Natural transformation
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a natural transformation provides a way of transforming one functor into another while respecting the internal structure (i.e., the composition of morphisms) of the categories involved. Hence, a natural transformation can be considered to be a "morphism of functors". Indeed, this intuition can be formalized to define so-called functor categories. Natural transformations are, after categories and functors, one of the most fundamental notions of category theory and consequently appear in the majority of its applications.
Definition
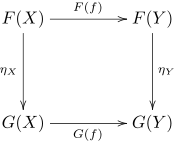
If F and G are functors between the categories C and D, then a natural transformation η from F to G is a family of morphisms that satisfies two requirements.
- The natural transformation must associate to every object X in C a morphism ηX : F(X) → G(X) between objects of D. The morphism ηX is called the component of η at X.
- Components must be such that for every morphism f : X → Y in C we have:
The last equation can conveniently be expressed by the commutative diagram
If both F and G are contravariant, the horizontal arrows in this diagram are reversed. If η is a natural transformation from F to G, we also write η : F → G or η : F ⇒ G. This is also expressed by saying the family of morphisms ηX : F(X) → G(X) is natural in X.
If, for every object X in C, the morphism ηX is an isomorphism in D, then η is said to be a natural isomorphism (or sometimes natural equivalence or isomorphism of functors). Two functors F and G are called naturally isomorphic or simply isomorphic if there exists a natural isomorphism from F to G.
An infranatural transformation η from F to G is simply a family of morphisms ηX: F(X) → G(X). Thus a natural transformation is an infranatural transformation for which ηY ∘ F(f) = G(f) ∘ ηX for every morphism f : X → Y. The naturalizer of η, nat(η), is the largest subcategory of C containing all the objects of C on which η restricts to a natural transformation.
Examples
Opposite group
Statements such as
- "Every group is naturally isomorphic to its opposite group"
abound in modern mathematics. We will now give the precise meaning of this statement as well as its proof. Consider the category Grp of all groups with group homomorphisms as morphisms. If (G, ∗) is a group, we define its opposite group (Gop, ∗op) as follows: Gop is the same set as G, and the operation ∗op is defined by a ∗op b = b ∗ a. All multiplications in Gop are thus "turned around". Forming the opposite group becomes a (covariant) functor from Grp to Grp if we define fop = f for any group homomorphism f: G → H. Note that fop is indeed a group homomorphism from Gop to Hop:
- fop(a ∗op b) = f(b ∗ a) = f(b) ∗ f(a) = fop(a) ∗op fop(b).
The content of the above statement is:
- "The identity functor IdGrp : Grp → Grp is naturally isomorphic to the opposite functor op : Grp → Grp."
To prove this, we need to provide isomorphisms ηG : G → Gop for every group G, such that the above diagram commutes. Set ηG(a) = a−1. The formulas (a∗b)−1 = b−1 ∗ a−1 = a−1 ∗op b−1 and (a−1)−1 = a show that ηG is a group homomorphism with inverse ηGop. To prove the naturality, we start with a group homomorphism f : G → H and show ηH ∘ f = fop ∘ ηG, i.e. (f(a))−1 = fop(a−1) for all a in G. This is true since fop = f and every group homomorphism has the property (f(a))−1 = f(a−1).
Abelianization
Given a group G, we can define its abelianization Gab = G/[G,G]. Let πG : G → Gab denote the projection map onto the cosets of [G,G]. For any homomorphism f : G → H, we have that [G,G] is contained in the kernel of πH ∘ f, because any homomorphism into an abelian group kills the commutator subgroup. Then πH ∘ f factors through Gab as fab ∘ πG = πH ∘ f for some unique homomorphism fab : Gab → Hab. This makes ab : Grp → Grp a functor and π a natural transformation, but not a natural isomorphism, from the identity functor to ab.
Determinant
Given commutative rings R and S with a ring homomorphism f : R → S, the respective groups of invertible n × n matrices GLn(R) and GLn(S) inherit a homomorphism which we denote by GLn(f), obtained by applying f to each matrix entry. Similarly, f restricts to a group homomorphism f* : R* → S*, where R* denotes the group of units of R. In fact, GLn and * are functors from CRing to Grp. The determinant on the group GLn(R), denoted by detR, is a group homomorphism from GLn(R) to R*; moreover, because the determinant is defined by the same formula for every ring, f* ∘ detR = detS ∘ GLn(f) holds. This makes the determinant a natural transformation from GLn to *.
Double dual of a vector space
If K is a field, then for every vector space V over K we have a "natural" injective linear map V → V** from the vector space into its double dual. These maps are "natural" in the following sense: the double dual operation is a functor, and the maps are the components of a natural transformation from the identity functor to the double dual functor.
Tensor-hom adjunction
Consider the category Ab of abelian groups and group homomorphisms. For all abelian groups X, Y and Z we have a group isomorphism
- Hom(X ⊗ Y, Z) → Hom(X, Hom(Y, Z)).
These isomorphisms are "natural" in the sense that they define a natural transformation between the two involved functors Abop × Abop × Ab → Ab. (Here "op" is the opposite category of Ab, not to be confused with the trivial opposite group functor on Ab!)
This is formally the tensor-hom adjunction, and is an archetypal example of a pair of adjoint functors. Natural transformations arise frequently in conjunction with adjoint functors, and indeed, adjoint functors are defined by a certain natural isomorphism. Additionally, every pair of adjoint functors comes equipped with two natural transformations (generally not isomorphisms) called the unit and counit.
Unnatural isomorphism
The notion of a natural transformation is categorical, and states (informally) that a particular map between functors can be done consistently over an entire category. Informally, a particular map (esp. an isomorphism) between individual objects (not entire categories) is referred to as a "natural isomorphism", meaning implicitly that it is actually defined on the entire category, and defines a natural transformation of functors; formalizing this intuition was a motivating factor in the development of category theory. Conversely, a particular map between particular objects may be called an unnatural isomorphism (or "this isomorphism is not natural") if the map cannot be extended to a natural transformation on the entire category. Given an object X, a functor G (taking for simplicity the first functor to be the identity) and an isomorphism proof of unnaturality is most easily shown by giving an automorphism that does not commute with this isomorphism (so ). More strongly, if one wishes to prove that X and G(X) are not naturally isomorphic, without reference to a particular isomorphism, this requires showing that for any isomorphism η, there is some A with which it does not commute; in some cases a single automorphism A works for all candidate isomorphisms η, while in other cases one must show how to construct a different Aη for each isomorphism. The maps of the category play a crucial role – any infranatural transform is natural if the only maps are the identity map, for instance.
This is similar (but more categorical) to concepts in group theory or module theory, where a given decomposition of an object into a direct sum is "not natural", or rather "not unique", as automorphisms exist that do not preserve the direct sum decomposition – see Structure theorem for finitely generated modules over a principal ideal domain § Uniqueness for example.
Some authors distinguish notationally, using ≅ for a natural isomorphism and ≈ for an unnatural isomorphism, reserving = for equality (usually equality of maps).
Example: fundamental group of torus
As an example of the distinction between the functorial statement and individual objects, consider homotopy groups of a product space, specifically the fundamental group of the torus.
The homotopy groups of a product space are naturally the product of the homotopy groups of the components, with the isomorphism given by projection onto the two factors, fundamentally because maps into a product space are exactly products of maps into the components – this is a functorial statement.
However, the torus (which is abstractly a product of two circles) has fundamental group isomorphic to Z2, but the splitting is not natural. Note the use of , , and :[lower-alpha 1]
This abstract isomorphism with a product is not natural, as some isomorphisms of T do not preserve the product: the self-homeomorphism of T (thought of as the quotient space R2/Z2) given by (geometrically a Dehn twist about one of the generating curves) acts as this matrix on Z2 (it’s in the general linear group GL(Z, 2) of invertible integer matrices), which does not preserve the decomposition as a product because it is not diagonal. However, if one is given the torus as a product – equivalently, given a decomposition of the space – then the splitting of the group follows from the general statement earlier. In categorical terms, the relevant category (preserving the structure of a product space) is "maps of product spaces, namely a pair of maps between the respective components".
Naturality is a categorical notion, and requires being very precise about exactly what data is given – the torus as a space that happens to be a product (in the category of spaces and continuous maps) is different from the torus presented as a product (in the category of products of two spaces and continuous maps between the respective components).
Example: dual of a finite-dimensional vector space
Every finite-dimensional vector space is isomorphic to its dual space, but there may be many different isomorphisms between the two spaces. There is in general no natural isomorphism between a finite-dimensional vector space and its dual space.[1] However, related categories (with additional structure and restrictions on the maps) do have a natural isomorphism, as described below.
The dual space of a finite-dimensional vector space is again a finite-dimensional vector space of the same dimension, and these are thus isomorphic, since dimension is the only invariant of finite-dimensional vector spaces over a given field. However, in the absence of additional constraints (such as a requirement that maps preserve the chosen basis), the map from a space to its dual is not unique, and thus such an isomorphism requires a choice, and is "not natural". On the category of finite-dimensional vector spaces and linear maps, one can define an infranatural isomorphism from vector spaces to their dual by choosing an isomorphism for each space (say, by choosing a basis for every vector space and taking the corresponding isomorphism), but this will not define a natural transformation. Intuitively this is because it required a choice, rigorously because any such choice of isomorphisms will not commute with, say, the zero map; see (MacLane & Birkhoff 1999, §VI.4) for detailed discussion.
Starting from finite-dimensional vector spaces (as objects) and the identity and dual functors, one can define a natural isomorphism, but this requires first adding additional structure, then restricting the maps from "all linear maps" to "linear maps that respect this structure". Explicitly, for each vector space, require that it come with the data of an isomorphism to its dual, . In other words, take as objects vector spaces with a nondegenerate bilinear form . This defines an infranatural isomorphism (isomorphism for each object). One then restricts the maps to only those maps that commute with the isomorphisms: or in other words, preserve the bilinear form: . (These maps define the naturalizer of the isomorphisms.) The resulting category, with objects finite-dimensional vector spaces with a nondegenerate bilinear form, and maps linear transforms that respect the bilinear form, by construction has a natural isomorphism from the identity to the dual (each space has an isomorphism to its dual, and the maps in the category are required to commute). Viewed in this light, this construction (add transforms for each object, restrict maps to commute with these) is completely general, and does not depend on any particular properties of vector spaces.
In this category (finite-dimensional vector spaces with a nondegenerate bilinear form, maps linear transforms that respect the bilinear form), the dual of a map between vector spaces can be identified as a transpose. Often for reasons of geometric interest this is specialized to a subcategory, by requiring that the nondegenerate bilinear forms have additional properties, such as being symmetric (orthogonal matrices), symmetric and positive definite (inner product space), symmetric sesquilinear (Hermitian spaces), skew-symmetric and totally isotropic (symplectic vector space), etc. – in all these categories a vector space is naturally identified with its dual, by the nondegenerate bilinear form.
Operations with natural transformations
If η : F → G and ε : G → H are natural transformations between functors F,G,H : C → D, then we can compose them to get a natural transformation εη : F → H. This is done componentwise: (εη)X = εXηX. This "vertical composition" of natural transformation is associative and has an identity, and allows one to consider the collection of all functors C → D itself as a category (see below under Functor categories).
Natural transformations also have a "horizontal composition". If η : F → G is a natural transformation between functors F,G : C → D and ε : J → K is a natural transformation between functors J,K : D → E, then the composition of functors allows a composition of natural transformations εη : JF → KG. This operation is also associative with identity, and the identity coincides with that for vertical composition. The two operations are related by an identity which exchanges vertical composition with horizontal composition.
If η : F → G is a natural transformation between functors F,G : C → D, and H : D → E is another functor, then we can form the natural transformation Hη : HF → HG by defining
If on the other hand K : B → C is a functor, the natural transformation ηK : FK → GK is defined by
Functor categories
If C is any category and I is a small category, we can form the functor category CI having as objects all functors from I to C and as morphisms the natural transformations between those functors. This forms a category since for any functor F there is an identity natural transformation 1F : F → F (which assigns to every object X the identity morphism on F(X)) and the composition of two natural transformations (the "vertical composition" above) is again a natural transformation.
The isomorphisms in CI are precisely the natural isomorphisms. That is, a natural transformation η : F → G is a natural isomorphism if and only if there exists a natural transformation ε : G → F such that ηε = 1G and εη = 1F.
The functor category CI is especially useful if I arises from a directed graph. For instance, if I is the category of the directed graph • → •, then CI has as objects the morphisms of C, and a morphism between φ : U → V and ψ : X → Y in CI is a pair of morphisms f : U → X and g : V → Y in C such that the "square commutes", i.e. ψ f = g φ.
More generally, one can build the 2-category Cat whose
- 0-cells (objects) are the small categories,
- 1-cells (arrows) between two objects and are the functors from to ,
- 2-cells between two 1-cells (functors) and are the natural transformations from to .
The horizontal and vertical compositions are the compositions between natural transformations described previously. A functor category is then simply a hom-category in this category (smallness issues aside).
More examples
Every limit and colimit provides an example for a simple natural transformation, as a cone (category theory) amounts to a natural transformation with the diagonal functor as domain. Indeed, if limits and colimits are defined directly in terms of their universal property, they are universal morphisms in a functor category.
Yoneda lemma
If X is an object of a locally small category C, then the assignment Y ↦ HomC(X, Y) defines a covariant functor FX : C → Set. This functor is called representable (more generally, a representable functor is any functor naturally isomorphic to this functor for an appropriate choice of X). The natural transformations from a representable functor to an arbitrary functor F : C → Set are completely known and easy to describe; this is the content of the Yoneda lemma.
Historical notes
Saunders Mac Lane, one of the founders of category theory, is said to have remarked, "I didn't invent categories to study functors; I invented them to study natural transformations."[2] Just as the study of groups is not complete without a study of homomorphisms, so the study of categories is not complete without the study of functors. The reason for Mac Lane's comment is that the study of functors is itself not complete without the study of natural transformations.
The context of Mac Lane's remark was the axiomatic theory of homology. Different ways of constructing homology could be shown to coincide: for example in the case of a simplicial complex the groups defined directly would be isomorphic to those of the singular theory. What cannot easily be expressed without the language of natural transformations is how homology groups are compatible with morphisms between objects, and how two equivalent homology theories not only have the same homology groups, but also the same morphisms between those groups.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Zn could be defined as the n-fold product of Z, or as the product of Zn − 1 and Z, which are subtly different sets (though they can be naturally identified, which would be notated as ≅). Here we've fixed a definition, and in any case they coincide for n = 2.
References
- ↑ (MacLane & Birkhoff 1999, §VI.4)
- ↑ (Mac Lane 1998, §I.4)
- Mac Lane, Saunders (1998), Categories for the Working Mathematician, Graduate Texts in Mathematics 5 (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, ISBN 0-387-98403-8
- MacLane, Saunders; Birkhoff, Garrett (1999), Algebra (3rd ed.), AMS Chelsea Publishing, ISBN 0-8218-1646-2.
External links
- nLab, a wiki project on mathematics, physics and philosophy with emphasis on the n-categorical point of view
- André Joyal, CatLab, a wiki project dedicated to the exposition of categorical mathematics
- Hillman, Chris. "A Categorical Primer". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.24.3264
 : formal introduction to category theory.
: formal introduction to category theory. - J. Adamek, H. Herrlich, G. Stecker, Abstract and Concrete Categories-The Joy of Cats
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: "Category Theory"—by Jean-Pierre Marquis. Extensive bibliography.
- List of academic conferences on category theory
- Baez, John, 1996,"The Tale of n-categories." An informal introduction to higher order categories.
- WildCats is a category theory package for Mathematica. Manipulation and visualization of objects, morphisms, categories, functors, natural transformations, universal properties.
- The catsters, a YouTube channel about category theory.
- "Category Theory". PlanetMath.
- Video archive of recorded talks relevant to categories, logic and the foundations of physics.
- Interactive Web page which generates examples of categorical constructions in the category of finite sets.