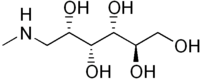
Meglumine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4R,5S)-6-(Methylamino)hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol | |
| Other names
N-methyl-D-glucamine; Methylglucamine; N-Methylglucamine; 1-Deoxy-1-(methylamino)-D-glucitol; 1-Deoxy-1-methylaminosorbitol; N-Methylsorbitylamine; Meglumin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.916 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H17NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 195.22 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| log P | −2.509 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.52 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 0.526 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Meglumine is an amino sugar derived from glucose. It is often used as an excipient in pharmaceuticals and in conjunction with iodinated compounds in contrast media such as diatrizoate meglumine, iothalamate meglumine and iodipamide meglumine.[1]
See also
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.