Munich Airport
| Munich Airport Flughafen München | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Flughafen München GmbH | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Munich, Germany | ||||||||||||||
| Location | near Freising | ||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||
| Focus city for |
| ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 1,487 ft / 453 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 48°21′14″N 011°47′10″E / 48.35389°N 11.78611°ECoordinates: 48°21′14″N 011°47′10″E / 48.35389°N 11.78611°E | ||||||||||||||
| Website | munich-airport.de | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
 MUC Location within Bavaria | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Helipads | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2016) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Munich Airport (IATA: MUC, ICAO: EDDM), German: Flughafen München, is a major international airport near Munich, the capital of Bavaria. It is the second busiest airport in Germany in terms of passenger traffic behind Frankfurt Airport, and the seventh-busiest airport in Europe, handling 42 million passengers in 2016. It is the world's 15th-busiest airport in terms of international passenger traffic,[4] and was the 34th-busiest airport worldwide in 2015.[5] As of February 2017, the airport features flights to 248 destinations, making it the airport with the fifth-most destinations worldwide.[6] Munich Airport serves as the secondary hub for Lufthansa including Lufthansa Regional and its Star Alliance partners besides Frankfurt.
The airport is located 28.5 km (17.7 mi) northeast of Munich near the old city of Freising and is named in memory of the former Bavarian Prime Minister Franz Josef Strauss. It features two passenger terminals with an additional midfield terminal and two runways as well as extensive cargo and maintenance facilities and is fully equipped to handle wide-body aircraft including the Airbus A380.
History
Development
From 1939 to 1992, Munich was served by Munich-Riem Airport. First plans to expand or build a new airport were made in 1954 owing to the traffic flow-rate and the population density in its proximity. The decision for building the new airport at Erdinger Moos was made on 5 August 1969 by the Bavarian government. When construction started on 3 November 1980, a village named Franzheim was demolished and the ~500 inhabitants were resettled. The airport is located on the territory of four different municipalities: Oberding (location of the terminals; district of Erding), Hallbergmoos, Freising, and Marzling in the district of Freising.
The airport is named after Franz Josef Strauß, who played a prominent, albeit sometimes controversial, role in politics of the Federal Republic of Germany from the 1950s until his death in 1988. Amongst other positions, Strauß was a long-time Minister-President (Governor) of the state of Bavaria, where the airport is located and was initiated under his government. Strauß, having been a private pilot himself, had a particular interest in the aviation industry. He is regarded one of the fathers of Airbus and served as initial chairman of its supervisory board.[7] Naming the airport by its full name "Flughafen München Franz Josef Strauß" is fairly uncommon. The company that owns and operates the airport is named "Flughafen München GmbH" and brands itself as "M – Flughafen München" or "M – Munich Airport". In the Munich area, most people use the term "Flughafen München" (Munich Airport), sometimes "Flughafen München II" in order to distinguish from the earlier airport, or simply "MUC" for its IATA-code.
Operations
The new Munich Airport commenced operation on 17 May 1992, when operations moved from the former site at Munich-Riem Airport, which was closed shortly before midnight on the day before. As their home base at Frankfurt Airport suffered from capacity limits back then, Lufthansa established a second hub offering several short- and long-haul connections through Munich in addition to Frankfurt. While Lufthansa serves more European destinations from Munich Airport than from Frankfurt Airport, Frankfurt has many more intercontinental routes.
Between 1995 and 2006 passenger numbers doubled from under 15 million per annum to over 30 million,[8] despite the impact of the 11 September attacks in 2001 and 2002. In 1996 the airport overtook Düsseldorf as Germany's second-busiest airport and currently handles almost twice as many passengers as the country's third-busiest airport.
In June 2003 construction of Terminal 2 was completed and it was inaugurated as an exclusive facility for Lufthansa and its Star Alliance partners.
In November 2013, the airport introduced its first new corporate design since its inauguration. The large letter 'M' remains in a new font type, and a dash has been added which changes between several colors. There are also animated color-changing versions of the 'M'-sign placed throughout the airport area, for example on the main entrance road and on the new Terminal 2 satellite.[9]
In May 2015, Munich Airport became the first airport outside Asia to be ranked as a "5-Star Airport" by Skytrax. It also won "Best Airport in Europe" for the eighth time.[10][11]
In June 2015, Condor announced it intends to establish a long-haul base at Munich Airport from the 2016 summer season. Condor has already based short- and mid-haul operations at the airport and resumed long-haul flights in winter 2013 after a six-year absence.[12] In November 2015, Transavia announced their intention to establish their first German base at Munich Airport which will consist of four aircraft serving 18 new routes by spring 2016.[13] As of June 2015, the biggest foreign carrier in Munich in terms of passenger numbers is Air Dolomiti.[14]
During 2015, Munich Airport counted more than 40 million passengers per year for the first time.[15]
In December 2016, Lufthansa's low-cost subsidiary Eurowings announced it intends to establish a major base at Munich Airport from March 2017, with 32 new routes.[16] These new base operations will be carried out by Air Berlin on a new wet-lease contract with Eurowings.[17] In February 2017, Transavia announced to shut down their entire base at Munich Airport by October 2017 after only a year of service due to a change in their business strategy and negative economic outlook.[1]
Terminals and facilities
Munich Airport covers 15.6 square kilometers (3,900 acres) of land area. Most of the airport's facilities are located in the area between the two runways. The approach road and railway divide the west part into a southern half, which contains cargo and maintenance facilities, and a northern half, which contains mostly administrative buildings and service facilities, a holiday long-term parking lot and the visitors' centre. It is followed by the west apron and Terminal 1, then the Munich Airport Center (MAC), Terminal 2 and the east apron. Munich Airport has two passenger terminals, and shuffled 20–25 million people through each terminal in 2014.[18]
Terminal 1


Terminal 1 is the older terminal and commenced operation when the airport was opened on 17 May 1992. It has a total capacity of 25 million passengers per year and is subdivided into five modules designated A, B, C, D and E. Modules A through D provide all facilities necessary to handle departures and arrivals, including individual landside driveways and parking, whereas module E is equipped to handle arrivals only. This design essentially makes each module a self-contained sub-terminal of its own. Modules A and D are used for flights within the Schengen-area, while modules B and C handle those to destinations outside it. Hall F is separate, located near Terminal 2, and handles flights with increased security requirements, i.e. those to Israel. Furthermore, the check-in counters for some flights departing from Terminal 1 are located in the central area Z (German: Zentralbereich) where most of the shopping and restaurant facilities of this Terminal as well as the airport's suburban railway station are also located.
The 1,081 m (3,547 ft) pier features 21 jet bridges, two of which have been rebuilt into waiting halls for bus transfers. One gate position has been equipped with three jet bridges to handle the Airbus A380 which is regularly used by Emirates. There are further 60 aircraft stands on the apron, some of which are equipped with specially designed apron jet bridges (German: Vorfeldfluggastbrücken), to which passengers are brought by bus. This unique concept allows passengers to board with full protection from the weather but without the high investments required for full satellite terminals connected through a passenger transport system.
Terminal 1 currently handles all airlines that are not members or partners of the Star Alliance with the exception of Turkish Airlines. However, owing to lack of capacity at Terminal 2, Lufthansa's subsidiary Germanwings and former affiliate Condor both moved back to Terminal 1 in 2007.[19][20] Germanwings however moved back to Terminal 2 in late 2015. Some of the major users at Terminal 1 are Air Berlin, Condor, Emirates, Qatar Airways, American Airlines, Delta Air Lines, easyJet and TUIfly amongst several others.
Terminal 1 extension
As of December 2015, a major redesign of Terminal 1 including a capacity increase and an extension of the central terminal building to the west for centralised security and shopping facilities was under preparation.[21] In November 2016, a major €400m extension and refurbishment for Terminal 1 has been announced. Terminal areas A and B will be entirely redesigned with the addition of a 320m long pier stretching out on the apron. The new facilities will provide capacity for 6 million additional passengers, will be able to handle 12 aircraft including two Airbus A380s at once, and are due to open by 2022.[22]
Terminal 2
_(MUC_-_EDDM)_AN0517640.jpg)
Terminal 2 commenced operation on 29 June 2003. It has a design capacity of 25 million passengers per year and is exclusively used by Lufthansa and all other Star Alliance members serving Munich except Turkish Airlines. Star Alliance partners Air Malta, Luxair and BMI Regional also use Terminal 2.
Having been designed as a hub terminal it is not divided into modules like Terminal 1. Instead, all facilities are arranged around a central Plaza. Owing to security regulations imposed by the European Union, the terminal has been equipped with facilities to handle passengers from countries considered insecure, i.e. not implementing the same regulations. This required the construction of a new level as, unlike other airports, the terminal does not have separate areas for arriving and departing passengers. The new level 06 opened on 15 January 2009.
The pier, which is 980 m (3,220 ft) long, is equipped with 24 jet bridges. As the total number of 75 aircraft stands on the east apron is not always sufficient, Terminal 2 sometimes also uses parking positions on the west apron, to which passengers are carried by airside buses. Terminal 2 is able to handle the Airbus A380 as well, however there are no designated stands or additional jet bridges for it until the opening of the Terminal 2 satellite building. As there is no airline currently serving Terminal 2 with the A380, the largest passenger aircraft regularly handled there are the Thai Airways Boeing 747-400s.
Terminal 2 has two main departure levels, 04 and 05 and additional bus gates on the lower level 03. Gates on level 05 (H) are designated non-Schengen gates. Until the new transfer level 06 opened, the northernmost gates were behind an additional security checkpoint for departures to the USA most of the day. The lower level 04 (G) contains Schengen gates. The bus gates on level 03 are also designated G and are also used for Schengen flights. Level 03 is smaller than the main levels and consists of two separate parts which can be reached from two points on level 04. One area of these gates is designated to Air Dolomiti.
The terminal is operated by Terminal-2-Betriebsgesellschaft (German for Terminal 2 Operating Company), which is owned by Flughafen München GmbH (60%) and Lufthansa (40%). This makes Terminal 2 the first terminal in Germany which is co-operated by an airline.
Terminal 2 Satellite

While Terminal 1 still has plenty of capacity left – in 2011, it handled only about 11 million passengers[23] – an extension of Terminal 2, which operated over full capacity handling 27.5 million passengers by 2013,[24] was required by Lufthansa and its Star Alliance partners to allow easy transfers within a single terminal and to provide more building parking positions equipped with jetbridges and additional waiting areas. When Terminal 2 and its east apron were built prior to 2003, preparations for a satellite terminal had already been made.
Construction for the satellite building was approved in 2010 and started in 2012; it was completed by the end of 2015.[25] The satellite terminal was inaugurated on 22 April 2016[26] and has been in operation since 26 April 2016[27] after trial runs made with the help of volunteers that had started in January 2016.[28] This extension to Terminal 2 saw the already existing baggage sorting hall on the east apron upgraded and heavily extended with new floors to become the satellite terminal. Besides the baggage transport tunnel, there already were three more unused tunnels beneath the Terminal 2 apron of which one was equipped with a fully automated people mover by Bombardier Transportation connecting the Terminal 2 main building with the new satellite.[29] In July 2016, less than three months after its opening, the satellite terminal recorded its one millionth passenger.[30]
The new satellite building is 609 meters (1,998 ft) long with 125,000 square meters (1,345,500 sq ft) of floor space.[31] It allows an additional 11 million passengers to be handled per year, adding 52 gates using 27 parking positions, of which 11 are able to handle wide-body aircraft including the Airbus A380.[25] The building is able to handle Schengen and Non-Schengen flights[32] on two main levels (K for Schengen and L for Non-Schengen destinations[33] as well as area J for some additional bus gates) and features 44 new passport control stations and 24 security lanes for transfer passengers[31] as well as new restaurants, shops and five new Lufhansa lounges.[31] However, the satellite is an airside only facility, check-in and arrivals is still located in the Terminal 2 main building only. The project did cost 650 million Euros, shared between the airport's operator (60%) and Lufthansa (40%).[32] An expansion for the satellite building into a 'T' shape is planned for the future along with another satellite and room for a possible third Terminal to the east.[34]
Munich Airport Center

The Munich Airport Center (sometimes shortened to MAC) is a shopping, business, and recreation area that connects the two terminals. The older Central Area (German: Zentralbereich), which was originally built as part of Terminal 1, hosts a shopping mall and the S-Bahn station. The newer MAC Forum built with Terminal 2 is a large outdoor area with a partly transparent tent-like roof. Next to it is the airport hotel managed by Hilton Hotels & Resorts which was designed by the world-famous architect Helmut Jahn and landscape architecture firm PWP Landscape Architecture in 1994.
The Munich Airport Center has the only supermarket in the entire state of Bavaria where one can shop from 05.30 to midnight every day, including Sundays,[35] as it is exempt from the Bavarian law governing retail hours of operation (German: Ladenschlussgesetz).[36]
Runways
The airport has two parallel runways and one concrete helipad. The two concrete runways (08R/26L and 26R/08L) are each 4,000 meters (13,120 ft) long and 60 meters (200 ft) wide.[37]
Planned third runway
A third runway would increase the number of schedulable aircraft movements per hour from 90 to 120.[38] It would run in parallel to the existing runways and be located to the north-east of the current north runway, significantly extending the total area occupied by the airport. According to Flughafen München GmbH (FMG), the airport's operator, the current two-runway system is already operating at full capacity during peak hours, and requests for additional slots from airlines have been denied. Further increase in air traffic is expected as Munich is to become a second major hub in Germany after Frankfurt.
In August 2007, the airport operator applied for planning permission from the government of Upper Bavaria. More than 60,000 objections have been filed during public display of the plans. The objections, lawsuits, and results of a citywide referendum against the 3rd runway were later overturned by the Bavarian Administrative Court, allowing for construction plans to proceed.
On 26 July 2011, the government of Upper Bavaria issued the zoning approval for the construction of a third runway. With this decision, the zoning authority, after the intensive examination and consideration of all ramifications, expressly approved the need presented by Flughafen München GmbH and the plans submitted for the third runway. Also tied to the approval by the government of Upper Bavaria is the prompt completion of the construction project. However, the airport operator has chosen to follow the advice of Bavaria’s Higher Administrative Court and not to proceed until the principal proceedings concerning the project have reached a conclusion. The decision is currently being reviewed by the court. The building permit associated with the zoning will continue to be valid for up to 15 years.
While according to ICAO Regulations (Annex XIV) the new runway would have to be named 08L/26R (renaming the existing north runway to 08C/26C), it is currently assigned the working title 09/27 in all plans.[39]
In 2015, the airport received approval from Germany's Federal Administrative Court to build a third runway, dismissing all complaints and appeals, and confirming the 2014 decision of Bavaria's Higher Administrative Court to grant approval. The plans include a new 4,000 m (13,100 ft) runway northeast of the existing airport and a new satellite building at Terminal 2, the latter of which did open in April 2016. However, construction of the new runway may yet be delayed as the project has to have unanimous approval by the airport's three shareholders: Bavaria, Federal Republic of Germany and the City of Munich. The last has opposed the plan since a 2012 referendum.[40]
Parking areas
Currently, there are five parking garages and six underground parking areas, amounting together to a total of 30,000 parking spaces[41] of which approximately 16,500 are under a roof. The parking garage P20 at Terminal 2, with 6400 parking spaces on eleven levels (including four that are under ground) since its commissioning in 2003 was the largest parking garage in Germany until the car park at the new Allianz Arena was opened in 2005.[42] A parking guidance system was installed in the parking garages, which detects whether a parking space is occupied and newly arriving vehicles are shown where the empty parking spaces are located.
Apart from the usual parking facilities, the Munich Airport offers, at additional cost, special parking spaces with additional benefits. This includes valet parking, in which the vehicle is picked up by an airport employee upon flight departure and parked, and the Park, Sleep & Fly option, in which a night at the Hilton hotel is included. Also there is an option for oversized parking spaces, the so-called XXL parking, and secure parking. And lastly there is a special separate parking level in the P20 parking garage, where the parked cars are guarded. In addition, you can book special services, such as interior/exterior cleaning and fuelling.
To make the shopping in the public areas more attractive for local residents of the airport area, there are special offers in which you can park up to three hours for free in the P20 parking garage.[43] In the east of the central region, you can find short-term parking, where you can park for free for a maximum of thirty minutes. During the holiday periods other cheaper options are provided in the P8 parking garage.
Visitor viewing facilities

The airport authorities have set out to cater for visitors and sightseers by creating a 'Visitors Park' which includes a 'Visitors Hill', from which a good view of the westerly aircraft apron and Terminal 1 can be obtained, as well as a restaurant and a shop for aircraft models and other collectors' items. This location is served by a railway station named 'Besucherpark'. The view from the hill is shown in the above widescreen image of the Terminal 1 apron. Three historic aircraft are on display in the park, a Super Constellation, a Douglas DC-3, and a Junkers Ju 52/3m.
There is also a visitors' viewing terrace on the roof of Terminal 2 that features a wide, glassed balcony with seating areas and gives a view of the easterly aircraft apron. All visitors can access the terrace from the landside. The entrance fee was abolished in September 2013. There are two additional smaller Visitor Hills on the north end of the north runway and at the center of the south runway.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
The following airlines offer regular scheduled and charter flights at Munich Airport:[44]
Cargo
Statistics
Passenger numbers


| Passengers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 23,125,872 | |||
| 2001 | | |||
| 2002 | | |||
| 2003 | | |||
| 2004 | | |||
| 2005 | | |||
| 2006 | | |||
| 2007 | | |||
| 2008 | | |||
| 2009 | | |||
| 2010 | | |||
| 2011 | | |||
| 2012 | | |||
| 2013 | | |||
| 2014 | | |||
| 2015[66] | | |||
| 2016[67] | | |||
| Source: ADV[68] | ||||
Route statistics
| Rank | Destination | Passengers | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continental | |||
| 1 | |
1,230,618 | |
| 2 | |
894,527 | |
| 3 | |
828,224 | |
| 4 | |
789,482 | |
| 5 | |
766,960 | |
| 6 | |
640,100 | |
| 7 | |
618,000 | |
| 8 | |
602,500 | |
| 9 | |
556,300 | |
| 10 | |
539,321 | |
| Intercontinental | |||
| 1 | |
768,594 | |
| 2 | |
437,586 | |
| 3 | |
395,784 | |
| 4 | |
306,178 | |
| 5 | |
274,530 | |
| 6 | |
253,400 | |
| 7 | |
245,621 | |
| 8 | |
233,600 | |
| 9 | |
228,900 | |
| 10 | |
207,500 | |
Other facilities
- Lufthansa maintains a Flight Operations Center at the airport for crews based here at its secondary hub.[70] In 2014, its subsidiary Lufthansa CityLine relocated their administration offices from Cologne to the grounds of Munich Airport.[71] Additionally, there is a large Lufthansa Technik maintenance facility which can handle up to six Boeing 747s at once.[72]
- Air Berlin maintains a technical division including technical training facilities.[73]
- There are two hotels directly on the airports grounds, the Hilton Munich Airport (which was the Kempinski Hotel Airport Munich until 31 December 2014)[74] near Terminal 2 and a Novotel at the long-term parking area[75] with several more in the nearby villages.
- German car manufacturer Audi established a large training facility for its retailers on the grounds of the airport in 2010.[76] Designated areas near the apron are used for drive training.
- The defunct German airline DBA, originally Deutsche BA, had its head office on the grounds of the airport and in Hallbergmoos.[77][78]
Environment
Since November 2005, the Munich Airport has a certified environmental management system according to DIN ISO 14001 and EMAS.
Munich Airport was involved in the Air Transport Initiative for Germany, which was also attended by Fraport, Deutsche Flugsicherung and Lufthansa. It developed a so-called "four-pillar strategy" with an overall concept designed to improve environmental protection; these four pillars include:
"Reduction of CO2 emissions through technological progress and innovation, particularly in the field of engine development; a more efficient infrastructure with a needs-based adaptation of airport capacity with concentration on the avoidance of, for example, polluting queues; operational measures such as the optimization of soil processes; economic incentives" - Perspectives. Environmental Statement 2008 Munich Airport GmbH[79]
Landscape
From the beginning, the state-administered parts of nature conservation aspects were considered in the planning of the airport. At the opening of the airport, 70% of the grounds were planted; today there are 925 of the 1560 hectares which remained planted, only 60%.[80] The prevalent Erdinger Moos area with its many intersecting small streams, and woodland series was taking into consideration in the planning by the landscape architect. At the same time, consideration was taking in making the airport unattractive to birds, in order to prevent bird strikes. An additional 230-acre green belt was placed around the airport as a compensation area, in which the overall compensation areas extend over 600 acres.[81] Even with the focus on the environment, environmental groups criticize the enormous land consumption of the airport and each additional expansion project. Also, they believe that the compensation areas are not sufficient enough in order to compensate for the damage caused by the airport.[82]
Water
The construction in the Erdinger Moos area had a large impact on the water budget of the region, since the groundwater levels in the marshy landscape had to be greatly reduced in which drainage ditches were created. Existing watercourses, such as small streams, were not interrupted, but redirected so that they run either around or underneath the property, lowering the effects of groundwater reduction to only the areas in which the airport is located.
The wastewater from the airport and the collected rain water are returned to the natural water cycle. In order to accomplish this, 100 km of sewer lines were laid, seven pumping stations, a water treatment plant and four rainwater sedimentation tanks were built and put into operation. The already rough cleansed water is then purified in a purification plant. For the necessary winter de-icing of the airport, deicing chemical such as glycol are used and collected together with the contaminated melted water and then either purified or reused. The cleaning is done in the degradation system area, where soil bacteria decompose the glycol into harmless components of water and carbon dioxide.[83]
Noise
- General
To reduce noise from thrust reversal during aircraft landings, the runways were built to a length of 4,000 meters, however the noise reduction is offset by increased taxiing times. To reduce noise pollution, a hall for engine testing was built. After 11pm engine tests may be carried out only with the approval of air traffic control. To motivate airlines to use low-noise aircraft, the airport charges are calculated according to the level of noise pollution.[84] There are 16 stationary noise measuring points at the airport.[85]
- Night flight regulations
At Munich airport there is no strict ban on night flights, but a ban on flights arriving and departing between 10pm and 6am. The only exemptions are flights from mail services and DFS survey flights. From midnight until 5am only those flights that operate in the interest of the public are generally possible, this includes so-called emergency flights: police and rescue helicopter missions or medical emergencies. Also, aircraft movements for security reasons such as for precautionary landings are allowed at all times. Flights with special permission from the Bavarian Ministry for Economic Affairs, Infrastructure, Transport and Technology are also feasible at this time.
From 10pm to midnight and 5am to 6am flights are possible through the so-called bonus list. Exceptions are delayed flights or premature landings if these aircraft are at least noise-admitted according to ICAO Chapter 3. In addition to both the bonus list and noise requirements they must fulfill further conditions, this includes that the airline must have a maintenance base at the airport, the maximum number of 28 scheduled flights per night (charter and scheduled services) must not be exceeded, the aircraft is not louder than 75 db (A) or it is an education or training flight.[86]
This rule applies until the total annual volume is exhausted in air traffic movements by these regulations. More flights of this type are then no longer allowed. The number of night flights increased from 1999 to 2007 from 42 to 60 flights average per night.[79]
Residents have been protesting for years against aircraft noise, in particular against the noise pollution at night. The Government of Upper Bavaria approved the night flight regulations currently in force in 2001.
Energy
- Cogeneration plant
Most of Munich airport's electricity and heat is generated by its own cogeneration plant (CHP), which is located south of the northern runway to the west of the airport. CHP has nine so-called cogeneration modules, seven run on diesel fuel, the other two on gasoline. The electrical generating capacity is 18.5 megawatts. The cogeneration modules run smoothly all year long; this creates surplus heat at certain times which is stored in heat storage to be used later. In summer, the heat generated is used for the operation of the absorption refrigerating machine. The total gross utilization rate is 78 percent (diesel) and 83 percent (gasoline). The cogeneration modules are an obligation, from the Renewable Energy Sources Act, so that Munich Airport can generate electricity from renewable energy sources, using biogas.[79] The airport also has a connection to the district heating network of the Zolling power plant.
- Photovoltaic system
There is a photovoltaic system on the roof of the central hall of Terminal 2. It is a joint project of BP Solar, German BP, Bundesdeutscher Arbeitskreis für Umweltbewusstes Management, Lufthansa, Munich Airport and others. In operation since 10 July 2003, it generates an average of 445,000 kilowatt hours per year, equivalent to the consumption of 155 households.[87] The power comes from 2,856 modules of silicon cells, covering a total area of 3,594 square meters. It is expected to save 12,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions over its 30-year lifetime.[79] €2.65 million EUR were invested in the plant. The plant produces direct current, which after conversion to alternating current is initiated immediately in the power system. In Terminal 2, the energy currently generated is displayed on an overhead screen, which also displays other information.
- Biofuel gas station
A biofuel gas station supplying rapeseed oil fuels, ethanol fuel and biomethane has been established, making it possible for the operating companies to convert their vehicle fleets to biofuels; the station can also be used by external companies operating at the airport.[79]
Bird sanctuary
Despite measures to prevent bird strikes, the northern part of Erdinger Moos is still an important habitat for birds, especially for grassland birds such as lapwing, curlew or rare winter visitors such as the harrier. This led automatically to the area being reported under the European Birds Directive as a bird sanctuary.
The fencing of the airport and the large meadows inside the fence attract open meadow birds. This leads to constant conflicts and the deaths, even of rare birds as a result of airplane accidents (vortices) and safety measures to avoid bird strikes. The planned third runway 3,440,000 square meters in the bird sanctuary will be laid with concrete, eliminating 8,000,000 square meters of living space. This would represent substantial interference with the bird sanctuary.[88]
Safety
Police
For the safety of passengers and flight operations, four[89] inspections by the Federal Police, departments of the Bavarian State Police (Police Inspection Munich Airport, PP Oberbayern Nord) and the security department of Flughafen München GmbH are responsible. The airport police station is located in Nordallee 6, and the police officers working there have an adapted qualification to the specific field of application, for example, they are also trained in the case of an aircraft hijacking. Bavaria's police helicopter squad is also based at the Munich Airport, where five of the Eurocopter EC135 helicopters are stationed. A move of the unit to Schleißheim airport is planned for 2020.
In addition, one of the world's two chambers for explosive goods (the second one is located at Kuala Lumpur International Airport) is located on the airport grounds. In this chamber explosive substances can be defused.
Fire department

The airport has its own fire department with 32 fire engines distributed over two fire stations, which are located near the runways. They are positioned in a way that the emergency vehicles can reach every point of the apron, taxiway and runway in a maximum of three minutes, as long as no adverse weather conditions prevail. Should larger missions occur, the fire departments of the surrounding municipalities can be called in, which can provide up to 36 vehicles and about 216 men; in exchange, the airport fire department helps in large fires in the region. Most recently, this happened when a BMW plant in Eching went up in flames.
| Year | Missions*) | Fires | Technical assistance | False alarms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 3997 | 104 | 1754 | 2139 |
| 2012 | 3613 | 107 | 1717 | 1789 |
| 2011 | 3582 | 118 | 1831 | 1633 |
| 2010 | 3946 | 128 | 2070 | 1748 |
| 2009 | 3254 | 118 | 1599 | 1537 |
| 2008 | 2999 | 107 | 1389 | 1503 |
| 2007 | 2651 | 116 | 1328 | 1207 |
| 2006 | 3011 | 123 | 1052 | 1209 |
| 2005 | 2095 | 127 | 1103 | 1116 |
| 2004 | 2704 | 119 | 950 | 1103 |
*) The sum of the missions also includes other missions such as guided tours.
Ambulance service
Emergency medical care is provided by a rescue guard on Nordallee operated by the Malteser Hilfsdienst under a public service contract. A rescue vehicle is ready for use around the clock, which is also used outside the airport area for normal emergencies. If necessary, other rescue workers from the region or supraregional are used, the deployment coordination is carried out by the integrated control center which is also responsible for the area of the airport.
On the premises of the airport is an emergency physician from the medical center that arrives on the emergency site, when required, in a separate vehicle according to the rendezvous procedure.
Ground transportation
Road
Munich Airport is accessible via nearby Motorway A 92, which connects to motorway A9 (towards Nuremberg) and Munich's ring motorway A99. Bavarian State Road St. 2584 connects A 92's exit 6 (Flughafen München) – an incomplete interchange that can only be used by traffic to and from the west – to the terminals. Access from the east is possible via exit 8 (Freising Ost) and Bavarian State Road St. 2580, which connects to St. 2584 in the east of the airport.
Suburban railway

There are two railway stations on the grounds of Munich Airport: Munich Airport Terminal station is located in a tunnel directly beneath the central area between both passenger terminals. A second station called Besucherpark (German for Visitors' Park) is located in the area that contains the cargo and maintenance areas, long-term parking, administrative buildings and the Visitors' Park from which the station gets its name.
The airport is connected to the city by Munich suburban railway (S-Bahn) lines S1 and S8. The ride takes approximately 45 minutes to the Marienplatz station in the city centre. S1 runs from the airport through the northwestern suburbs and reaches the city centre from the west (Hauptbahnhof – Marienplatz – München Ost), while S8 comes in from the eastern suburbs passing the stations from the opposite direction. The S-Bahn from the airport to the city runs approx. 20 hours a day with a short break between 01:30 and 04:00.[90]
Furthermore, a scheduled regional bus service (MVV line 635) connects the airport within 20 minutes to the Freising railway station, providing access to regional trains towards Munich as well as to Nuremberg, Regensburg and Prague.
A second tunnel beneath the terminals is currently unused. Originally, there were plans to use it for intercity railway, then for a Transrapid maglev train making the trip to München Hauptbahnhof in 10 minutes. However, this project was cancelled in March 2008 due to cost escalation. Discussions regarding a faster connection between Munich city center and the airport take place since several years as the journey time of 40–60 minutes faces ongoing criticism.[91]
Future regional railway services
As of September 2015, construction works to connect the airport with regional railway services of Deutsche Bahn to and from the north-east have started. This project, called Neufahrner Kurve (Neufahrn curve after the nearby town of Neufahrn), will see the existing south-west bound S-Bahn tracks being expanded with a curve leading to the north, connecting them with the already existing tracks of the Munich-Regensburg line. This new connection will enable hourly regional express train services from Regensburg via Landshut directly to the airport without the need to use a connecting bus coming from the north or to go to Munich city center at first and then all the way back to the airport. The entire project is scheduled to be completed in 2018.[92]
Bus
MVV regional bus lines connect the airport to the nearby city of Freising as well as Erding and Markt Schwaben. Lufthansa Airport Bus provides an alternative to the S-Bahn, stopping at Nordfriedhof U-Bahn station and Munich Central Station.
Planning
Improvements in public transport
At the beginning of the 1990s, the Deutsche Bundesbahn considered four options for a better railway connection to the airport. At an estimated cost of between 500 million and 2 billion Deutsche Mark, each option would have allowed the airport to be integrated into the ICE network.[93] However, the idea was rejected and instead concentration was placed on a better connection of the airport to regional transportation as well as to the München Hauptbahnhof.
Airport Express (S-Bahn)
In order to reach the central station and the Munich city center faster the proposal of an express S-Bahn was proposed by the critics of the unsuccessful proposal of a Transrapid connection in 2008. Due to the heavily utilized Stammstrecke (east west connection), its connection to the Munich East–Munich Airport railway is not possible, and the use of the Munich South Ring as an alternative would be a major time saving loss on the way to the main station. The central station could be reached directly from the airport via the Munich-Regensburg railway line, which, however, also does not offer regularly usable capacities. The neighboring communities oppose its development as the route leads through several local centers and crosses the federal road 471 in Oberschleißheim. Therefore, the new construction of railway lines for the implementation of an airport express would be necessary. The solution approach from MAEX via the Munich East–Munich Airport railway requires the construction of the second main route through Moosach and along the Bundesautobahn 92.[94]
Subway
Through the extension of different subway lines to the intersection with one of the two airport suburban railways, the travel time to the airport from different parts of the north of Munich can be considerably reduced. This was realized for the suburbs of Milbertshofen-Am Hart and Feldmoching-Hasenbergl with the subway line 2 to the S1 station Feldmoching 1996 and the construction of the airport spange near Neufahrn 1998. In 2010, the travel time to the airport from Moosach, Schwabing West and Neuhausen-Nymphenburg districts was shortened by connecting the subway line 3 to the S1 station Moosach. The extension of the U6 from Garching to Neufahrn was examined, but withdrawn, as part of a feasibility study in 2008.[95]
Erdinger ring connections
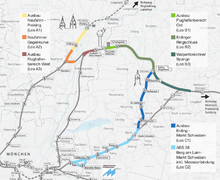

The Erdinger Ring connection is to extend the S-Bahn (S2) from Erding in the direction of the airport and connect to neighboring Freising through a connecting curve, the Neufahrn Link. It will fulfill the demand of a rail connection between Eastern Bavaria, including the neighboring airport commuter cities Moosburg and Landshut, to the airport, realized with its own regional railway line. A faster connection from the airport to the inner city is not achieved by the Erdinger ring connection, however a direct connection between the airport and the Munich Messe would be. For this, the S2 would also make a short route north of Messe München and have a stop North of the exhibition center. Already before the opening of the airport there were plans for a regional station at the airport. To this, a railway connection from Mühldorf am Inn is to be made between Erding and Dorfen with the help of the Erdinger ring connection as well as a short new construction single-track called Walpertskirchner Spange. The actual plannin phase for this also began, as in the case of the Erdinger ring connection, in August 2006. On 29 August 2013, the Bavarian Administrative Court rejected the complaints against the plan approval decision of the Neufahrn Link of October 2012 and therefore freed the way for a direct rail connection of the Munich airport from Regensburg, Landshut, Moosburg and Freising. The Neufahrner Kurve is to connect the railway line Landshut-Munich from Neufahr with the railway connection line Neufahr-Flughafen Munich, approximately 2.5 kilometers long, two-track and electrified section of the line. In the construction and financing agreement, signed by rail and free-trade in April 2013, it was agreed that the Neufahrn Link will be built and put into operation by the end of 2018.[96]
Third runway
Need for the expansion project
According to the airport, the average growth of air traffic in Munich from 1997 to 2006 was an average of 7% per year, and the airport's capacity was already exhausted. Since new airlines in Munich no longer received the desired slots, a traffic-spoiling effect occurred.[97] An air traffic forecast of Intraplan Consult GmbH estimated 58.2 million passengers for 2025, provided the airport has a tight-fitting growth.[98][99][100] In order to exploit the expected traffic potential in Munich, the operator plans to expand todays capacity from 90 movements per hour to 120 movements per hour by constructing a third runway.[101] The shareholders of Flughafen München GmbH (FMG) stated that the construction of a third runway was necessary for the Munich region and for Bavaria as a whole, for reasons of transport and economic policy. Various associations and institutions from economics and politics reacted in favor of the plan approval decision issued by the government of Oberbayern for the construction of a third runway at Munich Airport.[102]
Counterarguments

The project for the construction of a third runway is particularly appealing in the directly affected airport region of the counties of Freising and Erding, but also in other nearby counties.[103][104] Among other things, one calls for the use of larger machines in order to meet demands and, above all, the growth projections presented by FMG.[105]
The opponents of the expansion project joined forces to form the action alliance aufgeMUCkt (over 80 groups, including citizens' initiatives, ecclesiastical groups and environmental organizations), supported by, among others, the BUND in Bavaria,[106] that organized many demonstrations.[107][108] Also, the Catholic Church, which is the owner of some of the affected sites, also announced resistance to the construction.[109] Since the plan approval decision of 26 July 2011, more protests have taken place. On 29 October 2011, a large demonstration took place in Munich on the Marienplatz with around 7000 participants,[110] directly in front of the Old Town Hall.
See also
-
 Aviation portal
Aviation portal -
.svg.png) Bavaria portal
Bavaria portal -
 Germany portal
Germany portal - Transport in Germany
- List of airports in Germany
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 aero.de - "Transavia dissolves base in Munich" (German) 13 February 2017
- ↑ Flughafenverband ADV. "Statistiken IVF 2013 - Flughafenverband ADV – Unsere Flughäfen: Regionale Stärke, Globaler Anschluss". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "EAD Basic - Error Page". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "12 months". aci.aero. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- ↑ "Year to date". aci.aero. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- ↑ aero.de - "Frankfurt offers the most destinations" 20 February 2017
- ↑ "Early days (1967-1969)". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Munich's traffic doubles in 10 years; Lufthansa adds more routes than it drops as a host of new airlines announce new services". anna.aero. 20 April 2010.
- ↑ Achim Schaffrinna. "Flughafen München erhält neues Corporate Design". Design Tagebuch. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "aero.de - Luftfahrt-Nachrichten und -Community". aero.de. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ George Sensalis. "Munich Five Star airport gears up for busy summer season". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ airliners.de - "Condor announces new long-haul destinations from Munich" (German) retrieved 23 June 2015
- ↑ airliners.de - "Transavia starts German base in spring" (German) 30 November 2015
- ↑ "aero.de - Luftfahrt-Nachrichten und -Community". aero.de. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ airliners.de - Flughafen München knackt 40-Millionen-Marke bei Passagierzahlen 13 January 2016
- ↑ handelsblatt.com - "Eurowings in München: Lufthansa-Tochter fliegt 32 Ziele an" (German) 21 December 2016
- 1 2 routesonline.com - Eurowings outlines leased airberlin aircraft operation in S17 3 January 2017
- ↑ "Munich International Flight Hub". Flight Hub Reviews. 2 May 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Germanwings wechselt Terminals in München". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Travel ONE: Produkt". travel-one.net. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ munich-airport.de - Weitere Ausbauprojekte retrieved 6 December 2015
- ↑ aero.de - "Terminal 1 to be extended for €400m" (German) 19 November 2016
- ↑ "Erdinger Moos - Flughafen modernisiert Terminal 1". Süddeutsche.de. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ munich-airport.de - Ein Satellit für das Terminal 2 retrieved 6 December 2015
- 1 2 "München installiert erste Fluggastbrücken am Satellitengebäude - FLUG REVUE". FLUG REVUE. 2 April 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ aero.de - MUC celebrates T2 satellite opening (German) 22 April 2016
- ↑ "Munich Airport - New passenger facility at Munich Airport to open on April 26 2016".
- ↑ sueddeutsche.de - "Volunteers wanted for new satellite terminal" (German) 1 December 2015
- ↑ munich-airport.de - Personentransportsystem retrieved 6 December 2015
- ↑ merkur.de - "Already one million passengers in the satellite" (German) 1 July 2016
- 1 2 3 munich-airport.de - Service und Gastronomie retrieved 6 December 2015
- 1 2 munich-airport.de - Daten und Fakten zum Satelliten retrieved 6 December 2015
- ↑ http://www.ovb-online.de/politik/satellit-gelandet-6338587.html
- ↑ "Lufthansa and Munich operator approve Terminal 2 satellite". Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ↑ "Munich Airport – Edeka". Munich-airport.de. Retrieved 4 July 2013.
- ↑ Ladenschlussgesetz
- ↑ Munich Airport Facts and Figures: 2011/2012
- ↑ MUC Airport – Facts and Figures 2010/2011 (p.10)
- ↑ DC Airports (20 August 2007). "Erläuterungsbericht Technische Planung Luftseite" (PDF). Planfeststellungsverfahren 3. Start- und Landebahn (in German). pp. 16, 42. Retrieved 24 November 2008.
- ↑ "Green Light for Munich Expansion". Airliner World: 8. October 2015.
- ↑ "Parking areas". Munich Airport. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ↑ "Parkhaus Airport" (in German). BFK Architekten. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ↑ "Parking and shopping". Munich Airport. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ↑ "Munich Airport - Flightsearch/Timetable". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Air Arabia Maroc launches Agadir base from Oct 2017".
- ↑ "Air China moves forward nonstop Beijing – Athens to Sep 2017". routesonline. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Condor adds new Marrakech routes from Nov 2017". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Condor updates Munich - Caribbean routing in W17". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Condor S18 new short-haul routes as of 12JUN17". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ "Sea-Tac Adds New Nonstop Flight To Munich". Seattle Patch. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- 1 2 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Eurowings outlines new S18 long-haul routes". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ Ruane, Laura (7 July 2017). "RSW airport to gain nonstop flights to German cities of Munich, Cologne in May 2018". www.news-press.com. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- 1 2 "Eurowings new W17 routes as of 4 May 2017".
- ↑ "Eurowings W17 new short-haul routes as of 23 March 2017".
- ↑ "Flug ab Skopje (SKP) ab 49,99 €* - Eurowings".
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Lufthansa extends Munich – Glasgow service to year-round in W17". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ "Lufthansa to launch Singapore-Munich Airbus A350 flights". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Lufthansa S18 long-haul changes as of 21JUN17". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 2017, UBM (UK) Ltd. "Lufthansa ends Munich – Tehran service in Sep 2017". Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ TAROM Flight Schedule
- 1 2 "Transavia adds new routes from Munich in S17". routesonline. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ↑ "Turkish Airlines plans Ordu-Giresun – Munich seasonal route in S17". Retrieved 22 March 2017.
- ↑ "Volotea adds new Munich – Asturias service in S17".
- ↑ "BOEING 747 OF AIRBRIDGECARGO AIRLINES GOES TO BAVARIA". AirBridgeCargo. 29 April 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- ↑ "Senator International Launches Atlantic Air Bridge". cargoforwarder.eu. 24 July 2016. Retrieved 5 November 2016.
- ↑ http://www.munich-airport.de/en/company/facts/verkehr/berichte/stat_jahber/index.jsp
- ↑ https://www.munich-airport.de/_b/0000000000000001546959bb58c29610/Statistischer-Jahresbericht-2016.pdf
- ↑ Flughafenverband ADV. "Flughafenverband ADV – Unsere Flughäfen: Regionale Stärke, Globaler Anschluss". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ in German
- ↑ "Flughafen München - FOC - Flight Operations Center". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ COMKOM° GmbH, Germany. "Lufthansa CityLine - Contact". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Standort: München - Lufthansa Technik AG". www.lufthansa-technik.com.
- ↑ "airberlin technik – airberlin technical training in München". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Kempinski verliert Flughafen-Hotel in München – Erweiterung zu Hilton-Doppelmarke geplant". HOTTELLING 2.0 – DIGITAL NEWS FOR HOTELIERS. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Flughafen München - Hotels". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Audi eröffnet Trainingscenter in München". Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "World Airline Directory." Flight International. 29 March-4 April 1995. 68. "Wartungsallee 13, Munchen-Flughafen, Munchen D-85 356, Germany"
- ↑ "Contact Us." DBA. 4 February 2004. Retrieved on 21 January 2010. "dba Luftfahrtgesellschaft mbH Wartungsallee 13 85356 München,. Munich Airport Germany" The address on Google Maps goes to "Wartungsallee 13 85356 Hallbergmoos, Germany."
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Perspectives" (PDF). Munich Airport. 4 August 2008. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "General information". Munich Airport. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Landscape concept and planning". Munich Airport. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Bauernverband und BN kritisieren Landverbrauch" (in German). Bund Naturschutz Kreisgruppe Erding. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Water management". Munich Airport. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ ""Lärmsteuer" für laute Flugzeuge" (in German). Der Standard. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Noise control". Munich Airport. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Night flight operations". Munich Airport. Retrieved 17 December 2014.
- ↑ "Lufthansa celebrates 10th Anniversary of Solar Panels at Munich Airport". Airport World. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "Biodiversity". Munich Airport. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "Bundespolizeidirektion München" (in German). Bundespolizei. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- ↑ "MVV - Air travellers". 15 December 2014. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ sueddeutsche.de - "Faster to Munich Airport" (German) 13 November 2015
- ↑ br.de - "New train from Regensburg to Munich Airport" (German) 15 September 2015
- ↑ Ein Jahr Hochgeschwindigkeitsverkehr (in German). Deutsche Bahn. 1992. p. 4-6.
- ↑ Alexandra Vettori (11 July 2016). "Wo bleibt der "Humpel-Express"?" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 17 June 2017.
- ↑ "Verlängerung der U6 zum Flughafen ist sinnlos" (in German). Welt. 23 May 2008. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ↑ "Weg frei für eine direkte Schienenanbindung des Münchner Flughafens aus Nordostbayern" (in German). Wirtschaftsförderung im Landkreis Dingolfing-Landau. 30 August 2013. Retrieved 29 June 2017.
- ↑ "Planfeststellungsbeschluss für den Verkehrsflughafen München, 3. Start- und Landebahn" (in German). Regierung von Bayern. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Planfeststellungsbeschluss für den Verkehrsflughafen München, 3. Start- und Landebahn, Band 1" (PDF) (in German). Regierung von Oberbayern. 5 July 2011. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ Flughafen München GmbH. "Der Flughafen München – jetzt Perspektiven schaffen" (in German). Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Luftverkehrsprognosen 2020 für den Flughafen München" (PDF) (in German). Aufgemuckt Watch. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Flughafen München Prospekt" (PDF) (in German). Flughafen München. 26 October 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Große Zustimmung zum positiven Planfeststellungsbeschluss 3. Bahn" (in German). Flughafen München. 9 September 2011. Archived from the original on 10 October 2013. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Wutbürger im Erdinger Moos" (in German). taz. 29 July 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Streit um Startbahn spaltet die CSU" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 28 July 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Landtag streitet um Flugverkehr-Prognose" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 27 April 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Kleine Demonstration vor Reserl Sems verschlossener Haustür" (in German). Passauer Neue Presse. 27 April 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Flughafen München Contra: Laut, dreckig und überflüssig" (in German). Bayern Online. 15 April 2010. Archived from the original on 12 October 2010. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Weiter Protest gegen Münchner Flughafen-Ausbau" (in German). Augsburger Allgemeine. 1 August 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Erzbischof Marx: Kirche verkauft keinen Grund für dritte Startbahn" (in German). Münchner Merkur. 8 December 2009. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ "Tausende Münchner fordern "koa Dritte"" (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 29 October 2011. Retrieved 9 July 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Munich Airport. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Munich Airport. |
- Official website
- Airport information for MUC
- Charts for MUC / EDDM
- Current weather for EDDM at NOAA/NWS
- Accident history for MUC at Aviation Safety Network
.png)

