether there were other societies like those in the Chad Basin, and these questions led the team to investigate the Nok Culture. In the early steps of the Frankfurt Nok Project, researchers had difficulty finding sites to excavate. The team began collaborating with Umaru Yusuf Potiskum and they started finding distinct Nok culture sites, although most were looted.[9] A few sites, however, were still intact, and artefacts found at these sites are described below.
Stone tools
The shapes of stone tools found at Nok sites change little throughout the entire span of the Nok Culture. What tends to strike researchers is a lack of cutting tools. Apart from stone axes, no tools with a cutting edge have been found. Projectile points made of either iron or stone are also absent from Nok sites.
Grinding tools are very common at Nok sites. They are rarely preserved in one piece, but can still illustrate the different shapes and sizes of tools used throughout the Nok Culture. Grinding stones were made of quartzite, granitic, or metamorphic rock. At the site of Ungwar Kura, grinding stones seem to have been placed in a certain order, and at the site of Ido huge grinding slabs were arranged in an upright position with pots and stone beads next to them. This context is assumed to have been ritual in some way. Most of the grinders are merely hand-sized. Throughout Nok sites, there is an abundance of grinding slabs but there seems to be a low number of hand stones. It is a possibility that those of the Nok Culture used these grinders until they reached a certain state of wear and then were used as a sort of pestle.[9]
Another material used by the Nok are ground stone axes which seemed to be used for mostly food production which is typically made from fine-grained volcanic rock and a few made from siliceous rock. These ax blades tend to be smaller in size, the largest reaching 20 centimeters. Stone balls appear at almost every Nok site and are approximately palm-sized. They were probably used as hammerstones or for roughening the surface of a grinding stone. Not all of them are ball shaped, however, and many have chipping marks all over or at least in one place. These stone balls likely would have served as mobile grinding stones.These ax blades tend to be smaller in size, the largest reaching 20 centimeters.[9]
Stone rings have also been found at Nok Culture sites. They are normally just fragments but can be distinguished as rings because of their flat, oval or triangular cross sections and their shapes. These stone rings are very rare and their purpose is unknown. Another rare find is stone beads, which are typically found as if arrayed on strings. Beads tend to be carefully made out of hard siliceous rock such as quartz, chalcedony, jasper, or carnelian. There are three different bead shapes: cylindrical, which is the most common shape, as well as rod and ring-shaped.[9]
Ceramics
Potsherds are the most abundant archaeological artefacts at Nok sites. Since 2009, excavated pottery has been undergoing systematic analysis with a central aim to try and establish a chronology. Certain attributes of the pottery such as decoration, shape and size appear with an increasing frequency and then disappear being replaced with different pottery attributes. This change can sometime allow one to divide the progression into different intervals based on the different attributes. In total approximately 90,000 potsherds have been collected, and out of that 15,000 have been considered diagnostic meaning that they are decorated, sherds from the rim or the bottom of the vessel, or they have handles or holes in them. The results of the pottery analysis can be delineated into three distinct time periods: Early, Middle, and Late.
Early Nok Period ceramics
From approximately c. 1500–900 BC the pottery of the Early Nok Period are mostly small and not very well preserved. They seem to be richly decorated with various elaborate patterns directly below the vessels' rims and covering a large part of the ceramic body. The lines made on the pottery seem to be remarkably fine or curving lines. There tends to be many lines which are close together and some even have criss-crossing lines beneath the rim. Pottery frequently had everted and broad, thick rims.
Middle Nok Period ceramics
The Middle Nok Period is approximately from c. 900–300 BC and with this time period there is a dramatic increase of sites, terracotta fragments and iron objects. Instead of the early period's decoration which tended to cover most of the pot instead there is a decorative band which is bordered by deep horizontal lines. This band appears on the pots' upper half or directly under the rim of the bowls. Some bands have a sharp ends as well as impressed zigzag lines or an incised wave or arc. Unlike the Early Nok period the Middle Nok ceramics tend to have more variety in the rim with everted rims, open bowls, bowls with inverted rims and incised line ornaments on the rims' lips.
Late Nok Period ceramics
The Late Nok period is from approximately c. 300–1 BC and has only a few known sites. There is little pottery available for analysis but from the pottery that was found there is a decrease in the strictness of the ornamental band. While the band is still used they are being more complexly decorated with additional patterning. There also tends to be a returning pattern of body decoration. The variety of rim sizes and types seem to be increasing even more than in the Middle Nok period.
Farming
Grains
At almost all Nok sites there are charred plant remains consisting of firewood and plant material for cooking. Pearl millet remains tend to frequent Nok sites. Pearl millet is one of Africa's oldest grain crop. It is highly productive and are remarkably resistant to adverse growing conditions such as droughts. Cowpea also appears at sites but less frequently and valued upon their high protein content. So far, pearl millet and cowpeas seem to be the only crops with seem to be cultivated by the Nok people. It is unclear whether they ate or farmed tubers of any kind. The numerous grinding stones found at Nok sites indicate that the grains were most likely ground into flour and made into a type of porridge.[9]
Fruit
The collection of wild fruits is attested to the hard pits found at many Nok sites. At some sites, fruit and seeds of other wild plants such as grasses and legumes with small seeds were discovered. Overall there is not a huge selection of plant remains which could be due to different preservation abilities.[9]
Trees and Farming
The Nok people probably used an agroforestry system which is a plot of land of cultivated crops with useful trees in the same plot of land. These plots are ecologically sustainable and inter-cropping of trees and several cultivated plant species were common from the savannas to the rain forest with its origins going back to the first millennium BC, right at the time of the Nok culture. Most West African trees are not domesticated but are part of the wild vegetation which is left after farmers clear their fields of their crops. Because they are left to grow they multiply naturally without needing to be planted. Trees can produce food, medicine and animal feed.[9]
Animals
Because of the acidic soil, there are no bones that have preserved so there is no evidence for which animals if any the Nok people utilized. The only evidence for animals during the Nok culture period is the depictions of animals as figurines or terracotta sculptures.[9]
Looting and repatriation
Since the 1970s, Nok terracotta figures have been heavily looted. Even larger-scale looting commenced in the Nok cultural area in 1994, and by 1995 two main local traders emerged. Each of the main traders could employ approximately 1,000 diggers to unearth terracottas every day. Although the majority of the terracottas were fragmented, some were intact and sellable.[10] Because of this, hundreds of Nok Culture sites have been illegally dug in search of these terracotta sculptures. Valuable information about the Nok Culture is lost when these objects are taken from out of the ground and removed from their archaeological contexts.[9]
In 1979, Nigeria's National Commission of Museums and Monuments Decree established the National Commission for Museums and Monuments (NCMM), which is used to manage Nigeria's cultural heritage. NCMM Decree number 77 made it illegal for anyone other than authorized personnel to buy or sell antiquities within Nigeria or export an antiquity without a permit from the NCMM.[10] Towards the end of the 1990s the federal government of Nigeria implemented the NCMM, which initiated a series of actions to work out strategies for combating the problems of looting and to map out a plan of action. The general consensus was that laws governing antiquities and penalties for offenders needed to be strictly enforced and that all archaeological sites should be monitored. The NCMM also recommended more aggressive public enlightenment campaigns as well as a series of sensitization programs across the nation. These programs are considered a success in terms of increased awareness by law enforcement agents, as well as the Nigerian customs authorities and Interpol.[9] However, not all of the recommendations were implemented, because the Nigerian government did not have the resources to face the enormity of some of the challenges. For example, the government did not have the resources to place monitors at all archaeological sites, and terracotta figures still slip through Nigeria's borders.
Today, the terracotta sculptures are very highly sought after on the international art market, and so artifacts continue to be dug up without documentation of the contexts in which they were buried. A lack of extensive archaeological study has also severely limited our understanding of the Nok cultures.[11][12] A joint research project with Goethe University and the National Commission for Museums and Monuments conducted since 2005 showed that more than 90% of Nok Culture sites known in the research area have been illegally looted. Art historical studies carried out shows that over 1,000 Nok terracotta sculptures have been illegally excavated and smuggled into Europe, the USA, Japan, and elsewhere. In February 2013, Daily Trust reported that the Nigerian Ministry of Tourism, Culture, and National Orientation repossessed five Nok statuettes looted by a French thief in August 2010. The pieces had been seized by French customs agents and were repatriated following a Nigerian Government Directive.[13] What further complicates the problem are the many workshops which fake Nok sculptures and then put them on the market as authentic.[9]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nok culture. |
References
- 1 2 Fagg, Bernard. 1969. Recent work in west Africa: New light on the Nok culture. World Archaeology 1(1): 41–50.
- ↑ Duncan E. Miller and N.J. Van Der Merwe, 'Early Metal Working in Sub Saharan Africa' Journal of African History 35 (1994) 1-36
- ↑ Minze Stuiver and N.J. Van Der Merwe, 'Radiocarbon Chronology of the Iron Age in Sub-Saharan Africa' Current Anthropology 1968. Tylecote 1975 (see below)
- 1 2 Breunig, P. (2014). Nok. African Sculpture in Archaeological Context. Frankfurt: Africa Magna.
- ↑ Breunig, P. (2013). Nok - Ein Ursprung afrikanischer Skulptur. Frankfurt: Africa Magna Verlag.
- ↑ Breunig, Peter, Kahlheber, Stefanie, and Rupp, Nicole. Exploring the Nok enigma. In: Antiquity Vol 82 Issue 316 June 2008
- ↑ Chesi, G. & Merzeder, G. (2006). The Nok Culture: Art in Nigeria 2500 Years Ago
- 1 2 Shaw, Thurstan. 1981. The Nok sculptures of Nigeria. Scientific American 244(2): 154–166.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Breunig, Peter (editor). 2014. Nok: African sculpture in archaeological context. Africa Magna Verlag, Germany, October 15.
- 1 2 Brodie, Neil, and Donna Yates. 2012. Nok Terracottas. Trafficking Culture: Researching the Global Traffic in Looted Cultural Objects.
- ↑ Department of the Arts of Africa, Oceania, and the Americas. 2000. Nok Terracotta (500 B.C.–200 A.D.). The Met’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History.
- ↑ Anon. 2015. Research continues into 3000 year-old Nok culture of sub-Saharan Africa. Adventures in Archaeology. Archaeology News from Past Horizons, February 8.
- ↑ Mustapha Suleiman (February 3, 2013), France Hands Over Stolen Nigerian Artifacts Daily Trust.
Further reading
- Atwood, R. (2011). The NOK of Nigeria. Archaeology July/August 2011, 34-38.
- Breunig, P. (ed.) (2014). Nok. African Sculpture in Archaeological Context. Frankfurt: Africa Magna Verlag.http://news.uwlax.edu/archeology-students-uncovering-passion/ ISBN 978-3-937248-46-2
- Breunig, P. & Rupp, N. (2006). Nichts als Kunst. Archäologische Forschungen zur früheisenzeitlichen Nok-Kultur in Zentral-Nigeria. Forschung Frankfurt 2-3, 73-76.
- Boullier, C.; A. Person; J.-F. Saliège & J. Polet (2001). Bilan chronologique de la culture Nok et nouvelle datations sur des sculptures. Afrique: Archéologie & Arts 2, 9-28.
- Fagg, A. (1972). A preliminary report on an occupation site in the Nok valley, Nigeria: Samun Dukiya, AF/70/1. West African Journal of Archaeology 2, 75-79.
- Fagg, B. (1959). The Nok Culture in prehistory. Journal of the Historical Society of Nigeria 1 (4), 288-293.
- Fagg, B. (1968). The Nok Culture: Excavations at Taruga. The West African Archaeological Newsletter 10, 27-30.
- Fagg, B. (1969). Recent work in West Africa: new light on the Nok Culture. World Archaeology 1 (1), 41-50.
- Fagg, B., (1990): Nok terracottas. Lagos: National Commission for Museums and Monuments.
- Jemkur, J. (1992). Aspects of the Nok Culture. Zaria.
- Rupp, N.; Ameje, J.; Breunig, P. (2005). New studies on the Nok Culture of Central Nigeria. Journal of African Archaeology 3, 2: 283-290.
- Rupp, N.; Breunig, P.; Kahlheber, S. (2008). Exploring the Nok enigma. Antiquity, Project gallery. Online publication: http://www.antiquity.ac.uk/ProjGall/kahlheber/index.html
- Shaw, T., (1981). The Nok sculptures of Nigeria. Scientific American 244(2): 154-166.
- Tylecote, R. (1975a). The origin of iron smelting in Africa. Westafrican Journal of Archaeology. 5, 1-9.
- Tylecote, R. (1975b). Iron smelting at Taruga, Nigeria. Journal of Historical Metallurgy 9 (2), 49-56.
- Olubunmi A.O.(2007) The Rise and Fall of The Yoruba Race, The 199 Publishing Palace ISBN 978-2457-38-8
- Olubunmi A.O.(2009) On Ijesa Racial Purity, The 199 Publishing Palace ISBN 978-2458-17-1
- Ayoade J.O.(1983) Introduction To Climatology For The Tropics, John Wiley & Sons ltd UK ISBN 0-471-10407-8
