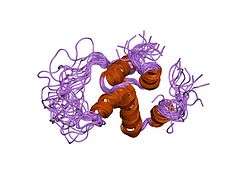
NLRP1
NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NLRP1 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
This gene encodes a member of the Ced-4 family of apoptosis proteins. Ced-family members contain a caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and are known to be key mediators of programmed cell death. The encoded protein contains a distinct N-terminal pyrin-like motif, which is possibly involved in protein-protein interactions. The NLRP1 protein interacts strongly with caspase 2 and weakly with caspase 9. Overexpression of this gene was demonstrated to induce apoptosis in cells. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined.[7]
Interactions
NLRP1 has been shown to interact with caspase 9[8][9] and APAF1.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000091592 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000070390 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Thorpe KL, Abdulla S, Kaufman J, Trowsdale J, Beck S (Oct 1996). "Phylogeny and structure of the RING3 gene". Immunogenetics. 44 (5): 391–6. PMID 8781126. doi:10.1007/BF02602785.
- ↑ Tschopp J, Martinon F, Burns K (Feb 2003). "NALPs: a novel protein family involved in inflammation". Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4 (2): 95–104. PMID 12563287. doi:10.1038/nrm1019.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: NLRP1 NLR family, pyrin domain containing 1".
- 1 2 Chu ZL, Pio F, Xie Z, Welsh K, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Godzik A, Reed JC (Mar 2001). "A novel enhancer of the Apaf1 apoptosome involved in cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation and apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 9239–45. PMID 11113115. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006309200.
- ↑ Hlaing T, Guo RF, Dilley KA, Loussia JM, Morrish TA, Shi MM, Vincenz C, Ward PA (Mar 2001). "Molecular cloning and characterization of DEFCAP-L and -S, two isoforms of a novel member of the mammalian Ced-4 family of apoptosis proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 9230–8. PMID 11076957. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009853200.
Further reading
- Bertin J, DiStefano PS (2001). "The PYRIN domain: a novel motif found in apoptosis and inflammation proteins.". Cell Death Differ. 7 (12): 1273–4. PMID 11270363. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400774.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, Liu W, Gibbs RA (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction.". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. PMID 8619474. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, Muzny DM, Ding Y, Liu W, Ricafrente JY, Wentland MA, Lennon G, Gibbs RA (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing.". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. PMC 139146
 . PMID 9110174. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353.
. PMID 9110174. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. - Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M, Kikuno R, Hirosawa M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XIII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro.". DNA Res. 6 (1): 63–70. PMID 10231032. doi:10.1093/dnares/6.1.63.
- Hlaing T, Guo RF, Dilley KA, Loussia JM, Morrish TA, Shi MM, Vincenz C, Ward PA (2001). "Molecular cloning and characterization of DEFCAP-L and -S, two isoforms of a novel member of the mammalian Ced-4 family of apoptosis proteins.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 9230–8. PMID 11076957. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009853200.
- Chu ZL, Pio F, Xie Z, Welsh K, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Godzik A, Reed JC (2001). "A novel enhancer of the Apaf1 apoptosome involved in cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation and apoptosis.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 9239–45. PMID 11113115. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006309200.
- Martinon F, Hofmann K, Tschopp J (2001). "The pyrin domain: a possible member of the death domain-fold family implicated in apoptosis and inflammation.". Curr. Biol. 11 (4): R118–20. PMID 11250163. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00056-2.
- Damiano JS, Stehlik C, Pio F, Godzik A, Reed JC (2001). "CLAN, a novel human CED-4-like gene.". Genomics. 75 (1-3): 77–83. PMID 11472070. doi:10.1006/geno.2001.6579.
- Nath SK, Kelly JA, Namjou B, Lam T, Bruner GR, Scofield RH, Aston CE, Harley JB (2002). "Evidence for a susceptibility gene, SLEV1, on chromosome 17p13 in families with vitiligo-related systemic lupus erythematosus.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69 (6): 1401–6. PMC 1235552
 . PMID 11592035. doi:10.1086/324470.
. PMID 11592035. doi:10.1086/324470. - Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J (2002). "The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta.". Mol. Cell. 10 (2): 417–26. PMID 12191486. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00599-3.
- Hiller S, Kohl A, Fiorito F, Herrmann T, Wider G, Tschopp J, Grütter MG, Wüthrich K (2004). "NMR structure of the apoptosis- and inflammation-related NALP1 pyrin domain.". Structure. 11 (10): 1199–205. PMID 14527388. doi:10.1016/j.str.2003.08.009.
- Spritz RA, Gowan K, Bennett DC, Fain PR (2004). "Novel vitiligo susceptibility loci on chromosomes 7 (AIS2) and 8 (AIS3), confirmation of SLEV1 on chromosome 17, and their roles in an autoimmune diathesis.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 74 (1): 188–91. PMC 1181907
 . PMID 14691733. doi:10.1086/381134.
. PMID 14691733. doi:10.1086/381134. - Damiano JS, Oliveira V, Welsh K, Reed JC (2004). "Heterotypic interactions among NACHT domains: implications for regulation of innate immune responses.". Biochem. J. 381 (Pt 1): 213–9. PMC 1133779
 . PMID 15107016. doi:10.1042/BJ20031506.
. PMID 15107016. doi:10.1042/BJ20031506. - Liu F, Lo CF, Ning X, Kajkowski EM, Jin M, Chiriac C, Gonzales C, Naureckiene S, Lock YW, Pong K, Zaleska MM, Jacobsen JS, Silverman S, Ozenberger BA (2005). "Expression of NALP1 in cerebellar granule neurons stimulates apoptosis.". Cell. Signal. 16 (9): 1013–21. PMID 15212762. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.02.006.