Port-wine stain
| Nevus flammeus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mikhail Gorbachev has a prominent port-wine stain on his forehead. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q82.5 (ILDS Q82.510) |
| ICD-9-CM | 757.32 |
| OMIM | 163000 |
| DiseasesDB | 10384 |
| MedlinePlus | 001475 |
| eMedicine | derm/295 |
| MeSH | D019339 |
A port-wine stain (nevus flammeus), also commonly called a firemark, is almost always a birthmark; in rare cases it can develop in early childhood.[1][2] It is caused by a vascular anomaly (a capillary malformation in the skin).[3] Port-wine stains are named for their coloration, which is similar in color to Port-wine, a fortified red wine from Portugal.
Port-wine stains ordinarily persist throughout life.[4] The area of skin affected grows in proportion to general growth. Port-wine stains occur most often on the face but can appear anywhere on the body, particularly on the neck and upper trunk.[1][5] Early stains are usually flat and pink in appearance. As the child matures, the color may deepen to a dark red or purplish color.[1] In adulthood, thickening of the lesion or the development of small lumps may occur.[1][6]
Port-wine stains may be part of a syndrome such as Sturge–Weber syndrome or Klippel–Trénaunay–Weber syndrome.[1]
Types
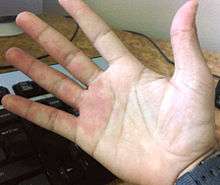
Nevus flammeus may be divided as follows:[7]
Genetics
Port-wine stains were shown to be caused by a somatic activating c.548G→A mutation in the GNAQ gene.[8] An association with RASA1 has also been described.[9]
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider can usually diagnose a port-wine stain based entirely upon the history and appearance. In unusual cases, a skin biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. Depending on the location of the birthmark and other associated symptoms, a physician may choose to order a measurement of intraocular pressure or X-ray of the skull.
A MRI scan of the brain may be performed (under anesthesia) on infants who have a port-wine stain in the head area in order to check for signs of Sturge-Weber syndrome.[1]
If the port-wine stain is inside the mouth, a provider may check the insides of a newborn baby's throat with a scope to see if there are any changes (growths) other than just the color.
If the port-wine stain is around the eye or on the eyelid, a referral may be made to an optometrist or ophthalmologist for a test of the ocular pressures in that eye. If swelling occurs in the port-wine stain, it may cause vision problems, glaucoma, or blindness.
Treatment
Many treatments have been tried for port-wine stains including freezing, surgery, radiation, and tattooing; port-wine stains can also be covered with cosmetics.
Lasers may be able to destroy the capillaries without significant damage to the overlying skin. Lasers and other light sources may therefore be able to reduce the redness of stains, although there is not enough evidence to recommend one form over another.
For most people in trials of pulsed dye laser, more than 25% of the redness was reduced by laser after one to three treatments. Adverse effects were rare in these trials, although some people had changes to the color of the skin, especially Chinese people with darker skin. There can be pain, crusting, and blistering in the two weeks after treatment. The trials only followed people for six months, so long-term outcomes are not known.[3] Up to 10 treatments may be necessary for improvement, but complete removal may not result.[4]
The use of topical rapamycin as an adjunct to pulsed dye laser may improve results.[10]
Treatment is generally given before one year of age.[11] However, as it is recommended to be performed under anesthesia (15 minutes) on small children, it is not always possible to get frequent treatments. For example in Finland a child gets treated 2-3 times per year, resulting in a target of "being ready before school age" (7 years).
After the laser treatment the skin is filled with black marks, the size of a pen. This is due to the laser instrument's size; the black marks disappear within 1–3 weeks. The treated area can be sore and swollen for a couple of days.
Prognosis
In the absence of successful treatment, hypertrophy (increased tissue mass) of the stains may cause problems later in life, such as loss of function (especially if the stain is near the eye or mouth), bleeding, and increasing disfigurement. Lesions on or near the eyelid can be associated with glaucoma.[1] If the port-wine stain is on the face or other highly visible part of the body, its presence can also cause emotional and social problems for the affected person.
It is suggested that gene therapy might be used as a cure in the future.
Epidemiology
Studies have recorded an incidence of about 3–5 cases per 1,000 newborn babies.[12][13][14]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Primary Care Dermatology Society, UK. "Port-wine stain". Clinical Guidance. Primary Care Dermatology Society, UK. Retrieved 8 July 2013.
- ↑ "information about port wine stains". private hospital.
- 1 2 Faurschou, A.; Olesen, AB; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Haedersdal, M. (9 November 2011). "Lasers or light sources for treating port-wine stains.". Cochrane database of systematic reviews (Online) (11): CD007152. PMID 22071834. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007152.pub2.
- 1 2 Patel, AM; Chou, EL; Findeiss, L; Kelly, KM (Jun 2012). "The horizon for treating cutaneous vascular lesions.". Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery. 31 (2): 98–104. PMC 3570568
 . PMID 22640429. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2012.02.001.
. PMID 22640429. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2012.02.001. - ↑ Ryan, E; Warren, L (May 2012). "Birthmarks--identification and management.". Australian family physician. 41 (5): 274–277. PMID 22558616.
- ↑ Minkis, K.; Geronemus, R. G.; Hale, E. K. (2009). "Port wine stain progression: A potential consequence of delayed and inadequate treatment?". Lasers in surgery and medicine. 41 (6): 423–6. PMID 19588535. doi:10.1002/lsm.20788.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 582–3. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Shirley, Matthew D.; Tang, Hao; Gallione, Carol J.; Baugher, Joseph D.; Frelin, Laurence P.; Cohen, Bernard; North, Paula E.; Marchuk, Douglas A.; Comi, Anne M.; Pevsner, Jonathan (8 May 2013). "Sturge–Weber Syndrome and Port-Wine Stains Caused by Somatic Mutation in". New England Journal of Medicine. 368 (21): 1971–9. PMC 3749068
 . PMID 23656586. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213507.
. PMID 23656586. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1213507. - ↑ Eerola I, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, et al. (December 2003). "Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation, a new clinical and genetic disorder caused by RASA1 mutations". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73 (6): 1240–9. PMC 1180390
 . PMID 14639529. doi:10.1086/379793.
. PMID 14639529. doi:10.1086/379793. - ↑ Marques L, Nunez-Cordoba JM, Aguado L, et al. Topical rapamycin combined with pulsed dye laser in the treatment of capillary vascular malformations in Sturge-Weber syndrome: phase II, randomized double-blind, intraindividual placebo controlled trial. JAAD 2015.
- ↑ McLaughlin, MR; O'Connor, NR; Ham, P. (1 January 2008). "Newborn skin: Part II. Birthmarks.". American family physician. 77 (1): 56–60. PMID 18236823.
- ↑ Jacobs, A. H.; Walton, R. G. (1976). "The incidence of birthmarks in the neonate". Pediatrics. 58 (2): 218–22. PMID 951136.
- ↑ Alper, J. C.; Holmes, L. B. (1983). "The incidence and significance of birthmarks in a cohort of 4,641 newborns". Pediatric dermatology. 1 (1): 58–68. PMID 6679890. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1983.tb01093.x.
- ↑ Dr Thajudheen MD (Dr Thaj laser skin hair clinic), Kannangath Jyothy, Arul Priyadarshini, "Treatment of port-wine stains with flash lamp pumped pulsed dye laser on Indian skin: A six year study", Dr. Thaj Laser Skin-Hair Clinic, 2 April 2014
External links
- Information about Port Wine Stains from Children's Hospital, Seattle.
- Birthmarks.com
- Sturge–Weber Syndrome Community