Monoclinic crystal system

In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a rectangular prism with a parallelogram as its base. Hence two vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third vector meets the other two at an angle other than 90°.
Bravais lattices
Two-dimensional
There is only one monoclinic Bravais lattice in two dimensions: the oblique lattice.
Three-dimensional
Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the centered monoclinic lattices.

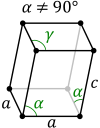
| Bravais lattice | Primitive monoclinic |
Base-centered monoclinic |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | mP | mS |
| Standard unit cell |  |
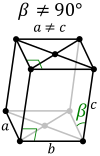 |
| Clinorhombic prism unit cell | 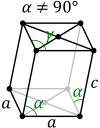 |
 |
In the monoclinic system there is a second choice of crystal axes that results in a unit cell with the shape of a clinorhombic prism,[1] although this axis setting is very rarely used; this is because the rectangular two-dimensional base layers can also be described with rhombic axes. In this axis setting, the primitive and base-centered lattices interchange in centering type.
Crystal classes
The monoclinic crystal system class names, examples, Schönflies notation, Hermann-Mauguin notation, point groups, International Tables for Crystallography space group number,[2] orbifold, type, and space groups are listed in the table below.
| # | Point group | Type (Example) |
Space groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Schoenflies notation (Schön.) | Hermann–Mauguin notation (Intl) | orbifold (Orb.) | Coxeter notation (Cox.) | |||
| 3–5 | Sphenoidal [3] | C2 | 2 | 22 | [2]+ | enantiomorphic polar (halotrichite) |
P2, P21 C2 |
| 6–9 | Domatic [3] | C1h (=C1v = Cs) | 2 = m | *11 | [ ] | polar (hilgardite) |
Pm, Pc Cm, Cc |
| 10–15 | Prismatic [3] | C2h | 2/m | 2* | [2,2+] | centrosymmetric (gypsum) |
P2/m, P21/m, C2/m P2/c, P21/c, C2/c |
Sphenoidal is also monoclinic hemimorphic; Domatic is also monoclinic hemihedral; Prismatic is also monoclinic normal.
The three monoclinic hemimorphic space groups are as follows:
- a prism with as cross-section wallpaper group p2
- ditto with screw axes instead of axes
- ditto with screw axes as well as axes, parallel, in between; in this case an additional translation vector is one half of a translation vector in the base plane plus one half of a perpendicular vector between the base planes.
The four monoclinic hemihedral space groups include
- those with pure reflection at the base of the prism and halfway
- those with glide planes instead of pure reflection planes; the glide is one half of a translation vector in the base plane
- those with both in between each other; in this case an additional translation vector is this glide plus one half of a perpendicular vector between the base planes.
See also
References
- ↑ See Hahn (2002), p. 746, row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β
- ↑ Prince, E., ed. (2006). International Tables for Crystallography. International Union of Crystallography. ISBN 978-1-4020-4969-9. doi:10.1107/97809553602060000001.
- 1 2 3 "The 32 crystal classes". Retrieved 2009-07-08.
Further reading
- Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis (1985). Manual of Mineralogy (20th ed.). pp. 69–73. ISBN 0-471-80580-7.
- Hahn, Theo, ed. (2002). International Tables for Crystallography, Volume A: Space Group Symmetry. A (5th ed.). Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-7923-6590-7. doi:10.1107/97809553602060000100.