Multinational state
A multinational state is a sovereign state that comprises two or more nations. This is in contrast to a nation state, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of "nation" (which touches on ethnicity, language, and political identity), a multinational state might also be multicultural or multilingual.
Present-day examples of multinational states are Afghanistan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Canada, China, Ethiopia, India, Iraq, Madagascar, Montenegro, Nigeria, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa, Spain, Turkey, and the United Kingdom. Historical multinational states that have since split into multiple sovereign states include Austria-Hungary, British India, Czechoslovakia, the Empire of Japan, the Soviet Union, and Yugoslavia. Some analysts have described the European Union as a multinational state or a potential one.[1][2]
Many attempts have been made to define what a multinational state is. One complicating factor is that it is possible for members of a group that could be considered a nation to identify with two different nationalities simultaneously. As Ilan Peleg wrote in Democratizing the Hegemonic State:
One can be a Scot and a Brit in the United Kingdom, a Jew and an American in the United States, an Igbo and a Nigerian in Nigeria ... One might find it hard to be a Slovak and a Hungarian, an Arab and an Israeli, a Breton and a Frenchman.[3]
A state may also be a society, and a multiethnic society has people belonging to more than one ethnic group, in contrast to societies that are ethnically homogeneous. By some definitions of "society" and "homogeneous", virtually all contemporary national societies are multiethnic. The scholar David Welsh argued in 1993 that fewer than 20 of the 180 sovereign states then in existence were ethnically and nationally homogeneous, if a homogeneous state was defined as one in which minorities made up less than 5 percent of the population.[4] Sujit Choudhry therefore argues that "[t]he age of the ethnoculturally homogeneous state, if ever there was one, is over".[5]
History
According to Neil MacGregor, Director of the British Museum, the Cyrus Cylinder written by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Persian Empire, was "the first attempt we know about running a society, a state with different nationalities and faiths—a new kind of statecraft."[6]
Modern multinational or multiethnic states
The CIA World Factbook provides a list[7] of the ethnic makeup of every country in the world.
Americas
Canada
Whether Canada should be described as "multinational" is an ongoing topic in academia[8] and popular discourse. The current policy of the federal government is that Canada is bilingual—English and French are both official languages—and multicultural. In 2006, the House of Commons of Canada voted in favor of Government Business No. 11, which states that the Québécois "form a nation within a united Canada".[9]
Bolivia
Since 2010, under the presidency of Evo Morales, Bolivia has been officially defined as a plurinational state, which recognizes the national distinctiveness of various indigenous peoples.
Asia
Many Asian countries recognize multiple ethnic groups:
| Country | Groups recognized | Largest groups | Date of recognition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 53 ethnic minorities (see list) | Viet/Kinh, 86.2% (1999) | Founding | |
| 47 ethnicities, 149 groups (see list) | Lao, 68% (1995) | Founding | |
| 38 ethnicities (see list) | Thai, 74%
Thai Chinese, 14% |
Founding | |
| 38 ethnicities (see list) | Khmer, 86.3% Vietnamese and Chinese, 5% each | Founding | |
| 56 ethnic groups (see list) | Han, 91% (2010) | Founding (1948) |
India
India has more than 2,000 ethnic groups, and every major religion is represented, as are four major language families (Indo-European, Dravidian, Austroasiatic, and Sino-Tibetan) and a language isolate (Nihali).
Each state and union territory of India has one or more official languages, and the Constitution of India recognizes in particular 21 "scheduled languages". It also recognizes 212 scheduled tribal groups, which together constitute about 7.5% of the country's population.
India has a Muslim-majority state (Jammu and Kashmir) and a Muslim-majority union territory (Lakshadweep); three Christian-majority states (Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Nagaland); and a Sikh-majority state (Punjab). Most of its states are based on ethnicity, including Tamil Nadu (Tamil), Andhra Pradesh (Telugu), Odisha (Odia), West Bengal (Bengali), Maharashtra (Marathi), Punjab (Punjabi), Haryana (Haryanvi), Kerala (Malyali), and Bihar (Bihari).
Furthermore, several Indian states are themselves ethnically, religiously, and linguistically diverse. Karnataka is home to the Tulu and Kannada people; Jammu and Kashmir consists of Hindu-majority Jammu, Muslim-majority Kashmir, and Buddhist-majority Ladakh; and Assam includes the Assamese, Bodo, and Karbi people.
Nepal
Nepal does not have a majority ethnic group, and its society is multiethnic, multireligious, and multilingual. Aside from the country's indigenous people, most Nepalese are descendants of migrants from Kashmir, Greater Nepal, Tibet, India, and parts of Myanmar and China's Yunnan Province.
Khas and Mongoloids populate the hilly areas of Nepal, while the Madhesis, a diverse group of Indian origin, live in the southeast. The indigenous Tharu people were the first settlers of the Terai region, before the arrival of the Madhesis. The Himalayas are sparsely populated above 3,000 m (9,800 ft), but north of the mountains, in central and western Nepal, ethnic Sherpas and Tamangs inhabit high, semi-arid valleys. The Kathmandu Valley, in the middle hill region, constitutes a small fraction of the nation's area but is the most densely populated, with almost 5 percent of the nation's population.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is inhabited by Sinhalese, Sri Lankan Tamils, Indian Tamils, Moors, Veddas, Burghers, and other small ethnic groups.
Afghanistan
Afghanistan has no ethnic majority, although the Pashtuns are estimated to account for over 45% of the population.[10] Under the sovereign governance of Pashtun rulers, the term "Afghan" was changed from an ethnonym for Pashtuns to a demonym for any citizen of Afghanistan, regardless of ethnic affiliation. This change was incorporated into the constitution, making it resemble that of a multinational state. However, irredentist disputes over Pakistan's Pashtun lands have continued.
Other ethnic groups in Afghanistan include Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks, Aimaqs, Turkmens, and Balochs.[11] The government gives equal status to Pashto and Dari as official languages.
Pakistan
Present-day Pakistan arose out of the Pakistan Movement, which demanded a separate state for the Muslims of the British Raj. The movement was based on the two-nation theory put forward by Muhammad Ali Jinnah: the idea that Hindus and Muslims in British India represented not only different religious communities but also distinct nations, and hence that, in the event of Indian independence, they should be divided into two nation states. Jinnah (known in Pakistan as "Quaid-e-Azm", meaning "the great leader") outlined the theory as follows:
It is extremely difficult to appreciate why our Hindu friends fail to understand the real nature of Islam and Hinduism. They are not religious in the strict sense of the word, but are, in fact, different and distinct social orders, and it is a dream that the Hindus and Muslims can ever evolve a common nationality, and this misconception of one Indian nation has troubles and will lead India to destruction if we fail to revise our notions in time. The Hindus and Muslims belong to two different religious philosophies, social customs, literatures. They neither intermarry nor interdine together and, indeed, they belong to two different civilizations which are based mainly on conflicting ideas and conceptions. Their aspect on life and of life are different. It is quite clear that Hindus and Mussalmans derive their inspiration from different sources of history. They have different epics, different heroes, and different episodes. Very often the hero of one is a foe of the other and, likewise, their victories and defeats overlap. To yoke together two such nations under a single state, one as a numerical minority and the other as a majority, must lead to growing discontent and final destruction of any fabric that may be so built for the government of such a state."[12][13]
This movement culminated in the creation of Pakistan in 1947 through the partition of India. Urdu was then promoted as the national language of all South Asian Muslims. However, Pakistan remains ethnically diverse. Punjabis are the largest language group, but at 45 percent of the population, they do not make up an absolute majority. Furthermore, only 8 percent of Pakistanis speak the national language, Urdu, as their mother tongue. As a result, many nationalist movements that oppose the two-nation theory have emerged, arguing that Pakistan is not only a linguistically diverse state but also a multinational one, and that, therefore, each ethnolinguistic group of Pakistan is a distinct nation.[14] Common grievances of these movements include the idea that Punjabis dominate Pakistan politically and economically, thus marginalizing other groups, and that the establishment of Urdu as the country's sole official language is a form of cultural imperialism that ignores the heritage of Pakistan's diverse peoples.
The most successful of these movements was Bengali nationalism, which led to the creation of the Bengali-speaking nation-state of Bangladesh. The movement asserted that Urdu's official status gave an unfair advantage to Muhajirs (most of whom speak Urdu as their mother tongue) and Punjabis (whose mother tongue, Punjabi, is similar to Urdu, and many of whom were educated in Urdu under British rule). Bengalis feared they would be marginalized despite their demographic strength as, at the time, the largest ethnic group of Pakistan. These grievances culminated in the secession of East Bengal (which had been part of the administrative unit of East Pakistan) and the creation of Bangladesh.
Today, nationalist movements within Pakistan include those of the Sindhis, Pashtuns, Balochs, Mohajirs, and Kashmiris. The members of these movements assert that Islam cannot be considered the sole basis for nationhood, and that Pakistan is therefore a multinational state. Their demands range from increased autonomy or the transformation of Pakistan into a federation, to the recognition of language rights for non-Urdu-speaking populations, to outright secession.
Despite the fact that Punjabis are widely seen as the dominant ethnic group in Pakistan, both economically and politically, there is also a small Punjabi movement that asserts that the Punjabi language has been unfairly subordinated to Urdu and supports the reestablishment of cultural and economic links with East Punjab in India.[15]
Malaysia
When it was formed on 16 September 1963, Malaysia comprised four independent, self-governing nations: Malaya, Singapore, Sabah, and Sarawak. In 1965, Singapore seceded from the federation. Today, Malaya, Sabah, and Sarawak each have their own ethnic majority. Generally, however, Malaysia is considered to have three major ethnic groups: Malays, Chinese, and Indians. The Iban people are the majority in Sarawak, while Sabah is dominated by the Kadazan-Dusun, Murut, and Bajau peoples. Malay is the primary national language, followed by English. In Sabah and Sarawak, English is the official language, although many locals speak a dialect of Malay.
People's Republic of China
Although the population of China is dominated numerically by the Han Chinese, the government recognizes 56 ethnic groups. Fifty-five of the 56 groups together account for less than 10 percent of the population.
Europe
Bosnia and Herzegovina and Montenegro are the only European states with no ethnic majority, but many others have ethnic minorities that form a majority within a province or region (see multilingual countries and regions of Europe).
Russian Federation
Russia has more than 160 ethnic groups and indigenous peoples. The largest population are the ethnic Russians, who are Slavs with Eastern Orthodox religious traditions, while the Tatars and Bashkirs are predominantly Muslim. Russia is also home to Buddhist populations, such as the nomadic Buryats and Kalmyks; the Shamanistic peoples of Siberia and the Far North; the Finno-Ugric peoples of the Russian Northwest and the Volga region; the Korean inhabitants of Sakhalin; and the peoples of the North Caucasus.[16]
Out of a total of more than 100 languages spoken in Russia, 27 have the status of official languages, the most widely spoken being Russian. More than 3 percent of the population speaks Tatar.[17]
Belgium
The territory of Belgium is almost equally divided between the two nations of Flanders and Wallonia. This led to political unrest throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, and in the aftermath of the difficult 2007–08 Belgian government formation, the Belgian media envisaged a partition of Belgium as a potential solution.
Bosnia and Herzegovina

Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "constituent peoples": Bosniaks (50.11%), Serbs (30.78%), and Croats (15.43%).[18] The country's political divisions were created by the Dayton Agreement, which recognized a second tier of government comprising two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (mostly Bosniaks and Croats) and the Republika Srpska (mostly Serbs), with each governing roughly half of the state's territory. A third region, the Brčko District, was governed locally. Today, all three ethnic groups have an equal constitutional status over the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The country has a bicameral legislature and a three-member presidency composed of one member of each major ethnic group.
France
In order to maintain a nation state, France does not recognize any national identity or language other than French in its territory. However, many of its current and former territories—Alsace, Brittany, Corsica, Flanders, Moselle, Northern Catalonia, Occitania, Savoy, and the Basque Country—were not culturally French until they were francized in the late 19th century. According to WikiLeaks, former Prime Minister Michel Rocard told the American ambassador to France, Craig Roberts Stapleton, in 2005, "France created itself by destroying five cultures: Breton, Occitan, Alsatian, Corsican, and Flemish."
Montenegro
Montenegro is a multiethnic state in which no ethnic group forms a majority. The preamble of the Constitution of Montenegro identifies numerous nationalities—Montenegrins, Serbs, Bosniaks, Albanians, Muslims, Croats, and others—as citizens of a civic and democratic state. The largest ethnic groups are Montenegrins (45%), Serbs (28.7%), Bosniaks (8.6%), Albanians (4.9%), and Muslims (3.3%).[19]
The official language is Montenegrin,[20] but Serbian, Bosnian, Albanian, and Croatian are also in official use. In the 2011 census, Serbian was the most common mother tongue (42.88%), Montenegrin the second (36.97%), and Bosnian the third (5.33%).
Norway
Official policy states that Norway was founded on the territory of two peoples, Norwegians and Samis.[21] In addition, Forest Finns, Kvens, Jews, Romani, and the Norwegian and Swedish Travellers are recognized as national minorities.[22]
Serbia
Nineteen ethnic groups are officially recognized as national minorities in Serbia.[23] Serbs are the largest ethnic group in the country, constituting 83.3 percent of the population (excluding Kosovo).[24] The largest national minorities are Hungarians, Roma, and Bosniaks, and there are also significant populations of Croats, Montenegrins, Albanians, Slovaks, Romanians, Vlachs, Rusyns, Gorani, Macedonians, and Bulgarians. Since 2002, minorities have been entitled to organize their own national councils. Through those councils, members of national minorities can exercise their rights in the spheres of culture, education, information, and the official use of their own languages and scripts.[25]
Vojvodina is a multiethnic autonomous province in northern Serbia,[26] with more than 26 ethnic groups[27][28] and six official languages.[29]
Spain
Definitions of ethnicity and nationality in Spain are politically fraught, particularly since the transition from Francoist Spain to the Kingdom of Spain in the 1970s, when local regionalisms and peripheral nationalisms became a major part of national politics.
The term Spanish people (Spanish: pueblo español) is defined in the Spanish Constitution of 1978 as the political sovereign, i.e., the citizens of the Kingdom of Spain. The same constitution, in its preamble, speaks of "peoples and nationalities of Spain" (pueblos y nacionalidades de España) and their respective cultures, traditions, languages, and institutions.
The CIA World Factbook (2011) describes Spain's ethnic makeup as a "composite of Mediterranean and Nordic types", instead of the usual breakdown of ethnic composition. This reflects the formation of the modern Kingdom of Spain by the accretion of numerous independent Iberian realms: Andalusia, Aragon, Asturias, Castile, Catalonia, Galicia, León, Majorca, Navarre, and Valencia. Thus, today's Spaniards include Andalusians, Aragonese, Asturians, Basques, Cantabrians, Castilians, Catalans, Galicians, Leonese, and Valencians, and individual members of these groups may or may not consider them distinct nations.
United Kingdom

While the Office for National Statistics describes the United Kingdom as a nation state,[30][31] other people, including former Prime Minister Gordon Brown,[32] describe it as a multinational state.[33][34] The term "Home Nations" is used to describe the national teams that represent the four nations of the United Kingdom: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales.[35]
The Kingdom of Great Britain was created on 1 May 1707 by the political union of the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland.[36] This unification was the result of the Treaty of Union, which was agreed to on 22 July 1706 and then ratified by the Parliament of England and the Parliament of Scotland in the 1707 Acts of Union.[37] The two kingdoms, along with the Kingdom of Ireland, had already been in a personal union as a result of the 1603 Union of the Crowns, in which James VI, King of Scots, inherited the Kingdoms of England and Ireland and moved his court from Edinburgh to London. However, until 1707, all three had remained separate political entities with separate political institutions.[38][39]
Prior to the Acts of Union, the Kingdoms of England and Scotland both had minority populations of their own that could themselves be called nations. Wales and Cornwall were part of the Kingdom of England (Wales had been officially incorporated into England by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, although it had been a de facto English territory since the 13th century; Cornwall had been conquered during the Anglo-Saxon period). The Northern Isles, with their Norse-derived culture, were part of Scotland, having been pledged by Norway as security against the payment of a dowry for Margaret of Denmark[40] and then integrated in 1471. When the Kingdom of Great Britain was created, many of its inhabitants retained a sense of English, Scottish, or Welsh identity. Many of them also spoke languages other than English: principally Scottish Gaelic, Scots, Welsh, Cornish, and Norn.
Almost a century later, the Kingdom of Ireland merged with the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland under the 1800 Acts of Union.[41] The United Kingdom thus became the union of the kingdoms of England, Ireland, and Scotland.[38][39] Eventually, disputes within Ireland over the terms of Irish home rule led to the partition of the island:[42] The Irish Free State received dominion status in 1922, while Northern Ireland remained part of the UK.[43] As a result, in 1927, the formal title of the UK was changed to its current form, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.[44]
Political, ethnic, and religious tensions between Irish and British groups in Northern Ireland culminated in The Troubles.[45] This period of armed conflict erupted in 1966 betweenloyalist paramillitaries, seeking to maintain the country's position in the UK, and republican paramillitaries, seeking to unify Ireland as a 32-county independent republic. The British Army also played a key role. Following the deaths of over 3,500 people,[46] a peace treaty was reached in 1998,[47] although divisions remain high in some areas and sporadic violence still occurs.[48]
The end of the 20th century brought major governing changes, with the establishment of devolved national administrations for Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales following pre-legislative referendums.[49]
The Scottish National Party, the current party of government in Scotland, is committed to the goal of an independent Scotland within the European Union, but this is opposed by the leadership of the next three largest parties in the Scottish Parliament. A referendum on Scottish independence was held in September 2014, and the electorate rejected it.[50] Plaid Cymru, a Welsh party, has a similar ambition for Wales.[51] Several parties in Northern Ireland, including the second- and third-largest,[52] seek to establish an independent United Ireland, and have repeatedly called for border polls.[53] The d'Hondt system used here means that either the First Minister or Deputy First Minister will be from one of these parties.[54]
Africa
Most countries in Sub-Saharan Africa are former colonies and, as such, are not drawn along national lines, making them truly multinational states.
Kenya
Kenya is home to more than 70 ethnic groups, the most populous of which are the Kikuyu, at about 20 percent of the population.[55] Together, the five largest groups—the Kikuyu, Luo, Luhya, Kamba, and Kalenjin—account for 70 percent of Kenyans.[55]
Nigeria
The largest nation in Nigeria is the Hausa-Fulani, which accounts for 29 percent of the country's population. However, the group actually encompasses two distinct ethnicities: the Hausa and the Fulani (or Fulbe). While both ethnicities are found in large areas of West Africa, it is only in Nigeria that they are classified as a single ethnic group for political expediency.
South Africa
Present-day South Africa is the successor state to the Union of South Africa, which was formed from four British colonies in 1910.
South Africa has eleven official languages (Afrikaans, English, Ndebele, Pedi, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, and Zulu) and formally recognizes several other languages spoken by minority nations. Speakers of each language may be of a different nationality—for example, some members of the Ndebele and Tswana nations speak Zulu, and groups such as the Thembu and Hlubi speak Xhosa.
As is the case throughout Africa, the nations of South Africa mostly correspond to specific regions. However, large cities such as Johannesburg are home to a mixture of national groups, leading to a "melting pot" of cultures. The government has continuously attempted to unify the country's various nationalities and to foster a South African identity.
Many of the nationalities found in South Africa are also found in bordering countries, and in some cases, more members live in South Africa than in the country where the group originated. For example, there are more Sotho, Tswana, and Swazi people living in South Africa than in the bordering nation states of Lesotho, Botswana, and Swaziland, respectively. In the past, this has led to conflict. Lesotho still claims large swathes of South Africa, and attempts have been made to cede some South African territory to Botswana and Swaziland. All three states were intended to be incorporated in the Union of South Africa, but those plans never came to fruition because of power struggles within their apartheid governments.
Former multinational states
Austria-Hungary
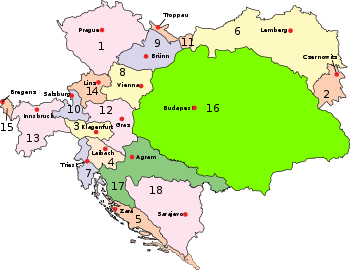 Bohemia (1), Bukovina (2), Carinthia (3), Carniola (4), Dalmatia (5), Galicia (6), Küstenland (7), Lower Austria (8), Moravia (9), Salzburg (10), Silesia (11), Styria (12), Tirol (13), Upper Austria (14), Vorarlberg (15), Hungary (16), Croatia-Slavonia (17), and Bosnia (18). |
Austria-Hungary, which succeeded the Austrian Empire, was a historical multinational state. The centrifugal forces within it, coupled with its loss in World War I, led to its breakup in 1918. Its successor states included the First Austrian Republic, the Kingdom of Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, which later became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. Parts of Austria-Hungary were also incorporated into Poland, Ukraine, the Kingdom of Romania, and the Kingdom of Italy.
The principal languages of Austria-Hungary were German, Hungarian, Polish, Czech, and Croatian, but there were also many minor languages, including Ukrainian, Romanian, Slovak, Serbian, Slovene, Rusyn, Italian, and Yiddish.[56]
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire was the dynastic state of the Turkish House of Osman. At its peak in the 16th and 17th centuries, it controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, the Caucasus, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa.
In addition to Turks, the ethnic groups of the Ottoman Empire included Albanians, Arabs, Armenians, Assyrians, Bosnians, Bulgarians, Circassians, Georgians, Greeks, Jews, Kurds, Laz, Macedonians, Romanians, Serbs, Tatars, and Zazas.
Through millet courts, confessional communities were allowed to rule themselves under their own legal systems: for example, sharia law for Muslims, Canon law for Christians, and halakha law for Jews. After the Tanzimat reforms from 1839–76, the term "millet" was used to refer to legally protected religious minority groups, similar to the way other countries use the word "nation". (The word "millet" comes from the Arabic word "millah" (ملة), which literally means "nation".) The millet system has been called an example of pre-modern religious pluralism.[57]
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was a state composed of the Soviet republics (of which there were 15 after 1956), with the capital in Moscow. It was founded in December 1922, when the Russian SFSR—which formed during the Russian Revolution of 1917 and emerged victorious in the ensuing Russian Civil War—unified with the Transcaucasian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian SSRs. Addressing the Extraordinary Eighth Congress of Soviets of the Soviet Union on 25 November 1936, Joseph Stalin stated that "within the Soviet Union there are about sixty nations, national groups, and nationalities. The Soviet state is a multinational state."[58]
In the late 1980s, some of the republics sought sovereignty over their territories, citing Article 72 of the USSR Constitution, which stated that any constituent republic was free to secede.[59] On 7 April 1990, a law was passed allowing a republic to secede if more than two-thirds of its residents voted for secession in a referendum.[60] Many held free elections, and the resulting legislatures soon passed bills that contradicted Soviet laws, in what became known as the War of Laws.
In 1989, the Russian SFSR—the largest constituent republic, with about half of the USSR's population—convened a new Congress of People's Deputies and elected Boris Yeltsin its chairman. On 12 June 1990, the Congress declared Russia's sovereignty over its territory and proceeded to pass legislation that attempted to supersede Soviet laws. Legal uncertainty continued through 1991 as constituent republics slowly gained de facto independence.
In a referendum on 17 March 1991, majorities in nine of the 15 republics voted to preserve the Union. The referendum gave Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev a minor boost, and in the summer of 1991, the New Union Treaty was designed and agreed upon by eight republics. The treaty would have turned the Soviet Union into a much looser federation, but its signing was interrupted by the August Coup—an attempted coup d'état against Gorbachev by hardline Communist Party members of the government and the KGB, who sought to reverse Gorbachev's reforms and reassert the central government's control over the republics. When the coup collapsed, Yeltsin—who had publicly opposed it—came out as a hero, while Gorbachev's power was effectively ended.
As a result, the balance of power tipped significantly toward the republics. In August 1991, Latvia and Estonia declared their independence (following Lithuania's 1990 example), while the other twelve republics continued to discuss new, increasingly loose models for the Union.
On 8 December 1991, the presidents of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus signed the Belavezha Accords, which declared the Soviet Union dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in its place. Doubts remained about the authority of the Belavezha Accords to dissolve the Union, but on 21 December 1991, representatives of every Soviet republic except Georgia—including those that had signed the Belavezha Accords—signed the Alma-Ata Protocol, which confirmed the dissolution of the USSR and reiterated the establishment of the CIS. On 25 December 1991, Gorbachev yielded, resigning as the president of the USSR and declaring the office extinct. He turned the powers vested in the Soviet presidency over to Yeltsin, the president of Russia.
The following day, the Supreme Soviet, the highest governmental body of the Soviet Union, dissolved itself. Many organizations, such as the Soviet Army and police forces, remained in place in the early months of 1992, but were slowly phased out and either withdrawn from or absorbed by the newly independent states.
Yugoslavia
The first country to be known by this name was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, known until 3 October 1929 as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. It was established on 1 December 1918 by the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia (to which the Kingdom of Montenegro had been annexed on 13 November 1918), and the Conference of Ambassadors gave international recognition to the union on 13 July 1922.[61]
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis powers in 1941 and abolished as a result of World War II. It was succeeded by Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, proclaimed in 1943 by the Yugoslav Partisans resistance movement. When a communist government was established in 1946, the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1963, it was renamed again, becoming the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). This was the largest Yugoslav state, with Istria and Rijeka having been added after World War II.
The country consisted of six constituent "socialist republics" (SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Slovenia, and SR Serbia) and two "socialist autonomous provinces" (SAP Vojvodina and SAP Kosovo, which became largely equal to other members of the federation after 1974).[62][63]
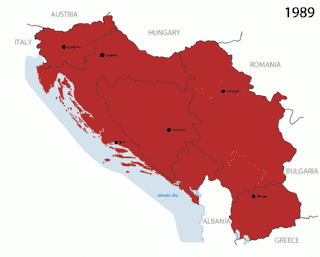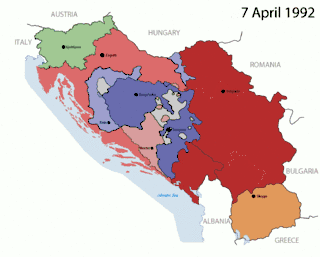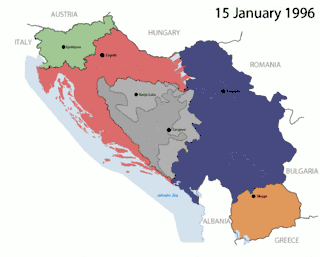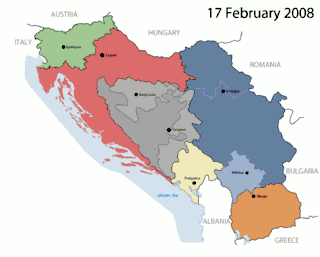
Starting in 1991, the SFRY disintegrated in the Yugoslav Wars, which followed the secession of most of the country's constituent entities. The next Yugoslavia, known as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, existed until 2003, when it was renamed Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, this last vestige separated into Serbia and Montenegro.
See also
References
- ↑ Kelemen, R. Daniel. (2007). "Built to Last? The Durability of EU Federalism?" (PDF). In Making History: State of the European Union, Vol. 8, edited by Sophie Meunier and Kate McNamara, Oxford University Press, p. 52.
- ↑ A Union of Diversity: Language, Identity and Polity-Building in Europe
- ↑ Ilan Peleg, 'Classifying Multinational States' in Democratizing the Hegemonic State (Cambridge University Press, 2007), pp. 78-80
- ↑ Welsh, David (1993). "Domestic politics and ethnic conflict". In Brown, Michael E. Ethnic Conflict and International Security. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 43–60. ISBN 0-691-00068-9.
- ↑ Choudhry, Sujit (2008). "Bridging comparative politics and comparative constitutional law: Constitutional design in divided societies". In Choudhry, Sujit. Constitutional Design for Divided Societies: Integration or Accommodation?. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 3–40. ISBN 0-19-953541-8.
- ↑ Barbara Slavin (6 March 2013). "Cyrus Cylinder a Reminder of Persian Legacy of Tolerance". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 21 September 2013.
- ↑ World Factbook / Field Listing :: Ethnic groups
- ↑ Cambridge Journals Online - Canadian Journal of Political Science/Revue canadienne de science politique - Abstract - Canada and the Multinational State. Journals.cambridge.org. Retrieved on 29 July 2013.
- ↑ House of Commons of Canada, 39th Parliament, 11th Session. Journals No. 87 for Monday, 27 November 2006, 11:00am
- ↑ "Ethnic groups". BBC News. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
Pashtun: Estimated to comprise more than 45% of the population, the Pashtuns have been the dominant ethnic group in Afghanistan.
- ↑ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 2017-01-05.
- ↑ "VIEW: March towards independence". Daily Times. 23 March 2011. Retrieved 29 September 2011.
- ↑ Excerpt from the Presidential Address delivered by Quaid-e-Azam at Lahore, March 22–23, 1940 Archived 2006-06-28 at the Wayback Machine., Nazariapak.info
- ↑ Tariq Rahman (1996). Language and Politics in Pakistan. Oxford University Press. p. 2.
- ↑ Tariq Rahman. 'The Punjabi Movement' from Language and Politics in Pakistan.
- ↑ Ethnic groups in Russia Archived 2011-06-22 at the Wayback Machine., at demoscope.ru
- ↑ Russia - Language, Culture, Customs and Etiquette at kwintessential.co.uk, accessed 31 January 2011
- ↑ "Census of population, households and dwellings in Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2013: Final results" (PDF). Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina. June 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- ↑ "Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in Montenegro 2011" (PDF). Monstat. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ↑ "Language and alphabet Article 13". Constitution of Montenegro. WIPO. 19 October 2007.
The official language in Montenegro shall be Montenegrin.
- ↑ Samepolitikk (in Norwegian) Regjeringen.no, retrieved 17 July 2013
- ↑ Nasjonale minoriteter (in Norwegian) Regjeringen.no, retrieved 17 July 2013
- ↑ Gojkovic N. System of minorities’ protection in Serbia Konrad Adenauer Foundation
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-11. Retrieved 2015-06-02.
- ↑ "The relation between the state and the National Minority Councils". International Radio Serbia. Archived from the original on 26 July 2013.
- ↑ "Покрајинска влада". vojvodina.gov.rs.
- ↑ "Serbian Government - Official Presentation". serbia.gov.rs.
- ↑ "Error". vip.org.rs.
- ↑ "Beogradski centar za ljudska prava - Belgrade Centre for Human Rights". bgcentar.org.rs. 29 March 2015.
- ↑ "ONS Glossary of economic terms". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 24 July 2010.
- ↑ Giddens, Anthony (2006). Sociology. Cambridge: Polity Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7456-3379-4.
- ↑ Gordon Brown: We must defend the Union www.telegraph.co.uk, 25 March 2008
- ↑ Hogwood, Brian. "Regulatory Reform in a Multinational State: The Emergence of Multilevel Regulation in the United Kingdom" (PDF). Retrieved 24 July 2010.
- ↑ DIVERSITY AND CITIZENSHIP CURRICULUM REVIEW Archived 2011-06-15 at the Wayback Machine. www.devon.gov.uk, accessed 13 August 2010
- ↑ Magnay, Jacquelin (26 May 2010). "London 2012: Hugh Robertson puts Home Nations football team on agenda". Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 11 September 2010.
- ↑ William E. Burns, A Brief History of Great Britain, p. xxi
- ↑ "Articles of Union with Scotland 1707". UK Parliament. Retrieved 19 October 2008.
- 1 2 D. Ross, Chronology of Scottish History (Glasgow: Geddes & Grosset, 2002), ISBN 1-85534-380-0, p. 56.
- 1 2 J. Hearn, Claiming Scotland: National Identity and Liberal Culture (Edinburgh; Edinburgh University Press, 2002), ISBN 1-902930-16-9, p. 104.
- ↑ "Orkney and Shetland Are Pawned as Dowry ⋆ History Channel". History Channel. 2016-06-20. Retrieved 2017-01-05.
- ↑ "The Act of Union". Act of Union Virtual Library. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ↑ SR&O 1921, No. 533 of 3 May 1921
- ↑ "The Anglo-Irish Treaty, 6 December 1921". CAIN. Retrieved 15 May 2006.
- ↑ P. Cottrell, The Irish Civil War 1922-23 (London: Osprey, 2008), ISBN 1-84603-270-9, p. 85.
- ↑ "The Troubles gallery - 40 years of conflict in Northern Ireland from the Belfast Telegraph archives - BelfastTelegraph.co.uk". BelfastTelegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ "BBC - History - The Troubles - Violence". Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ "The Belfast Agreement - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ Association, Press (2013-04-03). "Union flag protests: more than 200 arrested in Northern Ireland". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ Keating, Michael (1 January 1998). "Reforging the Union: Devolution and Constitutional Change in the United Kingdom". Publius: the Journal of Federalism. 28 (1): 217. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubjof.a029948. Retrieved 4 February 2009.
- ↑ "Scottish referendum: Scotland votes 'No' to independence". BBC News. 2014-09-19. Retrieved 2017-01-05.
- ↑ Simon Jenkins, We'd be a more united kingdom with an independent Scotland in The Sunday Times dated September 17, 2006
- ↑ "Northern Ireland Assembly election 2017 results". BBC News. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ "Sinn Fein chief Gerry Adams in fresh call for united Ireland border poll - BelfastTelegraph.co.uk". BelfastTelegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ "D'Hondt system for picking NI ministers in Stormont". BBC News. 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- 1 2 "East Africa Living Encyclopedia". www.africa.upenn.edu. Retrieved 2017-01-05.
- ↑ Volkszählung vom 31. Dezember 1910, published in Geographischer Atlas zur Vaterlandskunde an der österreichischen Mittelschulen (Vienna, 1911)
- ↑ Sachedina, Abdulaziz Abdulhussein (2001). The Islamic Roots of Democratic Pluralism. Oxford University Press. pp. 96–97. ISBN 0-19-513991-7.
The millet system in the Muslim world provided the pre-modern paradigm of a religiously pluralistic society by granting each religious community an official status and a substantial measure of self-government.
- ↑ On the Draft Constitution of the U.S.S.R marxists.org, accessed 15 January 2011
- ↑ The red blues — Soviet politics by Brian Crozier, National Review, 25 June 1990.
- ↑ Origins of Moral-Ethical Crisis and Ways to Overcome it by V.A.Drozhin Honoured Lawyer of Russia.
- ↑ http://www.orderofdanilo.org/en/family/index.htm
- ↑ Huntington, Samuel P. (1996). The clash of civilizations and the remaking of world order. Simon & Schuster. p. 260. ISBN 0-684-84441-9.
- ↑ "History, bloody history". BBC News. March 24, 1999. Retrieved December 29, 2010.