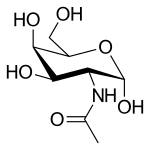
''N''-Acetylgalactosamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-galactose | |
| Other names
GalNAc; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose; N-Acetylchondrosamine; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactopyranose; N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 221.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F; 445 to 446 K) |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S24/25 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related monosaccharides |
N-Acetylglucosamine Galactosamine Galactose |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
Function
In humans it is the terminal carbohydrate forming the antigen of blood group A.[1]
It is typically the first monosaccharide that connects serine or threonine in particular forms of protein O-glycosylation.
N-Acetylgalactosamine is necessary for intercellular communication, and is concentrated in sensory nerve structures of both humans and animals.
See also
- Galactosamine
- Globoside
- (N-Acetylglucosamine) GlcNAc
References
- ↑ Donald M. Marcus; Elvin A. Kabat; Gerald Schiffman (1964). "Immunochemical Studies on Blood Groups. XXXI. Destruction of Blood Group A Activity by an Enzyme from Clostridium tertium Which Deacetylates N-Acetylgalactosamine in Intact Blood Group Substances". Biochemistry. 3: 437–443. doi:10.1021/bi00891a023.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.