Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) also called canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1 (cMOAT) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 (ABCC2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC2 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
MRP2 is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). More specifically, this protein is a member of the MRP subfamily, which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This protein is expressed in the canalicular (apical) part of the hepatocyte and functions in biliary transport. Substrates include anticancer drugs such as vinblastine; therefore, this protein appears to contribute to drug resistance in mammalian cells.
MRP2 is also expressed in the apical membrane of proximal renal tubule endothelial cells where they are involved in the excretion of small organic anions.[8]
MRP2 inhibitors
| Drug | Class | Indications | Source | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| probenecid | uricosuric | gout hyperuricemia |
[9] |  |
| furosemide | loop diuretic | heart failure edema |
[9] |  |
| ritonavir | protease inhibitor | antiretroviral | [10] |  |
| saquinavir | protease inhibitor | antiretroviral | [11] |  |
| lamivudine | Nucleoside analog | antiviral | [12] |  |
| abacavir | Nucleoside analog | antiretroviral | [12] |  |
| emtricitabine | Nucleoside analog | antiviral | [12] | 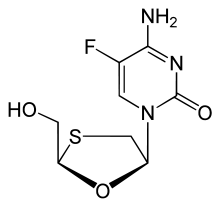 |
| efavirenz | NNRTI | antiretroviral | [12] |  |
| delavirdine | NNRTI | antiretroviral | [12] |  |
| nevirapine | NNRTI | antiretroviral | [12] |  |
| cidofovir | nucleoside phosphonate | antiviral | [13] |  |
| adefovir | nucleoside phosphonate | antiviral | [11] | |
| tenofovir | nucleoside phosphonate | antiviral | [12] |  |
Clinical significance
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Several different mutations in this gene have been observed in patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.[7][14]
Iatrogenic Fanconi syndrome
Many negatively charged metabolic waste products are eliminated from the body by the kidneys. These organic anions are transported from the blood into the endothelial cells of the renal proximal tubules by the OAT1 transporter. From there, these waste molecules are transported into the lumen of the tubule by the MRP2 transporter. Many drugs are eliminated from the body by this mechanism. Some of these drugs pass through the MRP2 transporter slowly. This may cause a buildup of organic anions in the cytoplasm of the cells.
Drugs that inhibit the MRP2 transporter can cause a buildup of organic anions inside renal proximal tubule cells. If some of these organic anions inhibit mitochondrial DNA synthesis, it may cause iatrogenic Fanconi syndrome. The nucleoside phosphonate adefovir is a MRP2 inhibitor that has been linked to kidney disease.[15] Tenofovir[16] and cidofovir[17] are also nucleoside phosphonates that inhibit MRP2 and have been associated with Fanconi syndrome.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
|{{{bSize}}}px|alt=Irinotecan Pathway edit]]
Irinotecan Pathway edit
- ↑ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "IrinotecanPathway_WP46359".
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000023839 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025194 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Taniguchi K, Wada M, Kohno K, Nakamura T, Kawabe T, Kawakami M, Kagotani K, Okumura K, Akiyama S, Kuwano M (Oct 1996). "A human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter (cMOAT) gene is overexpressed in cisplatin-resistant human cancer cell lines with decreased drug accumulation". Cancer Res. 56 (18): 4124–9. PMID 8797578.
- ↑ van Kuijck MA, Kool M, Merkx GF, Geurts van Kessel A, Bindels RJ, Deen PM, van Os CH (Sep 1997). "Assignment of the canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter gene (CMOAT) to human chromosome 10q24 and mouse chromosome 19D2 by fluorescent in situ hybridization". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 77 (3–4): 285–7. PMID 9284939. doi:10.1159/000134599.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: ABCC2 ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 2".
- ↑ Sekine T, Miyazaki H, Endou H (February 2006). "Molecular physiology of renal organic anion transporters". Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 290 (2): F251–61. PMID 16403838. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00439.2004.
- 1 2 Bakos E, Evers R, Sinkó E, Váradi A, Borst P, Sarkadi B (April 2000). "Interactions of the human multidrug resistance proteins MRP1 and MRP2 with organic anions". Mol. Pharmacol. 57 (4): 760–8. PMID 10727523.
- ↑ Peyrière H, Reynes J, Rouanet I, et al. (March 2004). "Renal tubular dysfunction associated with tenofovir therapy: report of 7 cases". J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 35 (3): 269–73. PMID 15076241.
- 1 2 Gimenez F, Fernandez C, Mabondzo A (June 2004). "Transport of HIV protease inhibitors through the blood–brain barrier and interactions with the efflux proteins, P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance proteins". J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 36 (2): 649–58. PMID 15167283. doi:10.1097/00126334-200406010-00001.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Weiss J, Theile D, Ketabi-Kiyanvash N, Lindenmaier H, Haefeli WE (March 2007). "Inhibition of MRP1/ABCC1, MRP2/ABCC2, and MRP3/ABCC3 by nucleoside, nucleotide, and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors". Drug Metab. Dispos. 35 (3): 340–4. PMID 17172311. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.012765.
- ↑ Miller DS (November 2001). "Nucleoside phosphonate interactions with multiple organic anion transporters in renal proximal tubule". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299 (2): 567–74. PMID 11602668.
- ↑ Morii, Kazuhiko; Yamamoto, Takeharu (2016-07-06). "Dubin–Johnson Syndrome". New England Journal of Medicine. 375 (1): e1. PMID 27406372. doi:10.1056/nejmicm1509529.
- ↑ Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, et al. (February 2003). "Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B". N. Engl. J. Med. 348 (9): 808–16. PMID 12606735. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020681.
- ↑ Atta MG, Fine DM (March 2009). "Editorial comment: tenofovir nephrotoxicity--the disconnect between clinical trials and real-world practice". AIDS Read. 19 (3): 118–9. PMID 19334329.
- ↑ Vittecoq D, Dumitrescu L, Beaufils H, Deray G (August 1997). "Fanconi syndrome associated with cidofovir therapy". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41 (8): 1846. PMC 164022
 . PMID 9257778.
. PMID 9257778.
Further reading
- Keppler D, König J (2001). "Hepatic secretion of conjugated drugs and endogenous substances.". Semin. Liver Dis. 20 (3): 265–72. PMID 11076395. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9391.
- Gerk PM, Vore M (2002). "Regulation of expression of the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) and its role in drug disposition.". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302 (2): 407–15. PMID 12130697. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.035014.
- Mayer R, Kartenbeck J, Büchler M, et al. (1995). "Expression of the MRP gene-encoded conjugate export pump in liver and its selective absence from the canalicular membrane in transport-deficient mutant hepatocytes.". J. Cell Biol. 131 (1): 137–50. PMC 2120605
 . PMID 7559771. doi:10.1083/jcb.131.1.137.
. PMID 7559771. doi:10.1083/jcb.131.1.137. - Büchler M, König J, Brom M, et al. (1996). "cDNA cloning of the hepatocyte canalicular isoform of the multidrug resistance protein, cMrp, reveals a novel conjugate export pump deficient in hyperbilirubinemic mutant rats.". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (25): 15091–8. PMID 8662992. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.25.15091.
- Paulusma CC, Kool M, Bosma PJ, et al. (1997). "A mutation in the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter gene causes the Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Hepatology. 25 (6): 1539–42. PMID 9185779. doi:10.1002/hep.510250635.
- Wada M, Toh S, Taniguchi K, et al. (1998). "Mutations in the canilicular multispecific organic anion transporter (cMOAT) gene, a novel ABC transporter, in patients with hyperbilirubinemia II/Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 7 (2): 203–7. PMID 9425227. doi:10.1093/hmg/7.2.203.
- Evers R, Kool M, van Deemter L, et al. (1998). "Drug export activity of the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in polarized kidney MDCK cells expressing cMOAT (MRP2) cDNA.". J. Clin. Invest. 101 (7): 1310–9. PMC 508708
 . PMID 9525973. doi:10.1172/JCI119886.
. PMID 9525973. doi:10.1172/JCI119886. - Kajihara S, Hisatomi A, Mizuta T, et al. (1999). "A splice mutation in the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter gene causes Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253 (2): 454–7. PMID 9878557. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9780.
- Toh S, Wada M, Uchiumi T, et al. (1999). "Genomic structure of the canalicular multispecific organic anion-transporter gene (MRP2/cMOAT) and mutations in the ATP-binding-cassette region in Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64 (3): 739–46. PMC 1377791
 . PMID 10053008. doi:10.1086/302292.
. PMID 10053008. doi:10.1086/302292. - Schaub TP, Kartenbeck J, König J, et al. (1999). "Expression of the MRP2 gene-encoded conjugate export pump in human kidney proximal tubules and in renal cell carcinoma.". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10 (6): 1159–69. PMID 10361853.
- Tsujii H, König J, Rost D, et al. (1999). "Exon-intron organization of the human multidrug-resistance protein 2 (MRP2) gene mutated in Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Gastroenterology. 117 (3): 653–60. PMID 10464142. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70459-2.
- Kocher O, Comella N, Gilchrist A, et al. (1999). "PDZK1, a novel PDZ domain-containing protein up-regulated in carcinomas and mapped to chromosome 1q21, interacts with cMOAT (MRP2), the multidrug resistance-associated protein.". Lab. Invest. 79 (9): 1161–70. PMID 10496535.
- Tanaka T, Uchiumi T, Hinoshita E, et al. (1999). "The human multidrug resistance protein 2 gene: functional characterization of the 5'-flanking region and expression in hepatic cells.". Hepatology. 30 (6): 1507–12. PMID 10573531. doi:10.1002/hep.510300617.
- St-Pierre MV, Serrano MA, Macias RI, et al. (2000). "Expression of members of the multidrug resistance protein family in human term placenta.". Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 279 (4): R1495–503. PMID 11004020.
- Keitel V, Kartenbeck J, Nies AT, et al. (2001). "Impaired protein maturation of the conjugate export pump multidrug resistance protein 2 as a consequence of a deletion mutation in Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". Hepatology. 32 (6): 1317–28. PMID 11093739. doi:10.1053/jhep.2000.19791.
- Ito S, Ieiri I, Tanabe M, et al. (2001). "Polymorphism of the ABC transporter genes, MDR1, MRP1 and MRP2/cMOAT, in healthy Japanese subjects.". Pharmacogenetics. 11 (2): 175–84. PMID 11266082. doi:10.1097/00008571-200103000-00008.
- Mor-Cohen R, Zivelin A, Rosenberg N, et al. (2001). "Identification and functional analysis of two novel mutations in the multidrug resistance protein 2 gene in Israeli patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (40): 36923–30. PMID 11477083. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105047200.
- Mallants R, Van Oosterwyck K, Van Vaeck L, Mols R, De Clercq E, Augustijns P (2005). "Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) affects hepatobiliary elimination but not the intestinal disposition of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and its metabolites". Xenobiotica. 35 (10–11): 1055–66. PMID 16393861. doi:10.1080/00498250500354493.
External links
- ABCC2 protein, human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.