Southern Min
| Southern Min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Mǐnnán Amoy–Swatow | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 閩南語 / 闽南语 Bân-lâm-gú | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Koa-a books, Minnan written in Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native to | China, Taiwan, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar and other areas of Southern Min and Hoklo settlement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Region | Southern Fujian province; the Chaozhou-Shantou (Chaoshan) area and Leizhou Peninsula in Guangdong province; extreme south of Zhejiang province; much of Hainan province (if Hainanese or Qiongwen is included); and most of Taiwan. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Native speakers | 47 million (2007)[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dialects | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese characters; Latin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official status | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Official language in | None; one of the statutory languages for public transport announcements in Taiwan[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regulated by | None (The Republic of China Ministry of Education and some NGOs are influential in Taiwan) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Language codes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 639-3 |
nan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glottolog |
minn1241[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguasphere |
79-AAA-j | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Southern Min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Subgroups of Southern Min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 闽南语 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 閩南語 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Language of Southern Min [Fujian]" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Southern Min, or Minnan (simplified Chinese: 闽南语; traditional Chinese: 閩南語), is a branch of Min Chinese spoken in certain parts of China including southern Fujian (the Minnan region), eastern Guangdong, Hainan, and southern Zhejiang, and in Taiwan.[4] The Minnan dialects are also spoken by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora, most notably the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore.
In common parlance, Southern Min usually refers to Hokkien, including Amoy and Taiwanese Hokkien; both are combinations of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou speeches. The Southern Min dialect group also includes Teochew, though Teochew has limited mutual intelligibility with Hokkien. Hainanese is not mutually intellgible with other Southern Min and is often considered a separate branch of Min. Southern Min is not mutually intelligible with Eastern Min, Pu-Xian Min, any other Min branch, Hakka, Cantonese, Shanghainese or Mandarin.
Geographic distribution
China and Taiwan
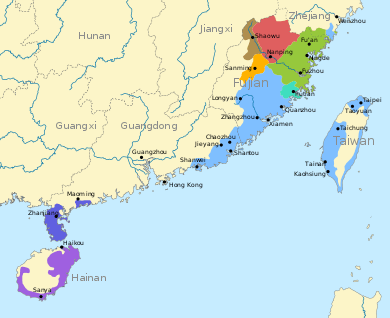
Southern Min dialects are spoken in the southern part of Fujian, three southeastern counties of Zhejiang, the Zhoushan archipelago off Ningbo in Zhejiang, and the Chaoshan (Teo-swa) region in Guangdong. The variant spoken in Leizhou, Guangdong as well as Hainan is Hainanese and is not mutually intelligible with other Southern Min or Teochew. Hainanese is classified in some schemes as part of Southern Min and in other schemes as separate. Puxian Min was originally based on the Quanzhou dialect, but over time became heavily influenced by Eastern Min, eventually losing intelligibility with Minnan.
A forms of Southern Min spoken in Taiwan, collectively known as Taiwanese, Southern Min is a first language for most of the Hoklo people, the main ethnicity of Taiwan. The correspondence between language and ethnicity is not absolute, as some Hoklo have very limited proficiency in Southern Min while some non-Hoklo speak Southern Min fluently.
Southeast Asia
There are many Southern Min speakers also among Overseas Chinese in Southeast Asia. Many ethnic Chinese immigrants to the region were Hoklo from southern Fujian and brought the language to what is now Burma, Indonesia (the former Dutch East Indies) and present-day Malaysia and Singapore (formerly British Malaya and the Straits Settlements). In general, Southern Min from southern Fujian is known as Hokkien, Hokkienese, Fukien or Fookien in Southeast Asia and is mostly mutually intelligible with Hokkien spoken elsewhere. Many Southeast Asian ethnic Chinese also originated in the Chaoshan region of Guangdong and speak Teochew language, the variant of Southern Min from that region. Philippine Hokkien is reportedly the native language of up to 98.5% of the Chinese Filipino community in the Philippines, among whom it is also known as Lan-nang or Lán-lâng-oē ("our people’s language"), although Hoklo people consist of only around 60% of the Chinese Filipino population.
Southern Min-speakers form the majority of Chinese in Singapore, with the largest group being Hokkien and the second largest being Teochew. Despite the similarities the two groups are rarely seen as part of the same "Minnan" Chinese subgroups.
Classification
The variants of Southern Min spoken in Zhejiang province are most akin to that spoken in Quanzhou. The variants spoken in Taiwan are similar to the three Fujian variants and are collectively known as Taiwanese.
Those Southern Min variants that are collectively known as "Hokkien" in Southeast Asia also originate from these variants. The variants of Southern Min in the Chaoshan region of eastern Guangdong province are collectively known as Teochew or Chaozhou. Teochew is of great importance in the Southeast Asian Chinese diaspora, particularly in Malaysia, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Sumatra and West Kalimantan. The Philippines variant is mostly from the Quanzhou area as most of their forefathers are from the aforementioned area.
The Southern Min language variant spoken around Shanwei and Haifeng differs markedly from Teochew and may represent a later migration from Zhangzhou. Linguistically, it lies between Teochew and Amoy. In southwestern Fujian, the local variants in Longyan and Zhangping form a separate division of Minnan on their own. Among ethnic Chinese inhabitants of Penang, Malaysia and Medan, Indonesia, a distinct form based on the Zhangzhou dialect has developed. In Penang, it is called Penang Hokkien while across the Malacca Strait in Medan, an almost identical variant is known as Medan Hokkien.
Varieties
There are three principal branches of Southern Min: Hokkien (also known as Quanzhang 泉漳), Datian (大田), and Teochew also known as Chaoshan or Teo-Swa (潮汕).
Hokkien
Xiamen (Amoy) dialect is a blend of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou dialects. Taiwanese Minnan is also a blend of Quanzhou and Zhangzhou dialect. Taiwanese in northern Taiwan tends to be based on Quanzhou dialect, whereas the Taiwanese spoken in southern Taiwan tends to be based on Zhangzhou dialect. There are minor variations in pronunciation and vocabulary between Quanzhou and Zhangzhou speech. The grammar is basically the same. Additionally, extensive contact with the Japanese language has left a legacy of Japanese loanwords. In contrast, Teochew speech is significantly different from Quanzhou and Zhangzhou speech in both pronunciation and vocabulary.
Teochew
Teochew, or Chaoshan, includes Swatow dialect. It has very low intelligibility with Amoy dialect.[5]
Datian
Datian Min, spoken in Datian County, Sanming Prefecture, northwest of Quanzhou, has a minimally mutual intelligibility with other Minnan, partially because of influence from Central Min and other Min branches. It is thus sometimes classified as a separate branch of Min.
Phonology
Southern Min has one of the most diverse phonologies of Chinese varieties, with more consonants than Mandarin or Cantonese. Vowels, on the other hand, are more-or-less similar to those of Mandarin. In general, Southern Min dialects have five to six tones, and tone sandhi is extensive. There are minor variations within Hokkien, and the Teochew system differs somewhat more.
Southern Min's nasal finals consist m, n, ŋ, ~.
Writing systems
Southern Min dialects lack a standardized written language. Southern Min speakers are taught how to read Standard Chinese in school. As a result, there has not been an urgent need to develop a writing system. In recent years, an increasing number of Southern Min speakers have become interested in developing a standard writing system (either by using Chinese Characters, or using Romanized script).
History
The Min homeland of Fujian was opened to Chinese settlement by the defeat of the Minyue state by the armies of Emperor Wu of Han in 110 BC.[6] The area features rugged mountainous terrain, with short rivers that flow into the South China Sea. Most subsequent migration from north to south China passed through the valleys of the Xiang and Gan rivers to the west, so that Min varieties have experienced less northern influence than other southern groups.[7] As a result, whereas most varieties of Chinese can be treated as derived from Middle Chinese, the language described by rhyme dictionaries such as the Qieyun (601 AD), Min varieties contain traces of older distinctions.[8] Linguists estimate that the oldest layers of Min dialects diverged from the rest of Chinese around the time of the Han dynasty.[9][10] However, significant waves of migration from the North China Plain occurred:[11]
- The Uprising of the Five Barbarians during the Jin dynasty, particularly the Disaster of Yongjia in 311 AD, caused a tide of immigration to the south.
- In 669, Chen Zheng and his son Chen Yuanguang from Gushi County in Henan set up a regional administration in Fujian to suppress an insurrection by the She people.
- Wang Chao was appointed governor of Fujian in 893, near the end of the Tang dynasty, and brought tens of thousands of troops from Henan. In 909, following the fall of the Tang dynasty, his son Wang Shenzhi founded the Min Kingdom, one of the Ten Kingdoms in the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
Jerry Norman identifies four main layers in the vocabulary of modern Min varieties:
- A non-Chinese substratum from the original languages of Minyue, which Norman and Mei Tsu-lin believe were Austroasiatic.[12][13]
- The earliest Chinese layer, brought to Fujian by settlers from Zhejiang to the north during the Han dynasty.[14]
- A layer from the Northern and Southern Dynasties period, which is largely consistent with the phonology of the Qieyun dictionary.[15]
- A literary layer based on the koiné of Chang'an, the capital of the Tang dynasty.[16]
Comparisons with Sino-Xenic character pronunciations
Minnan (or Hokkien) can trace its origins through the Tang Dynasty, and it also has roots from earlier periods. Minnan (Hokkien) people call themselves "Tang people", (唐人, pronounced as "唐儂" Thn̂g-lâng) which is synonymous to "Chinese people". Because of the widespread influence of the Tang culture during the great Tang dynasty, there are today still many Minnan pronunciations of words shared by the Sino-xenic pronunciations of Vietnamese, Korean and Japanese languages.
| English | Han characters | Mandarin Chinese | Taiwanese Minnan[17] | Teochew | Cantonese | Korean | Vietnamese | Japanese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Book | 冊 | Cè | Chhek/Chheh | ze1 | caak3 | Chaek (책) | Tập/Sách | Saku/Satsu/Shaku |
| Bridge | 橋 | Qiáo | Kiâu/Kiô | giê5 | kiu4 | Gyo (교) | Cầu/Kiều | Kyō |
| Dangerous | 危險 | Wēixiǎn | Guî-hiám | guîn5/nguín5 hiem2 | ngai4 him2 | Wiheom (위험) | Nguy hiểm | Kiken |
| Embassy | 大使館 | Dàshǐguǎn | Tāi-sài-koán | dai6 sái2 guêng2 | daai6 si3 gun2 | Daesagwan (대사관) | Đại Sứ Quán | Taishikan |
| Flag | 旗 | Qí | Kî | kî5 | kei4 | Gi (기) | Cờ/Kỳ | Ki |
| Insurance | 保險 | Bǎoxiǎn | Pó-hiám | Bó2-hiém | bou2 him2 | Boheom (보험) | Bảo hiểm | Hoken |
| News | 新聞 | Xīnwén | Sin-bûn | sing1 bhung6 | san1 man4 | Shinmun (신문) | Tân Văn | Shinbun |
| Student | 學生 | Xuéshēng | Ha̍k-seng | Hak8 sêng1 | hok6 saang1 | Haksaeng (학생) | Học sinh | Gakusei |
| University | 大學 | Dàxué | Tāi-ha̍k/Tōa-o̍h | dai6 hag8/dua7 oh8 | daai6 hok6 | Daehak (대학) | Đại học | Daigaku |
See also
Related languages
- Fuzhou dialect (Min Dong branch)
- Lan-nang (Philippine dialect of Minnan)
- Medan Hokkien (North-Sumatra, Indonesia dialect of Minnan)
- Penang Hokkien
- Singaporean Hokkien
- Southern Malaysia Hokkien
- Taiwanese Minnan
References
- ↑ Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in Nationalencyklopedin
- ↑ 大眾運輸工具播音語言平等保障法
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Minnan Chinese". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ CAI ZHU, HUANG GUO (1 October 2015). Chinese language. Xiamen: Fujian Education Publishing House. ISBN 7533469518.
- ↑ Minnan/ Southern Min at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Norman (1991), pp. 328.
- ↑ Norman (1988), pp. 210, 228.
- ↑ Norman (1988), pp. 228–229.
- ↑ Ting (1983), pp. 9–10.
- ↑ Baxter & Sagart (2014), pp. 33, 79.
- ↑ Yan (2006), p. 120.
- ↑ Norman & Mei (1976).
- ↑ Norman (1991), pp. 331–332.
- ↑ Norman (1991), pp. 334–336.
- ↑ Norman (1991), p. 336.
- ↑ Norman (1991), p. 337.
- ↑ Iûⁿ, Ún-giân. "Tâi-bûn/Hôa-bûn Sòaⁿ-téng Sû-tián" 台文/華文線頂辭典 [Taiwanese/Chinese Online Dictionary]. Retrieved 1 October 2014.
Further reading
- Branner, David Prager (2000). Problems in Comparative Chinese Dialectology — the Classification of Miin and Hakka. Trends in Linguistics series, no. 123. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-015831-0.
- Chung, Raung-fu (1996). The segmental phonology of Southern Min in Taiwan. Taipei: Crane Pub. Co. ISBN 957-9463-46-8.
- DeBernardi, Jean (1991). "Linguistic nationalism: the case of Southern Min". Sino-Platonic Papers. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania. 25. OCLC 24810816.
- Chappell, Hilary, ed. (2001). Sinitic Grammar. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-829977-X. "Part V: Southern Min Grammar" (3 articles).
External links
| Min Nan Chinese edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Southern Min test of Wikibooks at Wikimedia Incubator |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Minnan |
| Look up Minnan in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Minnan phrasebook. |
- Amoy Minnan Swadesh list (Wiktionary)
- Appendix:Sino-Tibetan Swadesh lists (Wiktionary)
- 當代泉州音字彙, a dictionary of Quanzhou speech
- Iûⁿ, Ún-giân (2006). "Tai-gi Hôa-gí Sòaⁿ-téng Sû-tián" 台文/華文線頂辭典 [On-line Taiwanese/Mandarin Dictionary] (in Chinese and Min Nan)..
- Iûⁿ, Ún-giân. 台語線頂字典 [Taiwanese Hokkien Online Character Dictionary] (in Taiwanese and Chinese).
- 臺灣閩南語常用詞辭典, Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan by Ministry of Education, Republic of China (Taiwan).
- 臺灣本土語言互譯及語音合成系統, Taiwanese-Hakka-Mandarin on-line conversion
- Voyager - Spacecraft - Golden Record - Greetings From Earth - Amoy The voyager clip says: Thài-khong pêng-iú, lín-hó. Lín chia̍h-pá--bē? Ū-êng, to̍h lâi gún chia chē--ô·! 太空朋友,恁好。恁食飽未?有閒著來阮遮坐哦!
- 台語詞典 Taiwanese-English-Mandarin Dictionary
- How to Forget Your Mother Tongue and Remember Your National Language by Victor H. Mair University of Pennsylvania
- ISO 639-3 change request 2008-083, requesting to replace code nan (Minnan Chinese) with dzu (Chaozhou) and xim (Xiamen), rejected because it did not include codes to cover the rest of the group.