New Zealand national rugby union team
 | |||
| Nickname(s) | All Blacks | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Emblem | Silver fern | ||
| Union | New Zealand Rugby Union | ||
| Head coach | Steve Hansen | ||
| Captain | Kieran Read | ||
| Most caps | Richie McCaw (148) | ||
| Top scorer | Dan Carter (1598) | ||
| Top try scorer | Doug Howlett (49) | ||
| |||
| World Rugby ranking | |||
| Current | 1 (as of 27 June 2016) | ||
| Highest | 1 (2016) | ||
| Lowest | 3 (2003) | ||
| First international | |||
|
Australia 3–22 New Zealand (Sydney, Australia; 15 August 1903) | |||
| Biggest win | |||
|
New Zealand 145–17 Japan (Bloemfontein, South Africa; 4 June 1995) | |||
| Biggest defeat | |||
|
Australia 28–7 New Zealand (Sydney, Australia; 28 August 1999) | |||
| World Cup | |||
| Appearances | 8 (First in 1987) | ||
| Best result | Champions, 1987, 2011, 2015 | ||
| Website | www.allblacks.com | ||
The New Zealand national rugby union team, commonly called the All Blacks, represent New Zealand in men's rugby union, which is regarded as the country's national sport.[1] The side has won the last two Rugby World Cups, in 2011 and 2015, as well as the inaugural tournament in 1987. They have a 77% winning record in test match rugby, and are the only international side with a winning record against every opponent. Since their international debut in 1903, they have lost to only six of the 19 nations they have played in test matches.[lower-alpha 1] Since the introduction of the World Rugby Rankings in 2003, New Zealand has held the number one ranking longer than all other teams combined.[2] The All Blacks are statistically the best side to have played the game, and jointly hold the record for the most consecutive test match wins for a tier one ranked nation.
New Zealand competes with Argentina, Australia and South Africa in The Rugby Championship. The All Blacks have won the trophy fourteen times in the competition's twenty-one-year history. New Zealand have achieved a Grand Slam (defeating England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland in one tour) four times – 1978, 2005, 2008 and 2010.
The All Blacks have been named the World Rugby Team of the Year ten times since the award was created in 2001, [3] and an All Black has won the World Rugby Player of the Year award nine times over the same period. Fifteen former All Blacks have been inducted into the International Rugby Hall of Fame. All Black coaches have won World Rugby Coach of the Year nine times since the award's 2001 launch.
The team's first match was in 1884, and their first international test match was in 1903 against Australia in Sydney. The following year they hosted their first ever home test, a match against a British Isles side in Wellington.[lower-alpha 2] This was followed by a 34-game (including 5 tests) tour of Europe and North America in 1905, where the team suffered only one defeat – their first ever test loss, against Wales.
New Zealand's early uniforms consisted of a black jersey with a silver fern and white knickerbockers. By the 1905 tour, they were wearing all black, except for the silver fern, and their name "All Blacks" dates from this time. The team perform a haka – a Māori challenge or posture dance – before each match. The haka performed has traditionally been Te Rauparaha's Ka Mate, although since 2005 Kapa o Pango is often performed.
History
Introduction of rugby to New Zealand

Rugby union – almost universally referred to as rugby in New Zealand – was introduced to New Zealand by Charles Monro in 1870;[4] Monro discovered the sport while completing his studies at Christ's College, Finchley, England.[5] The first recorded game in New Zealand took place in May 1870 in Nelson between the Nelson club and Nelson College.[6] The first provincial union, the Canterbury Rugby Football Union, was formed in 1879,[7] and in 1882 New Zealand's first internationals were played when New South Wales (NSW) toured the country.[8] NSW did not face a New Zealand representative team but played seven provincial sides – the tourists won four games and lost three.[9] Two years later the first New Zealand team to travel overseas toured New South Wales; where New Zealand won all eight of their games.[10]
A privately organised British team, which later became the British and Irish Lions, toured New Zealand in 1888. No test matches were played, and the side only played provincial sides.[11] The British players were drawn mainly from Northern England, but there were representatives from Wales and Scotland.[12]
International competition begins
In 1892, following the canvassing of provincial administrators by Ernest Hoben, the New Zealand Rugby Football Union (NZRFU) was formed by the majority of New Zealand's provincial unions, but did not include Canterbury, Otago or Southland.[13][lower-alpha 3] The first officially sanctioned New Zealand side toured New South Wales in 1893, where the Thomas Ellison captained team won nine of their ten matches.[14][15] The following year New Zealand played its first home "international" game, losing 8–6 to New South Wales.[lower-alpha 4][16] The team's first true test match occurred against Australia on 15 August 1903 at the Sydney Cricket Ground in front of over 30,000 spectators, and resulted in a 22–3 victory.[17]

A representative New Zealand team first toured the British Isles in 1905. The side is now known as the Originals, as the All Blacks name emerged during this tour when, according to team member Billy Wallace, a London newspaper reported that the New Zealanders played as if they were "all backs".[18] Wallace claimed that because of a typographical error, subsequent references were to "All Blacks". This account is most likely a myth – because of their black playing strip, the side was probably referred to as the Blacks before they left New Zealand. Even though the name All Blacks most likely existed before the trip, the tour did popularise it.[18]
The Originals played 35 matches on tour, and their only loss was a 3–0 defeat to Wales in Cardiff.[19] The match has entered into the folklore of both countries because of a controversy over whether All Black Bob Deans scored a try which would have earned his team a 3–3 draw.[20][lower-alpha 5] In contrast to the success of the Originals on the field, the team did antagonise some in the Home Nations' rugby establishment; both administrators and the press complained that the All Blacks did not play the game within the amateur and gentlemanly spirit promoted by the International Rugby Football Board. This complaint continued to dog New Zealand teams until the 1930s.[21]
The success of the Originals had uncomfortable consequences for the amateur NZRFU. In 1907, a party of professional players was assembled to tour the British Isles and play rugby league – a professional offshoot of rugby union that was played by clubs that split from England's Rugby Football Union (RFU) due to disagreements over financial compensation for players.[22] When the All Golds, as the team came to be known, returned they established rugby league in New Zealand, and a large number of players switched to the professional code.[22][23] English and Welsh authorities were alarmed by the threat of professionalism to rugby in New Zealand, and in 1908 an Anglo-Welsh side undertook a tour to New Zealand to help promote the amateur values[lower-alpha 6] under which they believed sport should be played.[25][26][lower-alpha 7] The tourists were defeated 2–0 in the three-test series by New Zealand, but the Anglo-Welsh did manage to draw the second test 3–3.[27]
Development of a legacy
International rugby was suspended during the First World War,[28] but a New Zealand Services team did compete in inter-services competition known as the King's Cup.[29] After their departure from Europe the side toured South Africa before their return to New Zealand, and that tour paved the way for a South African team to tour New Zealand in 1921.[30] The Springboks – as the South African team is known – played New Zealand in a test series that ended all square. New Zealand conducted a return tour to South Africa in 1928, and the test series was again drawn; both teams winning two tests each.[31]
The 1924 All Black tourists to the British Isles and France were dubbed the Invincibles because they won every game. However, the team was deprived of a potential Grand Slam when Scotland refused to play them because they were upset the tour was organised through the RFU rather than the IRFB.[32][33] The first British Isles side since 1908 toured New Zealand in 1930. Although the Lions won the first test, the home side regrouped and went on to win the series 3–1.[34] New Zealand toured the British Isles again in 1935–36, losing only three games – including two tests – during a 30-match tour.[35] In one of these losses, Prince Obolensky famously scored two tries to help England to a 13–0 win; their first over New Zealand.[36]

In 1937, South Africa toured New Zealand and decisively won the test series despite losing the first test; this 1937 South African team has been described as the best team ever to leave New Zealand.[37][38] It was not until 1949 that New Zealand next played the Springboks when they toured South Africa with Fred Allen as captain.[39][40] Although each test against South Africa was very close, New Zealand lost the series 4–0.[41] As part of the tour, a contingent of 26 All Blacks travelled to Rhodesia for two non-test exhibition matches. The Rhodesia side beat the All Blacks 10–8 in Bulawayo, and then drew 3–3 in the follow up match in Salisbury.[42][43]
At the same time as an All Black team was touring South Africa, Australia were touring New Zealand.[44] The two tours coincided because Māori players were not able to go to South Africa at the time, meaning the Australians, played against a New Zealand team made up of the best Māori and the reserve non-Māori players, while the South Africans encountered the best pākehā (non-Māori) players.[45][lower-alpha 8] On the afternoon of 3 September New Zealand, captained by Johnny Smith, were beaten 11–6 by Australia in Wellington.[47] New Zealand then lost their second test 16–9, which gave Australia a Bledisloe Cup series win in New Zealand for the first time.[44][45] 1949 was an annus horribilis for the All Blacks as they lost all six of their test matches, and the experience of playing two test series simultaneously has not been repeated.[44][48]
The two consecutive series losses to South Africa made their 1956 tour of New Zealand highly anticipated. New Zealand were captained by Bob Duff and coached by Bob Stuart, and their 3–1 series win was their first over the Springboks and the Springboks' first series loss that century.[49] During the series, New Zealand introduced Don Clarke, and brought prop Kevin Skinner out of retirement to help secure the win.[50] Skinner, a former New Zealand boxing champion, had retired from international rugby, but was convinced to return for the third and fourth tests.[51] One reason for Skinner's selection was to "sort out" the South African props, while Clarke become known as "The Boot" for his goal kicking.[52]
New Zealand's 3–1 series win over the Lions in 1959 proved to be the start of a dominant period in All Black rugby.[53] This was followed by the 1963–64 tour to Britain and Ireland, led by Wilson Whineray, in which New Zealand were deprived of a Grand Slam by a scoreless draw with Scotland.[54] The only loss on this tour was to Newport RFC, who won 3–0 at Rodney Parade, Newport on 30 October 1963.[55] The 1967 side won three tests against the home nations, but was unable to play Ireland because of a foot-and-mouth scare.[54] This tour formed part of New Zealand's longest winning streak, between 1965 and 1970, of 17 test victories.[56] This was also the longest test winning streak by any nation at the time; it would be equalled by the Springboks in 1998, and surpassed by Lithuania in 2010.[57][lower-alpha 9] Although the 1966 Lions were defeated 0–4 in their New Zealand tour, there was a reversal of fortune five years later when the 1971 Lions, under the captaincy of Welshman John Dawes, beat New Zealand in a test series, which remains the Lions' only series victory in New Zealand.
The 1972–3 tourists narrowly missed a Grand Slam with a draw against Ireland.[54] The tour was notable for the sending home of prop Keith Murdoch, who was alleged to have been involved in a brawl in a Cardiff hotel while celebrating the defeat of Wales.[58] It was on this tour New Zealand lost 9-3 in an epic battle against Llanelli RFC littered with Welsh and British Lions caps
In 1978, Graham Mourie captained New Zealand to their first Grand Slam, including a 13–12 victory over Wales. That game generated controversy after New Zealand won as the result of a late penalty. Lock Andy Haden had dived out of a line-out in an attempt to earn a penalty, but referee Roger Quittenden insisted the penalty was against Welsh lock Geoff Wheel for jumping off the shoulder of Frank Oliver.[59] New Zealand's only loss on the tour was the famous 12–0 defeat by Irish province Munster at Thomond Park.[60] Later a play which focused on the loss was written by John Breen, called Alone it Stands.[61]
Controversial tours

For the 1960 All Blacks tour of South Africa, the South African authorities insisted that Maori players be excluded from the team. The subsequent controversy led to the New Zealand Rugby Union refusing any other tour for the following 10 years until the 1970 tour, when Maori players were accepted as "honorary whites".[62][63] (See Halt All Racist Tours.)
The 1976 All Blacks tour of apartheid South Africa generated much controversy and led to the boycott of the 1976 Summer Olympics in Montreal by 33 African nations after the IOC refused to ban the team.[64][65] New Zealand again failed to win the test series in South Africa: they did not do so until 1996, after the fall of apartheid. The 1976 tour contributed to the Gleneagles Agreement being adopted by the Commonwealth Heads of State in 1977.[66]
The 1981 South African tour to New Zealand sparked protests against South Africa's apartheid policy, the likes of which had not been seen in New Zealand since the 1951 waterfront dispute.[67][68] The NZRU had invited the Springboks to tour as the Muldoon government refused to involve politics in sport.[69] Although New Zealand won the test series, two of the tour's provincial games were cancelled and the whole tour was marred by violence and protest.[70] The third and final test match of the tour is sometimes known as the Flour Bomb test, as an anti-apartheid activist in a Cessna light aircraft dropped leaflets, flares, a parachute-supported banner reading "Biko" and flour bombs into Auckland's Eden Park throughout the match, felling a New Zealand player. During the tour the country experienced unrest, and the tour had a significant impact on New Zealand society.[67][70][71]
The 1985 All Blacks tour to South Africa was cancelled after legal action on the grounds that it would breach the NZRU's constitution.[71] In 1986, a rebel tour to South Africa took place that had not been authorised by the NZRU and the team, named the Cavaliers, included many All Blacks.[72][73] Those that participated in the tour received a ban for two tests from the NZRU when they returned to New Zealand. Allegations that players received payment for the tour were never proved.[74]
Early World Cups
New Zealand hosted and won the inaugural World Cup in 1987 beating France 29–9 in the final. New Zealand conceded only 52 points and scored 43 tries in six games en route to the title, beating Italy, Fiji, Argentina, Scotland, Wales and France.[75]
By the 1991 World Cup New Zealand were an ageing side,[76] co-coached by Alex Wyllie and John Hart. After beating hosts England in the tournament opener, they struggled during pool matches against the United States and Italy, and won their quarter-final against Canada.[77] They were then knocked out by eventual winners Australia 16–6 in their semi-final at Lansdowne Road. In the wake of the tournament, there were many retirements, including coach Wyllie, who had enjoyed an 86% win rate during 29 tests in charge.[78]
Laurie Mains replaced Wyllie in 1992, and was given the job of preparing the side for the 1995 event in South Africa. New Zealand were again one of the favourites to take the championship. Their status as favourites was enhanced when a young Jonah Lomu scored four tries against England in the 45–29 semi-final win.[79][80] They managed to take hosts South Africa to extra time in the final, before losing 15-12 to Joel Stransky's drop goal.[81][82]
Professionalism

The professional era in rugby union began in 1995, spurred by creation of the SANZAR group (a combination of South Africa, New Zealand and Australia)[83] which was formed with the purpose of selling broadcast rights for two new competitions, the domestic Super 12 competition and the Tri-Nations.[83] The first Tri-Nations was contested in 1996, with New Zealand winning all four of their tests to take the trophy.[84] After a 1996 Tri-Nations match hosted by South Africa, won 29–18 by New Zealand,[85] preceded a separate three-match test series between the two sides.[86] Under new coach John Hart and the captaincy of Sean Fitzpatrick, New Zealand won a test series in South Africa for the first time.[87] Fitzpatrick rated the series win higher than the 1987 World Cup victory in which he had participated.[87]
The next three seasons saw mixed results for New Zealand, who won all their Tri-Nations tests in 1997 before losing the title for the first time in 1998.[88] In 1998 New Zealand lost all five tests in the Tri-Nations and Bledisloe Cup series (two to South Africa and three to Australia), the first time they had lost four tests in succession since 1949.[89] The following year they suffered their worst test loss, 28–7 to Australia in Sydney.[90] At the 1999 World Cup later that year, the All Blacks dominated their pool, handing England a 30–16 defeat at Twickenham. They advanced past Scotland 30–18 in the quarter-finals to play France at Twickenham. After New Zealand finished the first half 17–10 ahead,[90] France then produced a famous half of rugby to which New Zealand had no answer, winning 43–31.[90] Hart subsequently resigned as coach and was replaced by co-coaches Wayne Smith and Tony Gilbert.
Under Smith and Gilbert, New Zealand came second in the 2000 and 2001 Tri-Nations, and in neither season did the side reclaim the Bledisloe Cup – which had been lost in 1998. Both coaches were replaced by John Mitchell on 3 October 2001, and he went on to coach New Zealand to victory in both the 2002 and 2003 Tri-Nations, as well as regaining the Bledisloe Cup in 2003. The All Blacks entered the 2003 World Cup as one of the favourites and dominated their pool, running up wins against Italy, Canada and Tonga, before winning one of the most competitive matches of the tournament against Wales.[91] They defeated South Africa in their quarter-final, a team they had never beaten at the World Cup, 29–9, but lost to Australia 22–10 in the semi-final in Sydney. Afterwards, Mitchell had to reapply as coach, but the NZRU instead appointed Graham Henry.
Henry era
Henry's tenure began with a double victory over 2003 Rugby World Cup winners England in 2004. The two games had an aggregate score of 72–15, and England were kept try-less.[92][93] Despite the winning start to Henry's tenure, the Tri-Nations was a mixed success with two wins and two losses. The competition was the closest ever, bonus points decided the outcome, and New Zealand finishing last.[lower-alpha 10][94] The 2004 season finished with three wins in Europe, including a record 45–6 victory over France under new captain and outside centre Tana Umaga.[95][96]
In 2005 New Zealand whitewashed the touring British and Irish Lions during their three-match test series, won the Tri-Nations, and achieved a second Grand Slam over the Home Nations for the first time since 1978. They went on to sweep the major IRB (now World Rugby) awards in which they were named: Team of the Year, Henry was named Coach of the Year, and first five-eighth Dan Carter was Player of the Year.[3] New Zealand were nominated for the Laureus World Sports Award for Team of the Year in 2006 for their 2005 performance.[97] The following year they again took the Tri-Nations Series after winning their first five matches, three against Australia and two against South Africa. They lost their final match of the series against South Africa. They completed their end of year tour unbeaten, with record away wins over France, England and Wales.[98] New Zealand were named 2006 IRB Team of the Year and were nominated for the Laureus World Sports Award for the second time, while flanker and newly appointed captain Richie McCaw was named IRB Player of the Year for the first time.[3][97][99]
The 2007 season started off with two mid-year tests against France. New Zealand won the tests 42–11 at Eden Park and 61–10 at Westpac Stadium. A third game, against Canada, resulted in a 64–13 win, although the game was more competitive than the scoreline indicated.[100] New Zealand's first Tri-Nations game of 2007 was against the Springboks in Durban, South Africa. New Zealand scored two tries in the final ten minutes of the game to win 26–21. The following week against the Wallabies at the Melbourne Cricket Ground the Wallabies upset New Zealand to win 20–15, New Zealand's first loss to Australia since 2004. The All Blacks won their following home games to successfully defend the Tri-Nations Series for 2007. New Zealand entered the 2007 Rugby World Cup as favourites, and topped their pool, beating Scotland, Italy, Romania and Portugal by at least 40 points. However, they then suffered a defeat by hosts France in the quarter-finals in Cardiff. Following the loss to France coach Graham Henry's job was reappointed amid vocal debate and comment, despite then Crusaders coach Robbie Deans being a strong contender.
The 2008 season started with three mid-year tests, the first against Ireland at Westpac Stadium, Wellington. The final two games were against England, the first at Eden Park and the second at AMI Stadium in Christchurch. New Zealand played their first Tri-Nations game against South Africa at Westpac Stadium in Wellington winning 19–8 but a week later at Carisbrook in Dunedin they lost to South Africa 28–30, ending a 30-match winning streak at home, their previous loss in New Zealand being against England in 2003. New Zealand played their next Tri-Nations match on 26 July against Australia at Stadium Australia in Sydney, losing 34–19 but a week later against Australia at Eden Park in New Zealand won 39–10. The greatest victory for New Zealand in the 2008 season was beating South Africa 19–0 in Cape Town at Newlands Stadium. New Zealand played their final match on 13 September against Australia at Suncorp Stadium in Brisbane winning 28–24 and retaining the Bledisloe Cup and the Tri-Nations.
The All Blacks opened the 2009 season with a 22–27 loss to France at Carisbrook, but defeated them 14–10 in Wellington a week later. On points difference, France won the Dave Gallaher Cup for the first time. A week later the All Blacks defeated Italy 27–6 in Christchurch. They finished second in the Tri-Nations Series, behind South Africa who lost only one game, and ended the series with a 33–6 win over Australia in Wellington.
In 2010 the All Blacks won the Tri-Nations series for the tenth time after three successive victories against South Africa, also retaining the Bledisloe Cup after consecutive victories against Australia. During 2010 New Zealand were undefeated for 15 test matches. Despite losing the 2011 Tri-Nations after a loss to Australia in Brisbane, but still entered the 2011 Rugby World Cup as one of the favourites. The All Blacks went through their pool matches undefeated, and after defeating Argentina, and then Australia, faced France in the final. New Zealand scored one try and a penalty to narrowly win 8–7.[101] Henry stepped down as coach following the World Cup, and was replaced as head coach by his assistant Steve Hansen.
Hansen era
The Tri-Nations was expanded to include Argentina in 2012, and subsequently renamed The Rugby Championship. The All Blacks went undefeated in the inaugural tournament, and went through the year unbeaten until their last match of the year, where they lost to England at Twickenham. In 2013 New Zealand hosted France in a three-match series – their first meeting since the 2011 World Cup final. They won all three tests, before going unbeaten in the 2013 Rugby Championship.[102] In November 2013, New Zealand became the first rugby nation in the professional era to achieve a 100% record in a calendar year.[103]
At the 2014 Rugby Championship, the All Blacks drew Australia and lost to South Africa in the away matches, but won the other four matches and the tournament. At the shortened 2015 Rugby Championship, the All Blacks lost to Australia and was runner-up. The team entered the 2015 Rugby World Cup and again went undefeated in their pool matches. They defeated France 62-13 in the Quarter-Final, South Africa 20-18 in the Semi-Final and Australia 34-17 in the Final to become the first nation to retain their World Champion title and the first to win the Rugby World Cup three times.[104]
The All Blacks went undefeated at the 2016 Rugby Championship, claiming bonus points at each match, under new captain and Number 8, Kieran Read and vice-captain and fullback Ben Smith. Smith and wing Israel Dagg were also the joint highest try scorers in the competition with 5 each, while first-five-eighth Beauden Barrett was the highest points scorer of the competition with 81 in total.
Jersey
The current New Zealand jersey is entirely black (currently referred to as the 'blackest' jersey ever created) except the Adidas logo, the NZRU silver fern on the front and the AIG logo in the lower center (all of which are darkened from previously). The 1884 New Zealand tour to Australia was the first overseas New Zealand rugby tour, and featured clothing very different from today's jersey. Back then, the team donned a dark blue jersey, with gold fern on the left of the jumper.[105] In 1893 the NZRU stipulated at its annual general meeting that the uniform would be black jersey with a silver fern and white knickerbockers.[106] However historic photographs suggest white shorts may have been used instead during these early years. Sometime between 1897 and 1901 there was a change; by 1901 the team met NSW in a black jersey, a canvas top with no collar, and a silver fern.[107]
In 2006, New Zealand wore an embroidered remembrance poppy on their jersey sleeve when playing France during the end-of-year tour.[108] The poppy honours the ANZAC soldiers who died on the beaches of Gallipoli. Captain Richie McCaw said "We want to honour the overseas service of New Zealanders. It is an important part of our history as a country and a team."[109]
During the 2011 Rugby World Cup the All Blacks had an embroidered William Webb Ellis cup on the sleeve of their jerseys with the year '1987' underneath. This was to signify which year the team had won the tournament. Each of the four teams who had won the competition had the same detailing on their jerseys.
Adidas is paying the NZRFU $200 million over nine years, expecting New Zealand to win around 75% of their matches.[110] Nike also looked at sponsoring New Zealand in 1996, but went with Tiger Woods instead.[111]
The change kit has traditionally been white with black shorts. After a few years playing with a change kit of grey shirt and black shorts, the NZRU announced a return to the traditional white jersey and black shorts in May 2009. For the 30 July 2011 Springboks match in Wellington, the All Black jersey introduced a white collar in homage to that sported by the 1987 World Cup-winning team.
In 2012, the NZRU took the controversial step of allowing American insurance and financial services company, AIG, to promote themselves on the centre-front of the All Black jersey. In return, the NZRU would receive direct financial sponsorship that was not revealed; the deal was estimated to be worth approximately $80 million over five years.[112]
Adidas have been the All Black's kit suppliers since 1999, taking over from Canterbury. In June 2017, after releasing a special edition jersey for the impending three tests against the British and Irish Lions, it was announced that the partnership between the All Blacks and Adidas had been extended to at least 2023.
1905 "Originals" Home |
1950s-1999 Home |
1999-2003 Home |
2003-2005 Home |
2007-2009 Home |
2007-2009 Away |
2011-2012 Home |
2011-2012 Away |
2015-2016 Home |
2015 Rugby World Cup Home |
Haka

The All Blacks perform a haka (Māori challenge) before each international match. The haka has been closely associated with New Zealand rugby ever since a tour of Australia and the United Kingdom by the 1888–89 New Zealand Native football team,[113][114] though the New Zealand team that toured New South Wales in 1884 may also have performed a haka.[115] The New Zealand native team that toured Britain in 1888 and 1889 used Ake Ake Kia Kaha, and the 1903 team in Australia used a mocking haka, Tupoto koe, Kangaru!. The 1905 All Blacks began the tradition of using Ka Mate – a haka composed in the 19th century by Ngāti Toa leader Te Rauparaha. The 1924 All Blacks used a specially composed haka Ko Niu Tireni, but later All Blacks reverted to Ka Mate.[116][117][118]
In August 2005, before the Tri-Nations test match between New Zealand and South Africa at Carisbrook stadium in Dunedin, New Zealand performed a new haka, Kapa o Pango, specially composed by Derek Lardelli and intended to reflect the Polynesian-influenced multicultural make-up of contemporary New Zealand.[119] Kapa o Pango was to be performed on special occasions and was not intended to replace Ka Mate.[119] Kapa o Pango concludes with what has been interpreted as a "throat slitting" gesture that led to accusations that Kapa o Pango encourages violence, and sends the wrong message to All Blacks fans.[120] However, according to Lardelli, the gesture represents "drawing vital energy into the heart and lungs".[121]
In November 2006, at the Millennium Stadium, Cardiff, New Zealand performed the haka in the dressing room prior to the match – instead of on the field immediately before kick-off – after a disagreement with the Welsh Rugby Union, which had wanted Wales to sing their national anthem after the haka.[122] In 2008, New Zealand played Munster at Thomond Park. Before the match, Munster's four New Zealanders challenged their opponents by performing a haka before the All Blacks started theirs.[123] On the same tour, Wales responded by silently refusing to move after New Zealand's haka, and the two teams simply stared at each other until the referee forced them to start the game.[124]
Record
Overall
| Top 30 rankings as of 31 July 2017[125] | |||
| Rank | Change* | Team | Points |
| 1 | 94.78 | ||
| 2 | 90.14 | ||
| 3 | 85.39 | ||
| 4 | 84.63 | ||
| 5 | 84.16 | ||
| 6 | 82.47 | ||
| 7 | 81.73 | ||
| 8 | 79.63 | ||
| 9 | 79.50 | ||
| 10 | 79.48 | ||
| 11 | 73.79 | ||
| 12 | 73.41 | ||
| 13 | 71.72 | ||
| 14 | 71.00 | ||
| 15 | 70.27 | ||
| 16 | 69.67 | ||
| 17 | 65.84 | ||
| 18 | 63.15 | ||
| 19 | 63.15 | ||
| 20 | 63.13 | ||
| 21 | 60.27 | ||
| 22 | 59.78 | ||
| 23 | 59.47 | ||
| 24 | 58.66 | ||
| 25 | 57.26 | ||
| 26 | 57.17 | ||
| 27 | 56.94 | ||
| 28 | 54.76 | ||
| 29 | 54.50 | ||
| 30 | 53.63 | ||
| *Change from the previous week | |||
| New Zealand's historical rankings | |||
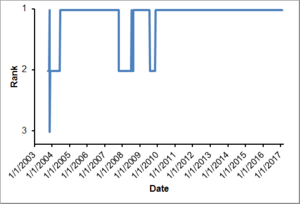 | |||
| Source: World Rugby - Graph updated to 20 February 2017[125] | |||
New Zealand have only ever been beaten by six test nations,[lower-alpha 11] and they are the only international team to have a winning record against every nation they have played. They have won 428 of their 556 test matches – 76.98% (see table), and have lost at home only 38 times. Since World Rankings were introduced by World Rugby in October 2003, New Zealand have occupied the number one ranking the majority of the time.[2] In the decade from 2000 to 2009, New Zealand won 100 tests (82% winning percentage). As of 24 June 2017, the All Blacks have won a record 47 consecutive tests at home. However on 1 July, they lost to the British and Irish Lions to end that 47-match winning streak at home.
New Zealand's longest winning streak is 18 test victories (a Tier 1 joint world record), achieved between 2015 and 2016. In 2013 they won every test they played during a calendar year. Their longest unbeaten streak is 23 tests (from 1987 to 1990) with one game being drawn.[126]
Their all-time points record for tests stands at 15,068 points for and 7,259 against (updated 10 July 2017). Many national teams' heaviest defeats have occurred against New Zealand – the national teams of France, Ireland, Argentina, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga, Japan, and Portugal have all suffered their greatest defeats at the hands of New Zealand. The All Blacks' largest test win was 145–17 against Japan in 1995,[127] while their heaviest loss was a 28–7 loss to Australia in 1999.[90]
Below is summary of New Zealand test results, updated 10 July 2017:[128]
| Opponent | Played | Won | Lost | Drawn | Win % | For | Aga | Diff |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 24 | 23 | 0 | 1 | 95.83% | 974 | 333 | +641 |
| | 158 | 109 | 42 | 7 | 68.99% | 3268 | 2187 | +1081 |
| British and Irish Lions | 41 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 73.17% | 700 | 399 | +301 |
| | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 313 | 54 | +259 |
| | 40 | 32 | 7 | 1 | 80.00% | 969 | 560 | +409 |
| | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 364 | 50 | +314 |
| | 57 | 44 | 12 | 1 | 77.19% | 1431 | 745 | +686 |
| | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 43 | 10 | +33 |
| | 30 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 93.33% | 862 | 359 | +503 |
| | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 754 | 128 | +626 |
| | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 282 | 30 | +252 |
| | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 58 | 14 | +44 |
| Pacific Islanders | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 41 | 26 | +15 |
| | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 108 | 13 | +95 |
| | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 99 | 14 | +85 |
| | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 411 | 72 | +339 |
| | 30 | 28 | 0 | 2 | 93.33% | 900 | 332 | +568 |
| | 93 | 55 | 35 | 3 | 59.14% | 1863 | 1458 | +405 |
| | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 326 | 35 | +291 |
| | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 100.00% | 171 | 15 | +156 |
| | 33 | 30 | 3 | 0 | 90.91% | 1037 | 356 | +681 |
| World XV | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 66.67% | 94 | 69 | +25 |
| Total | 556 | 428 | 108 | 20 | 76.98% | 15068 | 7259 | +7809 |
World Cup
| Year | Round | Played | Won | Drew | Lost | Pts For | Against |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | Champions | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 298 | 52 |
| 1991 | Third place | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 142 | 74 |
| 1995 | Runners-up | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 327 | 119 |
| 1999 | Fourth place | 6 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 255 | 111 |
| 2003 | Third place | 7 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 361 | 101 |
| 2007 | Quarter-finals | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 327 | 55 |
| 2011 | Champions | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 301 | 72 |
| 2015 | Champions | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 290 | 97 |
| Total | – | 50 | 44 | – | 6 | 2,301 | 681 |
New Zealand have won the World Cup three times, the only team to have done so. They beat France in the final of the 1987 inaugural competition held in New Zealand and Australia, defeated France again in the final of the 2011 tournament, also hosted in New Zealand, and most recently defeated Australia in England in 2015, making them the first and only team to win the World Cup in consecutive tournaments. In 1991, they lost their semi-final to Australia before winning the playoff for third. In 1995, they reached the final, before losing in extra time to hosts South Africa. They finished in fourth place in 1999, after losing their semi-final and then the third-place playoff game. In 2003, New Zealand were knocked out by hosts Australia in their semi-final, before finishing third. The 2007 World Cup saw their worst tournament, being knocked out in the quarterfinals by the host nation France;[129] until this they were the only team to have reached the semifinals of every tournament.[130] As a result of the poor performance in the 2007 World Cup the NZRU commissioned a 47-page report to detail the causes of the failure. The All Blacks have never lost a World Cup pool match, and have finished top of their pool in all seven tournaments.
New Zealand holds several World Cup records: most World Cup Matches (48), most points in one match (145 versus Japan in 1995), most cumulative points over all World Cups (2,248), most tries overall (306), most conversions (222) and also the record for the most points scored in the first half of a knockout game at the Rugby World Cup (29) (against France 2015) along with the largest knockout margin (49) in the same match.[131] Several individual players also hold World Cup records; Jonah Lomu for most World Cup tries (15 over two World Cups)(Currently tied with South Africa's Bryan Habana), Marc Ellis with most tries in a match (6 versus Japan in 1995), Grant Fox with most points in one tournament (126 in 1987), and Simon Culhane with most points in a single game (45 versus Japan in 1995).[131]
Tri Nations and The Rugby Championship
New Zealand's only annual tournament is a competition involving the Southern Hemisphere's top national teams. From 1996 through 2011, they competed in the Tri Nations against Australia and South Africa. In 2012, Argentina joined the competition, which was renamed The Rugby Championship. New Zealand's record of 14 tournament wins (the most recent in 2016) and 74 match wins is well ahead of the other teams' records. The Bledisloe Cup is contested between New Zealand and Australia, and the Freedom Cup between New Zealand and South Africa, as part of the Tri Nations and The Rugby Championship.
| Tri Nations (1996–2011) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nation | Games | Points | Bonus points |
Table points |
Championships | |||||
| played | won | drawn | lost | for | against | diff | ||||
| 72 | 50 | 0 | 22 | 1936 | 1395 | +541 | 32 | 232 | 10 | |
| 72 | 29 | 1 | 42 | 1531 | 1721 | −190 | 34 | 152 | 3 | |
| 72 | 28 | 1 | 43 | 1480 | 1831 | −351 | 24 | 138 | 3 | |
| Rugby Championship (2012– ) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nation | Games | Points | Bonus points |
Table points |
Championships | |||||
| played | won | drawn | lost | for | against | diff | ||||
| 27 | 24 | 1 | 2 | 890 | 421 | +469 | 17 | 115 | 4 | |
| 27 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 553 | 662 | −109 | 5 | 59 | 1 | |
| 27 | 12 | 1 | 14 | 639 | 604 | +35 | 12 | 62 | 0 | |
| 27 | 3 | 1 | 23 | 466 | 861 | −395 | 9 | 23 | 0 | |
Updated: 10 October 2016
Source: espnscrum.com
Players
Current squad
New Zealand's 34-man squad for the 2017 Rugby Championship.[132]
On 10 August, Jordie Barrett withdrew from the squad due to injury and was replaced by David Havili.[133]
All squad members play rugby in New Zealand.
Note: Caps correct as of 10 July 2017
Notable players Captain of the "Original All Blacks" that toured Britain and Ireland in 1905, Dave Gallaher is an inductee into the World Rugby Hall of Fame Fifteen former All Blacks have been inducted into the World Rugby Hall of Fame; Sir Fred Allen, Don Clarke, Sean Fitzpatrick, Grant Fox, Dave Gallaher, Michael Jones, Ian Kirkpatrick, Sir John Kirwan, Sir Brian Lochore, Jonah Lomu, Sir Colin Meads, Graham Mourie, George Nepia, Joe Warbrick and Sir Wilson Whineray.[134][135] Joe Warbrick represented New Zealand on their historic 1884 tour to Australia, but is better known for selecting and captaining the 1888–89 New Zealand Native football team that embarked on a 107-match tour of New Zealand, Australia and the British Isles.[136] The New Zealand Natives were the first New Zealand team to wear black uniforms, and the first to perform a haka.[137] Dave Gallaher played in New Zealand's first ever test match in 1903 and also captained the 1905 Originals. Along with Billy Stead, Gallaher authored the famous rugby book The Complete Rugby Footballer.[138] At the age of only 19, George Nepia played in all 30 matches on the Invincibles tour of 1924–25.[139] Nepia played 37 All Blacks games; his last was against the British Isles in 1930.[139] Sir Fred Allen captained all of his 21 matches for New Zealand, including six tests, between 1946 and 1949.[140] He eventually moved on to coaching New Zealand between 1966 and 1968. New Zealand won all 14 of their test matches with Allen as coach.[140] Five hall of Fame inductees, including the first New Zealander named to the World Rugby Hall of Fame, played during the 1960s. Don Clarke was an All Black between 1956 and 1964 and during this period he broke the record at the time for All Black test points.[141] Clarke famously scored six penalties in one match – a record at the time – to give New Zealand an 18–17 victory over the British Isles at Dunedin in 1959.[141][142] Sir Wilson Whineray played 32 tests, captaining New Zealand in 30 of them.[143] He played prop and also number 8 between 1957 and 1965. New Zealand lost only four of their 30 tests with Whineray as captain.[143] On 21 October 2007, Whineray became the first New Zealander to earn induction to the World Rugby Hall of Fame.[144] In Sir Colin Meads' New Zealand Rugby Museum profile, he is described as "New Zealand's equivalent of Australia's Sir Donald Bradman or the United States of America's Babe Ruth."[145] Meads, nicknamed Pinetree, played 133 games for New Zealand, including 55 tests.[145] In 1999 the New Zealand Rugby Monthly magazine named Meads the New Zealand player of the century.[145] Ian Kirkpatrick played 39 tests, including 9 as captain, between 1967 and 1977.[146] He scored 16 tries in his test career, a record at the time.[146] The only All Blacks Hall of Famer to debut in the 1970s was flanker Graham Mourie. He captained 19 of his 21 tests and 57 of his 61 overall All Blacks matches between 1976 and 1982. Most notably, in 1978 he was captain of the first All Blacks side to complete a Grand Slam over the four Home Nations sides.[147]  Colin Meads, New Zealand's player of the century. The 1987 World Cup champions were coached by Sir Brian Lochore who had represented New Zealand in 25 tests between 1964 and 1971, including 17 as captain.[148] He was knighted in 1999 for his lifetime services to rugby.[149] Four of the 1987 World Cup squad that he had coached are also inductees in the Hall of Fame. Sir John Kirwan played a total of 63 tests between 1984 and 1994, scoring 35 tries, an All Blacks record at the time.[150] In the 1987 World Cup opener against Italy, Kirwan raced 90 meters to score one of the tries of the tournament.[150][151] An All Black from 1984 to 1993, Grant Fox was one of New Zealand's greatest point-scorers with 1067 points, including 645 test points.[152] Fox played 46 tests, including the 1987 World Cup final against France. Known as The Iceman, Michael Jones was one of the greatest open side flankers of all time.[153] Born in Auckland, New Zealand, Jones first played international rugby for Samoa, then for New Zealand, playing 55 tests between 1987 and 1998.[153] Due to his Christian faith, Jones never played rugby on Sundays, resulting in him not playing in the 1991 World Cup semi-final against Australia, and also in him not being picked for the 1995 World Cup squad.[153][154] The team's captain, David Kirk, was inducted into the World Rugby Hall alongside Lochore; all other World Cup-winning captains through 2007 (minus the already-inducted Australian John Eales) were also enshrined at this ceremony. For many years the most capped test All Black was Sean Fitzpatrick, with 92 appearances.[155] He played in the 1987 World Cup after incumbent Andy Dalton was injured, and was appointed All Blacks captain in 1992, continuing in the role until his retirement in 1997.[155] He played 346 first class rugby matches.[156] Jonah Lomu is generally regarded as the first true global superstar of rugby union.[157] He was the youngest player ever to appear in a test as an All Black, making his debut at age 19 years, 45 days in 1994. Lomu, a wing, had unique physical gifts; even though he stood 1.96 m (6 ft 5 in) and weighed 119 kg (262 lb), making him both the tallest[158] and heaviest[159] back ever to play for New Zealand, he could run 100 metres in under 11 seconds. He burst on the international scene in the 1995 Rugby World Cup, scoring seven tries in the competition. Four of those tries came in New Zealand' semifinal win over England, including an iconic try in which he bulldozed England's Mike Catt on his way to the try line. He would add eight more tries in the 1999 Rugby World Cup. Perhaps most remarkably, Lomu played virtually his entire top-level career in the shadow of a serious kidney disorder which ended his test career in 2002 and ultimately led to a transplant in 2004. Even with his career hampered and eventually shortened by his health issues, he scored 37 tries in 63 tests.[160] Lomu was inducted into the World Rugby Hall in October 2011, and was specifically recognised as one of four new inductees "who had left an indelible mark on Rugby World Cup for their moments of magic, inspiration or feats". Individual all-time records Richie McCaw is the most capped rugby player of all time, and was the first New Zealander to play 100 test matches The record for most test points for not only New Zealand, but any nation, is held by Dan Carter with 1,598 from 112 tests.[161] He surpassed Andrew Mehrtens' All Black record total of 967 points from 70 tests[162] in the All Blacks' win over England on 21 November 2009.[163] On 27 November 2010 Dan Carter scored a penalty against Wales to pass Jonny Wilkinson's previous world record of 1,178 points.[164] Carter also holds the record for points against Australia with 366. The All Blacks' record test try scorer is Doug Howlett with 49 tries, who overtook Christian Cullen's 46 during the 2007 World Cup.[165] The world record for tries in a calendar year is held by Joe Rokocoko, with 17 tries in 2003; he also became the first All Black to score ten tries in his first five tests, as well as the first All Black to score at least two tries in each of four consecutive tests.[166] In test matches, the most capped All Black is Richie McCaw with 148 caps.[167] The record for most tests as captain is held by Richie McCaw with 110.[168] The youngest All Black in a test match was Jonah Lomu, capped at age 19 years, 45 days, whilst the oldest test player was Ned Hughes at 40 years, 123 days.[160][169][lower-alpha 12] CoachesThe current head coach of the All Blacks is Steve Hansen, who has held the position since 2012. He is assisted by Ian Foster and Wayne Smith. Due to the definition and role of All Blacks coach varying so much prior to the 1949 All Blacks tour of South Africa, the following table only includes coaches appointed since.[78]
Home groundsLike other major rugby nations Argentina, Australia, France and South Africa, New Zealand does not have an official stadium for its national team. Instead, the All Blacks play their test matches at a variety of venues throughout New Zealand. Prior to the construction of Westpac Stadium in 1999, Wellington's test venue was Athletic Park. Athletic Park was the venue for the first All Blacks test match in New Zealand against Great Britain in 1904.[172] The first home test match played outside the main centres of Auckland, Christchurch, Dunedin or Wellington was in 1996 at McLean Park in Napier.[173] Eden Park and AMI Stadium were upgraded in preparation for the 2011 Rugby World Cup. By that time, the NZRU no longer considered Carisbrook a suitable test venue, and a covered sports stadium was proposed as a replacement.[174] Dunedin City Council approved the new stadium in March 2008,[175] land acquisition proceeded from August to October of that year,[176] and the new venue opened in August 2011, in time for the World Cup. AMI Stadium was significantly damaged during the February 2011 Christchurch earthquake, with cracks in some stands and the playing surface badly damaged by liquefaction as well as damage to infrastructure and streets surrounding the venue. As a result of the damage all scheduled 2011 World Cup games to be held in Christchurch were moved to other regions. test rugby returned to Christchurch in 2012 at Rugby League Park. Although the stands at that venue were damaged severely enough that they had to be torn down, infrastructure damage was much less severe than at AMI Stadium, and the playing surface survived relatively intact. The stadium was rebuilt with a permanent capacity of 17,000, with temporary seating allowing for 9,000 more spectators.
See alsoNotes
References
Works cited
External linksListen to this article (info/dl)
This audio file was created from a revision of the "New Zealand national rugby union team" article dated 2007-07-29, and does not reflect subsequent edits to the article. (Audio help)
More spoken articles
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
