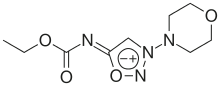
Molsidomine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-Ethoxy-N-(3-morpholino-5-oxadiazol-3-iumyl)methanimidate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.902 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 242.23 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| C01DX12 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Molsidomine is an orally active, long acting vasodilating drug. Molsidomine is metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite linsidomine. Linsidomine is an unstable compound that releases nitric oxide (NO) upon decay as the actual vasodilating compound.[1]
Release of nitric oxide[2]

Chemistry
Molsidomine as well as linsidomine are sydnone imines, a class of mesoionic heterocyclic aromatic chemical compounds.
Synthesis
A mesoionic sydnone is active as an antianginal agent.

Molsidomine synthesis:[3]
Its synthesis starts by reacting 1-aminomorpholine with formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide to give 2. Nitrosation gives the N-nitroso analog (3) which cyclizes to the sydnone (4) on treatment with anhydrous acid. Formation of the ethyl urethane is then made possible by reacting Linsidomine with Ethyl chloroformate.
See also
References
- ↑ Rosenkranz, B.; Winkelmann, B. R.; Parnham, M. J. (1996). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of molsidomine". Clinical pharmacokinetics. 30 (5): 372–384. PMID 8743336. doi:10.2165/00003088-199630050-00004.
- ↑ Mutschler, Ernst; Schäfer-Korting, Monika (2001). Arzneimittelwirkungen (in German) (8 ed.). Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft. p. 558. ISBN 3-8047-1763-2.
- ↑ Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin 19(1), 72-79, 1971-01-25.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.