New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway
 | |
 | |
| Reporting mark | NYSW |
|---|---|
| Locale |
New York New Jersey Pennsylvania |
| Dates of operation | 1881–Present |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Headquarters | Cooperstown, New York |
| Website |
www |
The New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (reporting mark NYSW) (or New York, Susquehanna and Western Railroad and also known as the Susie-Q or the Susquehanna) is a Class II American freight railway operating over 500 miles (800 km) of track in the northeastern states of New York, Pennsylvania and New Jersey.[1]
It was formed in 1881 from the merger of several smaller railroads.[2] Passenger service in Northern New Jersey was offered until 1966. The New York, Susquehanna and Western was purchased by the Delaware Otsego Corporation in 1980,[3] and became a regional player during the 1980s in the intermodal freight transport business.
The NYS&W operates over 500 miles of track in three states. The railroad uses three main routes, one running from Northern New Jersey to Binghamton, New York and the other two branching north from Binghamton to serve Utica, New York and Syracuse, New York.
History
Before the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway

.jpg)
The New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway can trace its roots back to the Hoboken, Ridgefield & Paterson Railroad, chartered in 1866 to connect industrial Paterson, New Jersey, with the ports along the Hudson Waterfront opposite New York City at Hoboken. That same year, the New York and Oswego Midland Railroad (NY&OM) was chartered to connect the Great Lakes port at Oswego, New York, with New York City. Several competing companies sprang up in 1867, but the New Jersey Western Railroad (NJW) was the most successful, constructing westward from Paterson and Hawthorne. Cornelious Wortendyke, president of the NJW, signed a lease agreement with DeWitt Clinton Littlejohn of the NY&OM giving his road a through route into New Jersey. Construction on the NY&OM started in 1868 and progressed rapidly. The NJW changed its name to the New Jersey Midland Railway (NJM) in 1870, and construction had stretched from Hackensack, New Jersey, all the way through to Hanford.[5]
The NY&OM reached Middletown, New York, and leased the connecting Middletown, Unionville and Water Gap Railroad (MU&WG), which reached the NJM at Hanford. The last stretch of construction from Hackensack to Jersey City completed the NJM in 1872. The first through train from Oswego to Jersey City operated on July 9, 1873. While the goals of the two partners had been reached, the Panic of 1873 caused financial ruin for both companies. The NY&OM suspended lease payments, and the agreement was broken. The NY&OM was reorganized as the New York, Ontario and Western Railway in 1879, and went its separate way. The NJM took over the lease of the MU&WG as well. Unable to weather the financial storm, the NJM was put into receivership in 1875.[5] In 1880, the NJM was reorganized as the New Jersey Midland Railroad (NJM), and attention was turned to the lucrative coal fields of eastern Pennsylvania.
Formation and as an independent railroad
In 1881, the New Jersey Midland Railroad was consolidated with five other railroads to form the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway. The new New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway had extended west to Gravel Place, Pennsylvania, and a connection with the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railway (DL&W). The NYS&W also had a connection to the DL&W at Delaware, New Jersey via the Blairstown Railway. Due to the increased volume of traffic, the railroad was double-tracked from Paterson to Jersey City in 1887. To reach the port on the Hudson River waterfront, traffic was handed off to the Pennsylvania Railroad at Marion Junction via the Hudson Connecting Railway. To keep more of the line haul revenue for themselves, the Susquehanna extended their line from their Little Ferry Yard through the new Palisades Tunnel to a new terminal at Edgewater where they had constructed coal docks for transfer from train to boat in 1892. The NYSW also reached west of the Delaware River and leased the Wilkes-Barre and Eastern Railroad to access the Scranton area directly and divert traffic away from the Lackawanna.[6]
American financier J.P. Morgan began to take notice of this rapidly expanding coal-hauler, and quietly bought up its stock on behalf of the Erie Railroad. The railroad was leased by the Erie in 1898, and soon after took over complete operation of the line.[7][8][9]
The NYS&W fell on hard times during the economic recession of 1957. The NYS&W lost its western connection to the Lehigh and New England Railroad when the L&NE ceased operations in 1961, resulting in the NYS&W pulling up all its track west of Sparta Jct. (which now comprises what is now known as the Paulinskill Valley Trail). Thereafter, the NYS&W sold off its nearly new Budd passenger cars and replaced them with second-hand used equipment. Desperate to close its money-losing commuter service, the railroad's trustees offered its commuters $1,000 each to stop using the trains. Permission to end commuter service was granted in 1966. Washouts caused by Tropical Storm Doria (1971) cut off other connections, and the railroad retreated to Butler, New Jersey.
Under ownership of the Delaware Otsego Corporation
The NYS&W declared bankruptcy in 1976 after failing to pay New Jersey state taxes, though managed to stay out of Conrail, which had surrounded it. The bankruptcy court ordered that the railroad be abandoned and its assets sold. By then, the NYS&W was down to a 43-mile line from Croxton and Edgewater through Paterson to Butler. The State of New Jersey, aware of Delaware Otsego Corporation's reputation at rehabilitating short lines, asked them to take over the railroad.
Delaware Otsego was founded in 1966 to operate a small section of the former New York Central Railroad Catskill Mountain Branch outside Oneonta, New York. This was the first of many cast-off short line acquisitions. Between 1971 and 1986, D.O. acquired several other branches and short lines, including the Cooperstown Branch of the Delaware & Hudson Railway in 1971; the Richfield Springs Branch of the Erie Lackawanna Railway (EL) in 1973, the Fonda, Johnstown and Gloversville Railroad in 1974, and the EL Honesdale Branch in 1976.[8]
In 1980, the Delaware Otsego Corporation purchased the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway.[8]
The New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway was ordered to operate the Delaware and Hudson Railway until a new buyer was found for the Delaware and Hudson. The Delaware and Hudson Railway went bankrupt while owned by the Guilford Rail System (now Pan Am Railways).

1990 saw the NYS&W end service on its Edgewater Branch, a 1.5-mile (2.4 km) long line connecting its former Hudson River terminal with the mainline in Fairview at Undercliff Junction. As of 2008, the tunnel carries a pipeline owned by the Amarada Hess Corporation.
In 1994, Onondaga County, New York purchased the former Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W) line into Syracuse, with the provision that the NYS&W operate RDC service in Syracuse between Syracuse University, Armory Square, and the Carousel Mall with the option for further routes, leading to the creation of OnTrack. With operations on this segment, the Syracuse branch was rehabilitated and the Conrail interchange relocated. Regular steam excursions were offered and RDCs refurbished for OnTrack use. Intermodal trains rolled beyond Binghamton to Syracuse for interchange with Conrail. After a few years, regular excursions were halted.
With the impending break-up of the Conrail system to Norfolk Southern Railway and CSX Transportation, the NYS&W was a ripe target for acquisition, as it could potentially siphon lucrative traffic away from either road. On October 3, 1997, DOCP Acquisition LLC announced it had completed the short-form merger of Delaware Otsego Corporation (NASDAQ:DOCP) with a wholly owned subsidiary via a stock tender offer of $22 per share.[10]
This deal essentially brought the D.O. System of Railroads, including the subsidiary New York, Susquehanna & Western Railway (NYS&W), under control of the much larger Norfolk Southern and CSX rail systems, because the new owner DOCP Acquisition LLC is owned 40% by Norfolk Southern, 40% by CSX and 20% by Walter G. Rich of the Delaware Otsego Corporation.[11]
In 2005, the NYS&W leased the former Erie Main Line from Port Jervis to Binghamton from Norfolk Southern. Leased and operated under the name Central New York Railroad (CNYK). The CNYK is a "paper" railroad and all train operations and line maintenance is performed by Susquehanna personnel, while Norfolk Southern Railway retains overhead trackage rights. Currently there are only 6 trains a week operated by the NYS&W on the line, one in each direction, three times a week. At this time there is no traffic from the Norfolk Southern. The newly reactivated Stourbridge Railroad (SBRR) depends on the NYS&W for interchange at Lackawaxen, Pennsylvania.
In 2006, NYSW's Utica Main Line had storm damage. The storm damage washed out sections of track in Chenango County putting the branch to Utica out of service. NYS&W continued serving customers on the line in the Utica area and south to Sangerfield from the CSX interconnection in Utica. In 2011, a project to restore the line was started by the Chenango County Industrial Development Agency with funding by the agency, Chenango County, the New York State Department of Transportation, and the federal Economic Development Administration. Work began in March 2016 with the clearing of brush along the 45.5 miles (73.2 km) right-of-way in Chenango County. Subsequent work will include filling in washouts, replacing ties, resurfacing bridge decks, reactivating crossing signals, and other repairs. The restoration project is expected to be complete in June 2017.[12][13]
On August 9, 2007, D.O. founder Walter Rich died of pancreatic cancer.[14] After President Rich's death, the new President Nathan Fenno, almost immediately cancelled all passenger operations and excursions and the fleet used on them was sold off. Many older diesel locomotives were sidelined, retired, and sold during this time as well.
In July 2011, NYS&W took possession of five leased CEFX locomotives, to ease the railroad's continually worsening power shortage. These five locomotives were used as a supplement to its current EMD 645 fleet in road train service, and occasionally local duty. It was not uncommon to see road train line-ups consisting of entirely leased power.
| Year | Traffic |
|---|---|
| 1925 | 119 |
| 1933 | 91 |
| 1944 | 114 |
| 1960 | 67 |
| 1967 | 15 |
Passenger service
The Bergen-Passaic Rail Line was a New Jersey Transit initiative in the mid-2000s studying restoration of passenger service on a segment of NYS&W trackage between Sparta and Hackensack, New Jersey to alleviate traffic congestion on Route 23. The project hit a snag when a suitable location for a NJ Transit rail storage yard in or near Sparta could not be agreed upon.
New FRA-compliant diesel multiple unit rail cars will be used.[15][16][17] The project has been promoted via social networking blogs and Facebook,[18][19] resulting in Kinnelon officials publicly voicing support for the project.[20]
Chinese steam operations and history
In the 1990s, Walter Rich wanted a China Railways SY type steam locomotive. The engine purchased, SY 1698M, was to be NYS&W #141, delivered eventually to Syracuse, New York. Delivery was to be by cargo ship from the Tangshan Works in China through the Indian Ocean, the Red Sea, and the Suez Canal to the Mediterranean Sea, and then across Atlantic Ocean to New York City where then it would get to Syracuse by rail. Due to the Gulf War, shipment was delayed for several months and then ship, the Norwegian freighter Braut Team encountered bad weather in the Indian Ocean, flooded and sank on June 7, 1991 in the Bay of Bengal losing all cargo.[21][22]
After news broke of this, NYS&W made an offer to the Valley Railroad to sell their #1647. The Valley Railroad accepted in 1992 (because both of Valley Railroads engines, the 40 and 97, were repaired).[23] The engine, altered and painted to look like a 1920s era engine, was lettered and renumbered to #142, as the next locomotive after #141. The engine made many runs throughout the NYS&W system, participating in such events such as the Steamtown National Historic Site grand opening in 1995, the Dunellen Railroad Days and Lincoln Park Railroad Days. The engine also has double-headed with other steam locomotives, such as Chesapeake & Ohio #614 and Milwaukee Road #261. The engine now resides on the Belvidere and Delaware River Railroad where it runs tourist excursions along the Delaware River.
Connections with other railroads
- The railroad has connections with two Class I railroads:[24]
- CSX Transportation - Syracuse, New York, Utica, New York, North Bergen, New Jersey
- Norfolk Southern Railway - Binghamton, New York, Marion Junction (New Jersey) and the Passaic Junction (rail yard) rail yard in Saddle Brook, New Jersey
- The railroad has connections with four other railroads:
- Morristown & Erie Railway and New Jersey Transit - Passaic Junction (rail yard), Saddle Brook, New Jersey
- Middletown and New Jersey Railroad - Warwick, New York
- Finger Lakes Railway - Syracuse, New York
- Mohawk, Adirondack and Northern Railroad (MHWA) - Utica, New York
Gallery

 ALCO C636 #3660 at Ridgefield Park, New Jersey, September 2005
ALCO C636 #3660 at Ridgefield Park, New Jersey, September 2005 N and HO scale model trains representing the NYS&W
N and HO scale model trains representing the NYS&W The Paulinskill Valley Trail in Warren County, New Jersey
The Paulinskill Valley Trail in Warren County, New Jersey Historical route of NYS&W
Historical route of NYS&W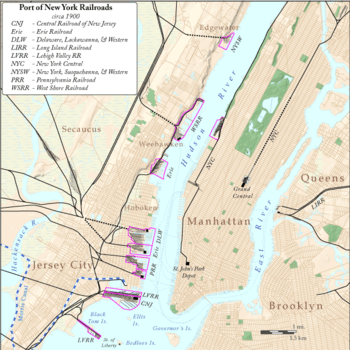 Edgewater Terminal, circa 1900
Edgewater Terminal, circa 1900
See also
- Delaware Otsego Corporation - Parent Company for NYS&W
- Susquehanna Transfer (NYS&W station)
- Hawthorne (NYS&W station)
- Maywood Station Museum, Maywood, NJ
References
- ↑
- ↑ "Six Railroads Consolidated; The New-Jersey Midland To Be Carried Into The Coal-Fields". The New York Times. June 12, 1881.
- ↑
- ↑ Mohowski, Robert E. (2003). The New York, Susquehanna & Western Railroad. Baltimore: JHU Press. p. 175. ISBN 9780801872228.
- 1 2 Krause, John, New York, Susquehanna & Western Railroad, Carstens Publications, 1991, p. 5
- ↑ Krause, John, New York, Susquehanna & Western Railroad, Carstens Publications, 1991, p. 6
- ↑ Robert E. Mohowski (2003). The New York Susquehanna & Western Railroad. The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-7222-7
- 1 2 3 Drury, George H. (1992). The Train-Watcher's Guide to North American Railroads: A Contemporary Reference to the Major railroads of the U.S., Canada and Mexico. Waukesha, Wisconsin: Kalmbach Publishing. pp. 173–175. ISBN 0-89024-131-7.
- ↑ "Six Railroads to Consolidate". The New York Times. Retrieved June 5, 2012.
- ↑
- ↑ "" Docp Acquisition LLC " - Filings - Page 1". SEC Info. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑
- ↑ "Commerce Chenango". Chenangony.org. 1969-12-31. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑ Grace, Tom (2007-08-10). "Railroad chairman Rich dies". The Daily Star.
- ↑ "NJ Transit design and engineering services for the Passaic-Bergen Passenger restoration project". Systra Consulting. Retrieved 2012-05-05.
- ↑ Freemark, Yonah (May 14, 2009). "Making Links in North Jersey". The Transport Politic. Retrieved 2014-05-16.
- ↑ "Passaic-Bergen Rail Plan Advances" (Press release). New Jersey Transit. April 1, 2007. Retrieved 2005-05-21.
- ↑ "Restore Passenger Service on the New York, Susquehanna and Western Rail Line". Nyswpassengerrail.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑ "Restore Passenger Service on the NYS&W Rail Line in New Jersey". Facebook. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑ "Kinnelon mayor wants commuter trains to return - News". NorthJersey.com. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑ Hudson, Mike; Atkins, Philip (September 2007). "Locos lost at sea. The all-time definitive record". The Railway Magazine. IPC Media Ltd. 153 (1277): 14–19. ISSN 0033-8923.
- ↑ "The Business Times". Singapore. June 10, 1991. p. 30.
- ↑ Soloman, Brian (2012). North American Locomotives:A Railroad-by-Railroad Photohistory. Voyageur Press.
- ↑ "Home Page of NYSW". Nysw.com. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
Other sources
- Maywood Station Historical Committee
- George Povall (1986). The New Susquehanna Great Spots for Shots.
- Krause, John and Crist, Ed (1991). Susquehanna: New York Susquehanna & Western RR. Carstens Publications. ISBN 0-911868-38-0.
- Kaminski, Edward S., (2010). New York, Susquehanna & Western Railroad in New Jersey. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-7367-0.
- Kaminski, Edward S. (2010). Maywood - The Borough, The Station, and The Railroad.Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-7234-5.
- Ontario & Western Railway Historical Society
- The Unofficial NYS&W Web Page
- Volunteer Railroaders Association
- Maywood Station Museum
- Southern Tier Timetable
- "THE NEW-JERSEY MIDLAND.; THE STOCKHOLDERS DEMANDING A SHARE UNDER THE REORGANIZATION." The New York Times, March 11, 1880
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway. |
- NYS&W Web Site — Official Corporate Site
- New York, Susquehanna & Western Technical & Historical Society
- Railfan.net NYS&W Site
- The New Jersey Midland Railway — NYS&W Early History
- Details operations at Hanford
- Photographs of the Northern Division
- Historical Photographs
- Susquehanna Surviving Locomotives and All-Time Roster.
