Natashquan River
| Natashquan River | |
| Country | Canada |
|---|---|
| Province | Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec |
| Source | Unnamed wilderness |
| - location | About 210 km (130 mi) ESE of Labrador City, Newfoundland and Labrador |
| - elevation | 630 m (2,067 ft) |
| - coordinates | 52°31′00″N 63°45′45″W / 52.51667°N 63.76250°W |
| Mouth | Gulf of Saint Lawrence |
| - location | Natashquan FN Reserve, Quebec |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 50°07′07″N 61°48′26″W / 50.11861°N 61.80722°WCoordinates: 50°07′07″N 61°48′26″W / 50.11861°N 61.80722°W |
| Length | 410 km (255 mi) [1] |
| Basin | 16,100 km2 (6,200 sq mi) [1] |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 410 m3/s (14,480 cu ft/s) [1] |
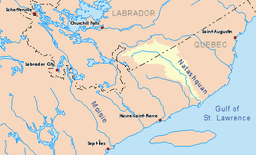 Drainage basin in yellow | |
The Natashquan [nəˈtæʃkn][2] is a river in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador.
Geography
The river has its source just south of the boundary between the Atlantic and Saint Lawrence river watersheds. It flows south-east to the Labrador–Quebec border from where it flows southward. In Quebec, the river forms the boundary between the Minganie and Golfe-du-Saint-Laurent Regional County Municipalities before draining into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, about 370 kilometers (230 mi) east from Sept-Îles. The name is of Innu origin, who call it Nutahquaniu Hipu, meaning "river where black bear is hunted".[3]
Together with the Moisie River, the Natashquan is one of the most renowned salmon rivers on the North Shore of the Gulf.[4]
Geology
The Natashquan River is entirely within the Grenville geologic province of the Canadian Shield, characterized by a hilly plateau, ranging in altitude from 140 meters (460 ft) to 620 meters (2,030 ft), and consisting of felsic and metamorphic rock (such as gneiss, migmatite and granite), clastic rock (quartzite) and schists in the lower portion, with a few intrusions of mafic rock (diorite and gabbro) in the central part. The river largely runs through narrow valleys, and is fed by about 30 tributaries, of which the most significant are in downstream order: the Lejamtel, Mercereau, Mahkunipiu, Mistanipisipou, East Natashquan, Pehatnaniskau, Doré, West Natashquan, and Akaku Rivers.[4]
The last 18 kilometers (11 mi) of the river forms a large sandy estuary, separated from the gulf by Natashquan Point and Cape Tiennot. Sainte-Hélène Island (île Sainte-Hélène) is located at the very mouth of the river.
The climate of the basin is subarctic continental, with a short growing season. The upper portion has a cold subhumid climate, whereas the lower part is humid.[4]
History
In 1534, Jacques Cartier sailed by the area and named Cape Thiennot after a ship captain that had settled at that location. The river was mapped in 1684 by Louis Jolliet who called it "Noutascoüan". Jacques-Nicolas Bellin identified it as "Grand R. Natachquoin" on his map of 1744, while the 1776 map by Carver showed "Great Natashkwen".[3]
From as early as 1710, a trading post was established on the left (south) bank of the Natashquan River and later on the opposite bank (at the river's mouth at present-day Natashquan FN Reserve) to conduct fur trade with the indigenous Innu people. The post was acquired by the Hudson's Bay Company in the middle of the 19th century, but abandoned circa 1914 due to lack of profitability.[5]
A bridge carrying Quebec Route 138 across the river was opened on September 26, 2013.[6][7]
Conservation
An area of 4,089 square kilometres (1,579 sq mi) is being considered for protection in a biodiversity reserve. The reserve, mostly within the Petit-Mécatina unorganized territory, will extend 190 kilometres (120 mi) along the Natashquan River southward from the Labrador–Quebec border and also include 105 kilometres (65 mi) of the East Natashquan River.[4] Furthermore, some 16,000 square kilometres (6,200 sq mi) is under study to be included in a new park, the Natashquan-Aguanus-Kenamu National Park.[8]
The landscape of proposed reserve is deemed to have great beauty, exceptional value, recognized heritage interest, and considerable cultural interest. Therefore, the reserve is meant to protect favourable Atlantic salmon habitats, biodiversity of aquatic and riparian habitats, and old-growth forests. It will also manage sustainable harvesting of fur-bearing animals and develop tourism opportunities, while prohibiting mining, forestry, and hydro-electric development.[4]
See also
Related articles
- Natashquan, Quebec, municipality
- Minganie Regional County Municipality, Quebec, MRC
- Le Golfe-du-Saint-Laurent Regional County Municipality, Quebec, MRC
- Côte-Nord (North-Shore)
References
- 1 2 3 Natural Resources Canada, Atlas of Canada - Rivers
- ↑ SVN mail from Gnome.org
- 1 2 "Natashquan (Rivière)" (in French). Commission de toponymie du Québec. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Proposed Natashquan river valley biodiversity reserve - Conservation plan" (PDF), Quebec strategy for protected areas, Ministère du Développement durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs, Quebec, 2008-03-20
- ↑ "Natashquan (Municipalité de canton)" (in French). Commission de toponymie du Québec. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- ↑ "Une nouvelle route pour Kegaska".
- ↑ "Le pont de Natashquan inauguré".
- ↑ Ministère du Développement durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs, Quebec - Parc national Natashquan-Aguanus-Kenamu project