Monopod (creature)
.jpg)

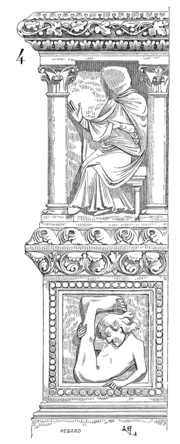
Monopods (also sciapods, skiapods, skiapodes) are mythological human creatures with a single, large foot extending from a leg centered in the middle of their bodies. The names monopod and skiapod (σκιάποδες) are both Greek, respectively meaning "one-foot" and "shadow-foot".
In Ancient Greece and Rome
Monopods appear in Aristophanes' play The Birds, first performed in 414 BC. They are described by Pliny the Elder in his Natural History, where he reports travelers' stories from encounters or sightings of Monopods in India. Pliny remarks that they are first mentioned by Ctesias in his book Indika (India), a record of the view of Persians of India which only remains in fragments. Pliny describes Monopods like this:
He [Ctesias] speaks also of another race of men, who are known as Monocoli, who have only one leg, but are able to leap with surprising agility. The same people are also called Sciapodae, because they are in the habit of lying on their backs, during the time of the extreme heat, and protect themselves from the sun by the shade of their feet.[1]
Philostratus mentions Skiapodes in his Life of Apollonius of Tyana, which was cited by Eusebius in his Treatise Against Hierocles. Apollonius of Tyana believes the Skiapodes live in India and Ethiopia, and asks the Indian sage Iarkhas about their existence.
St. Augustine (354–430) mentions the "Skiopodes" in The City of God, Book 16, chapter 8 entitled, "Whether Certain Monstrous Races of Men Are Derived From the Stock of Adam or Noah's Sons."
In the middle ages
Reference to the legend continued into the Middle Ages, for example with Isidore of Seville in his Etymologiae, where he writes:
The race of Sciopodes are said to live in Ethiopia; they have only one leg, and are wonderfully speedy. The Greeks call them σκιαπόδεϛ ("shade-footed ones") because when it is hot they lie on their backs on the ground and are shaded by the great size of their feet.[2]
The Hereford Mappa Mundi, drawn c. 1300, shows a sciapod on one side of the world,[3] as does a world map drawn by Beatus of Liébana (c. 730 – c. 800).[4]
Origin
According to Carl A.P. Ruck, the Monopods's cited existence in India refers to the Vedic Aja Ekapad ("Not-born Single-foot"), an epithet for Soma. Since Soma is a botanical deity the single foot would represent the stem of an entheogenic plant or fungus.[5]
Modern references
Chronicles of Narnia
C.S. Lewis introduces monopods in the book The Voyage of the Dawn Treader, a part of his children's series The Chronicles of Narnia.
In the story, the Duffers or 'Dufflepuds', a tribe of monopodal dwarves, inhabit a small island near the edge of the Narnian world along with a Star magician named Coriakin, who transformed them into monopods as a punishment. They were so unhappy with their appearance that they made themselves invisible. Lucy Pevensie later made them visible again. They were (re)discovered by explorers from the Narnian ship the Dawn Treader which had landed on the island to rest and resupply.[6]
According to Brian Sibley's book The Land of Narnia, Lewis may have based their appearance on drawings from the Hereford Mappa Mundi.
Saga of Erik the Red
In the Saga of Erik the Red, Karlsefni, accompanied by Thorvald Eriksson and others, sails around Kjalarnes and then south, keeping land on their left side, hoping to find Thorhall. After sailing for a long time, while moored on the south side of a west-flowing river, they are shot at by a one-footed man, and Thorvald dies from an arrow-wound:
| “ | True it was that our men tracked a one-legged creature down to the shore. The uncanny fellow fled in a flash, though rough was his way, hear us Karlsefni![7] | ” |
Baudolino
Umberto Eco in his novel Baudolino describes a sciapod named Gavagai. The name of the creature "Gavagai" is a reference to Quine's example of indeterminacy of translation.
See also
References
- ↑ Pliny the Elder. Natural History VII:2
- ↑ Barney, Stephen A. et al (translators) (2006). The Etymologies of Isidore of Seville. Cambridge University Press. p. 245.
- ↑ "The Hereford Mappamundi". Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- ↑ Beato del Burgo de Osma (c. 750–800). Hereford Mappa Mundi. Folios 34v-35.
- ↑ "Mushrooms and philosophers", Journal of Ethnopharmacology.
- ↑ Lewis, C.S. (1965) [1952]. The Voyage of the Dawn Treader. Puffin. pp. 114–124, 139–147.
- ↑ Keneva Kunz (Translator) The Saga of Erik the Red, in The Saga of Icelanders, Penguin Books, New York, 2001. ISBN 0-670-88990-3
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sciapod. |
- http://web.cn.edu/kwheeler/monster_list.html
- http://www.henry-davis.com/MAPS/EMwebpages/207.1mono.html
- http://www.westgallerychurches.com/Suffolk/indexsflk.html
- http://kunst.no/mono/panot/utgivelser.htm