Geothermal areas of Yellowstone
The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles. The number of thermal features in Yellowstone is estimated at 10,000.[1] A study[2] that was completed in 2011 found that a total of 1,283 geysers have erupted in Yellowstone, 465 of which are active during an average year. These are distributed among nine geyser basins, with a few geysers found in smaller thermal areas throughout the Park. The number of geysers in each geyser basin are as follows: Upper Geyser Basin (410), Midway Geyser Basin (59), Lower Geyser Basin (283), Norris Geyser Basin (193), West Thumb Geyser Basin (84), Gibbon Geyser Basin (24), Lone Star Geyser Basin (21), Shoshone Geyser Basin (107), Heart Lake Geyser Basin (69), other areas (33). Although famous large geysers like Old Faithful are part of the total, most of Yellowstone's geysers are small, erupting to only a foot or two. The hydrothermal system that supplies the geysers with hot water sits within an ancient active caldera.[3] Many of the thermal features in Yellowstone build up sinter, geyserite, or travertine deposits around and within them.
The various geyser basins are located where rainwater and snowmelt can percolate into the ground, get indirectly superheated by the underlying Yellowstone hotspot, and then erupt at the surface as geysers, hot springs, and fumaroles. Thus flat-bottomed valleys between ancient lava flows and glacial moraines are where most of the large geothermal areas are located. Smaller geothermal areas can be found where fault lines reach the surface, in places along the circular fracture zone around the caldera, and at the base of slopes that collect excess groundwater.[3] Due to the Yellowstone Plateau's high elevation the average boiling temperature at Yellowstone's geyser basins is 199 °F (93 °C). When properly confined and close to the surface it can periodically release some of the built-up pressure in eruptions of hot water and steam that can reach up to 390 feet (120 m) into the air (see Steamboat Geyser, the world’s tallest geyser).[4] Water erupting from Yellowstone's geysers is superheated above that boiling point to an average of 204 °F (95.5 °C) as it leaves the vent. The water cools significantly while airborne and is no longer scalding hot by the time it strikes the ground, nearby boardwalks, or even spectators. Because of the high temperatures of the water in the features it is important that spectators remain on the boardwalks and designated trails. Several deaths have occurred in the park as a result of falls into hot springs.
Prehistoric Native American artifacts have been found at Mammoth Hot Springs and other geothermal areas in Yellowstone. Some accounts state that the early people used hot water from the geothermal features for bathing and cooking. In the 19th century Father Pierre-Jean De Smet reported that natives he interviewed thought that geyser eruptions were "the result of combat between the infernal spirits."[5] The Lewis and Clark Expedition traveled north of the Yellowstone area in 1806. Local natives that they came upon seldom dared to enter what we now know is the caldera because of frequent loud noises that sounded like thunder and the belief that the spirits that possessed the area did not like human intrusion into their realm.[6] The first white man known to travel into the caldera and see the geothermal features was John Colter, who had left the Lewis and Clark Expedition. He described what he saw as "hot spring brimstone." Beaver trapper Joseph Meek recounted in 1830 that the steam rising from the various geyser basins reminded him of smoke coming from industrial smokestacks on a cold winter morning in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In the 1850s famed trapper Jim Bridger called it "the place where Hell bubbled up."[3]
Types of features found in the park
The heat that drives geothermal activity in the Yellowstone area comes from brine (salty water) that is 1.5 to 3 miles (2.4 to 4.8 km) below the surface.[3] This is actually below the solid volcanic rock and sediment that extends to a depth of 3,000 to 6,000 feet (900 to 1,800 m) and is inside the hot but mostly solid part of the pluton that contains Yellowstone’s magma chamber.[7] At that depth the brine is superheated to temperatures that exceed 400 °F or 205 °C but is able to remain a liquid because it is under great pressure (like a huge pressure cooker).[8]
Convection of the churning brine and conduction from surrounding rock transfers heat to an overlaying layer of fresh groundwater. Movement of the two liquids is facilitated by the highly fractured and porous nature of the rocks under the Yellowstone Plateau. Some silica is dissolved from the fractured rhyolite into the hot water as it travels through the fractured rock. Part of this hard mineral is later redeposited on the walls of the cracks and fissures to make a nearly pressure-tight system. Silica precipitates at the surface to form either geyserite or sinter, creating the massive geyser cones, the scalloped edges of hot springs, and the seemingly barren landscape of geyser basins.
There are at least five types of geothermal features found at Yellowstone:
- Fumaroles: Fumaroles or steam vents, are the hottest hydrothermal features in the park. They have so little water that it all flashes into steam before reaching the surface. At places like Roaring Mountain, the result is loud hissing of steam and gases.
- Geysers: Geysers such as Old Faithful are a type of geothermal feature that periodically erupt scalding hot water. Increased pressure exerted by the enormous weight of the overlying rock and water prevents deeper water from boiling. As the hot water rises it is under less pressure and steam bubbles form. They, in turn, expand on their ascent until the bubbles are too big and numerous to pass freely through constrictions. At a critical point the confined bubbles actually lift the water above, causing the geyser to splash or overflow. This decreases the pressure of the system and violent boiling results. Large quantities of water flash into tremendous amounts of steam that force a jet of water out of the vent: an eruption begins. Water (and heat) is expelled faster than the geyser’s recharge rate, gradually decreasing the system’s pressure and eventually ending the eruption.[8]
- Hot springs: Hot springs such as Grand Prismatic Spring are the most common hydrothermal features in the park. Their plumbing has no constrictions. Superheated water cools as it reaches the surface, sinks, and is replaced by hotter water from below. This circulation, called convection, prevents water from reaching the temperature needed to set off an eruption. Many hot springs give rise to streams of heated water.
- Mudpots: Mudpots such as Fountain Paint Pots are acidic hot springs with a limited water supply. Some microorganisms use hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg smell), which rises from deep within the earth, as an energy source. They convert the gas into sulfuric acid, which breaks down rock into clay.
- Travertine terraces: Travertine terraces, found at Mammoth Hot Springs, are formed from limestone (a rock type made of calcium carbonate). Thermal waters rise through the limestone, carrying high amounts of dissolved carbonate. Carbon dioxide is released at the surface and calcium carbonate deposited as travertine, the chalky white rock of the terraces.[8] These features constantly and quickly change due to the rapid rate of deposition.
Geyser basins
Norris Geyser Basin

The Norris Geyser Basin 44°43′43″N 110°42′16″W / 44.72861°N 110.70444°W is the hottest geyser basin in the park[9] and is located near the northwest edge of Yellowstone Caldera near Norris Junction and on the intersection of three major faults. The Norris-Mammoth Corridor is a fault that runs from Norris north through Mammoth to the Gardiner, Montana, area. The Hebgen Lake fault runs from northwest of West Yellowstone, Montana, to Norris. This fault experienced an earthquake in 1959 that measured 7.4 on the Richter scale (sources vary on exact magnitude between 7.1 and 7.8; see 1959 Hebgen Lake earthquake). Norris Geyser Basin is so hot and dynamic because these two faults intersect with the ring fracture zone that resulted from the creation of the Yellowstone Caldera of 640,000 years ago.[10]
The Basin consists of three main areas: Porcelain Basin, Back Basin, and One Hundred Springs Plain. Unlike most of other geyser basins in the park, the waters from Norris are acidic[11] rather than alkaline (for example, Echinus Geyser has a pH of ~3.5). The difference in pH allows for a different class of bacterial thermophiles to live at Norris, creating different color patterns in and around the Norris Basin waters.
The Ragged Hills that lie between Back Basin and One Hundred Springs Plain are thermally altered glacial kames. As glaciers receded the underlying thermal features began to express themselves once again, melting remnants of the ice and causing masses of debris to be dumped. These debris piles were then altered by steam and hot water flowing through them. Madison lies within the eroded stream channels cut through lava flows formed after the caldera eruption. The Gibbon Falls lies on the caldera boundary as does Virginia Cascades.[9]
The tallest active geyser in the world is Steamboat Geyser[10] and it is located in Norris Basin. Unlike the slightly smaller but much more famous Old Faithful Geyser located in Upper Geyser Basin, Steamboat has an erratic and lengthy timetable between major eruptions. During major eruptions, which may be separated by intervals of more than a year (the longest recorded span between major eruptions was 50 years), Steamboat erupts over 300 feet (90 m) into the air. Steamboat does not lie dormant between eruptions, instead displaying minor eruptions of approximately 40 feet (12 m).
Norris Geyser Basin periodically undergoes a large-scale, basin-wide thermal disturbance lasting a few weeks. Water levels fluctuate, and temperatures, pH, colors, and eruptive patterns change throughout the basin. During a disturbance in 1985, Porkchop Geyser continually jetted steam and water; in 1989, the same geyser apparently clogged with silica and blew up, throwing rocks more than 200 feet (61 m). In 2003 a park ranger observed it bubbling heavily, the first such activity seen since 1991. Activity increased dramatically in mid-2003. Because of high ground temperatures and new features beside the trail much of Back Basin was closed until October. In 2004 the boardwalk was routed around the dangerous area and now leads behind Porkchop Geyser.[12]
North of Norris, Roaring Mountain is a large, acidic hydrothermal area (solfatara) with many fumaroles. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the number, size, and power of the fumaroles were much greater than today. The fumaroles are most easily seen in the cooler, low-light conditions of morning and evening. Artists' Paintpots is a small hydrothermal area south of Norris Junction that includes colorful hot springs and two large mudpots.
Monument Geyser Basin
The Monument Geyser Basin 44°41′03″N 110°45′14″W / 44.68417°N 110.75389°W has no active geysers, but its 'monuments' are siliceous sinter deposits similar to the siliceous spires discovered on the floor of Yellowstone Lake. Scientists hypothesize that this basin's structures formed from a hot water system in a glacially dammed lake during the waning stages of the Pinedale Glaciation. The basin is on a ridge reached by a very steep one-mile (1.6 km) trail south of Artists' Paint Pots.

Upper Geyser Basin
![]() Media related to Upper Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Upper Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons

South of Norris along the rim of the caldera is the Upper Geyser Basin 44°27′52″N 110°49′45″W / 44.46444°N 110.82917°W, which has the highest concentration of geothermal features in the park. This complement of features includes the most famous geyser in the park, Old Faithful Geyser, as well as four other predictable large geysers. One of these large geysers in the area is Castle Geyser which is about 1,400 feet (430 m) northwest of Old Faithful. Castle Geyser has an interval of approximately 13 hours between major eruptions, but is unpredictable after minor eruptions. The other three predictable geysers are Grand Geyser, Daisy Geyser, and Riverside Geyser. Biscuit Basin and Black Sand Basin are also within the boundaries of Upper Geyser Basin.
The hills surrounding Old Faithful and the Upper Geyser Basin are reminders of Quaternary rhyolitic lava flows. These flows, occurring long after the catastrophic eruption of 640,000 years ago, flowed across the landscape like stiff mounds of bread dough due to their high silica content.
Evidence of glacial activity is common, and it is one of the keys that allows geysers to exist. Glacier till deposits underlie the geyser basins providing storage areas for the water used in eruptions. Many landforms, such as Porcupine Hills north of Fountain Flats, are made up of glacial gravel and are reminders that 70,000 to 14,000 years ago, this area was buried under ice.[13]
Signs of the forces of erosion can be seen everywhere, from runoff channels carved across the sinter in the geyser basins to the drainage created by the Firehole River. Mountain building is evident on the drive south of Old Faithful, toward Craig Pass. Here the Rocky Mountains reach a height of 8,262 feet (2,518 m), dividing the country into two distinct watersheds.[14]
Midway Geyser Basin

![]() Media related to Midway Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Midway Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Midway Geyser Basin 44°31′04″N 110°49′56″W / 44.51778°N 110.83222°W is much smaller than the other basins found alongside the Firehole River. Despite its small size, it contains two large features, the 200-by-300-foot (60 by 90 m) wide Excelsior Geyser which pours over 4,000 U.S. gallons (15,000 L; 3,300 imp gal) per minute into the Firehole River. The largest hot spring in Yellowstone, the 370-foot (110 m) wide and 121-foot (37 m) deep Grand Prismatic Spring is also found here.[15]
Lower Geyser Basin

![]() Media related to Lower Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lower Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Further north is the Lower Geyser Basin 44°32′58″N 110°50′09″W / 44.54944°N 110.83583°W, which has a much less concentrated set of geothermal features, including Fountain Paint Pots. Fountain Paint Pots are mud pots, that is, a hot spring that contains boiling mud instead of water. The mud is produced by a higher acidity in the water which enables the spring to dissolve surrounding minerals to create an opaque, usually grey, mud. Also found in this basin is Great Fountain Geyser, whose eruptions reach 100 to 200 feet (30–61 m) in the air, while waves of water cascade down its sinter terraces.[15]
West Thumb Geyser Basin


![]() Media related to West Thumb Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to West Thumb Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
The West Thumb Geyser Basin 44°25′07″N 110°34′23″W / 44.41861°N 110.57306°W, including Potts Basin to the north, is the largest geyser basin on the shores of Yellowstone Lake. The heat source of the thermal features in this location is thought to be relatively close to the surface, only 10,000 feet (3,000 m) down. West Thumb is about the same size as another famous volcanic caldera, Crater Lake in Oregon, but much smaller than the great Yellowstone Caldera which last erupted about 640,000 years ago. It is interesting to note that West Thumb is a caldera within a caldera.
West Thumb was created approximately 162,000 years ago when a magma chamber bulged up under the surface of the earth and subsequently cracked it along ring fracture zones. This in turn released the enclosed magma as lava and caused the surface above the emptied magma chamber to collapse.[16] Water later filled the collapsed area of the caldera, forming an extension of Yellowstone Lake. This created the source of heat and water that feed the West Thumb Geyser Basin today.
The thermal features at West Thumb are not only found on the lake shore, but extend under the surface of the lake as well. Several underwater hydrothermal features were discovered in the early 1990s and can be seen as slick spots or slight bulges in the summer. During the winter, the underwater thermal features are visible as melt holes in the icy surface of the lake.[16] The surrounding ice can reach three feet (one meter) in thickness.[17]
Perhaps the most famous hydrothermal feature at West Thumb is a geyser on the lake shore known as Fishing Cone. Walter Trumbull of the 1870 Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition described a unique event while a man was fishing adjacent to the cone: "...in swinging a trout ashore, it accidentally got off the hook and fell into the spring. For a moment it darted about with wonderful rapidity, as if seeking an outlet. Then it came to the top, dead, and literally boiled." Fishing Cone erupted frequently to the height of 40 feet (12 m) in 1919 and to lesser heights in 1939. One fisherman was badly burned in Fishing Cone in 1921. Fishing at the geyser is now prohibited.[18]
Early visitors would arrive at West Thumb via stagecoach from the Old Faithful area. They had a choice of continuing on the stagecoach or boarding the steamship Zillah to continue the journey by water to Lake Hotel. The boat dock was located near the south end of the geyser basin near Lakeside Spring.
Backcountry Geyser Basins
![]() Media related to Gibbon Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Gibbon Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Media related to Heart Lake Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Heart Lake Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Media related to Lone Star Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lone Star Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Media related to Shoshone Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Shoshone Geyser Basin at Wikimedia Commons
The Gibbon 44°41′58″N 110°44′34″W / 44.69944°N 110.74278°W, Heart Lake 44°18′00″N 110°30′56″W / 44.30000°N 110.51556°W, Lone Star 44°24′50″N 110°49′04″W / 44.41389°N 110.81778°W, and Shoshone Geyser Basins 44°21′16″N 110°47′57″W / 44.35444°N 110.79917°W are located away from the heavily traveled portions of the park. Some require several miles of off-trail hiking to reach. These areas also generally lack the boardwalks and other safety features of the developed areas. As falling into geothermal features can be fatal, it is usually advisable to visit these areas with an experienced guide or at the very least, travelers need to ensure they remain on well marked trails.
Lying in the Snake River watershed east of Lewis Lake and south of Yellowstone Lake, Heart Lake was named sometime before 1871 for Hart Hunney, a hunter. Other explorers in the region incorrectly assumed that the lake's name was spelled 'heart' because of its shape. The Heart Lake Geyser Basin begins a couple miles from the lake and descends along Witch Creek to the lakeshore. Five groups of hydrothermal features comprise the basin, and all of them contain geysers, although some are dormant.[18]
The Shoshone Geyser Basin, reached by hiking or by boat, contains one of the highest concentrations of geysers in the world – more than 80 in an area 1,600 by 800 feet (240 m).[19] Hot springs and mudpots dot the landscape between the geyser basin and Shoshone Lake.
Hot Springs Basin is located 15 miles (24 km) north-northeast of Fishing Bridge and has one of Yellowstone's largest collections of hot springs and fumaroles.[20] The geothermal features there release large amounts of sulfur. This makes water from the springs so acidic that it has dissolved holes in the pants of people who sit on wet ground and causes mounds of sulfur three feet (1 m) high to develop around fumaroles. The very hot acidic water and steam have also created voids in the ground that are only covered by a thin crust.
Mammoth Hot Springs
See Mammoth Hot Springs.
Mud Volcano and Sulfur cauldron
![]() Media related to Hayden Valley geothermal features at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Hayden Valley geothermal features at Wikimedia Commons

The thermal features at Mud Volcano and Sulfur cauldron 44°37′29″N 110°26′03″W / 44.62472°N 110.43417°W are primarily mud pots and fumaroles because the area is situated on a perched water system with little water available. Fumaroles or "steam vents" occur when the ground water boils away faster than it can be recharged. Also, the vapors are rich in sulfuric acid that leaches the rock, breaking it down into clay. Because no water washes away the acid or leached rock, it remains as sticky clay to form a mud pot. Hydrogen sulfide gas is present deep in the earth at Mud Volcano. As this gas combines with water and the sulfur is metabolized by cyanobacteria, a solution of sulfuric acid is formed that dissolves the surface soils to create pools and cones of clay and mud. Along with hydrogen sulfide, steam, carbon dioxide, and other gases explode through the layers of mud.
A series of shallow earthquakes associated with the volcanic activity in Yellowstone struck this area in 1978. Soil temperatures increased to nearly 200 °F (93 °C). The slope between Sizzling Basin and Mud Geyser, once covered with green grass and trees, became a barren landscape of fallen trees known as "the cooking hillside."
- Trail maps
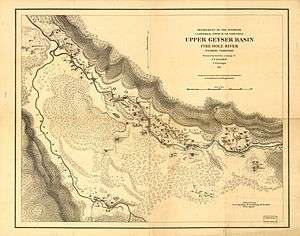 Upper Geyser Basin, 1871
Upper Geyser Basin, 1871 Lower Geyser Basin, 1872
Lower Geyser Basin, 1872
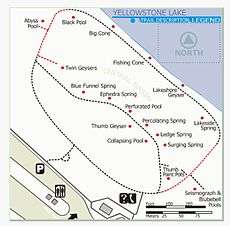 West Thumb Geyser Basin
West Thumb Geyser Basin- Norris Geyser Basin
- Fountain Paint Pots
- Upper Geyser Basin - North
- Upper Geyser Basin - South
- Mammoth Hot Springs
Video
See also
References
- Bryan, T. Scott (1995). The Geysers of Yellowstone. Niwot, Colorado: University Press of Colorado. ISBN 0-87081-365-X
- Harris, Ann G.; Tuttle, Esther; and Tuttle, Sherwood D. (1995). Geology of national parks: fifth edition. Iowa: Kendall/Hunt Publishing. ISBN 0-7872-5353-7
- "Natural Highlights of Yellowstone". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-08-28.
- "Hydrothermal Features and How They Work". National Park Service.
- "Norris Geyser Basin Tour". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-06-05.
- "Geological Overview of the Norris Area". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-05-08.
- "Norris Area Natural Highlights". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-05-30.
- "Steamboat Geyser". National Park Service.
- "Old Faithful Area Geologic Highlights". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-05-28.
- "Old Faithful Area Natural Features, Page 1". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-08-30.
- "Grant Village Area Geologic Highlights". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-05-18.
- "Mammoth Hot Springs Terraces Tour". National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2010-06-09.
Notes
- ↑ Geothermal Features and How They Work
- ↑ Cross, Jeff. "How many geysers are found in Yellowstone?" Program and Abstracts, The 11th Biennial Scientific Conference on the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. October 8–10, 2012, Mammoth Hot Springs Hotel, Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming.
- 1 2 3 4 Windows into the Earth, page 73
- ↑ Windows into the Earth, page 79
- ↑ Windows into the Earth, page 70
- ↑ Windows into the Earth, page 71
- ↑ Windows into the Earth", page 69
- 1 2 3 Yellowstone Resources and Issues: 2006, page 41
- 1 2 Norris Geyser Basin Tour
- 1 2 Geological Overview of the Norris Area
- ↑ Natural Highlights of the Norris Area
- ↑ For the whole paragraph: ’’Yellowstone Resources and Issues: 2006’’, pages 190–191
- ↑ Yellowstone Resources and Issues, 2006, page 193
- ↑ Geological Overview of the Old Faithful Area
- 1 2 Yellowstone Resources and Issues, 2006, page 194
- 1 2 Yellowstone Resources and Issues: 2006, page 198
- ↑ Geological Overview of the Grant Village & West Thumb Areas
- 1 2 For the whole paragraph: Yellowstone Resources and Issues: 2006’’, page 199
- ↑ Yellowstone Resources and Issues, 2006, page 200
- ↑ For the whole paragraph, except where noted: Windows into the Earth, page 73, paragraph 5
External links
- "Yellowstone Photos & Multimedia". National Park Service.
- "Geysers of Yellowstone". The Geyser Observation and Study Organization.
- "Yellowstone National Park Thermal Features Database". Montana State University.
- West Thumb Ranger Station, East of Old Faithful & north of Grant Village on Grand Loop Road, West Thumb, Teton, WY at the Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS)
- West Thumb Hamilton's Store, General Store, 300' east of Grand Loop Road & 150' northwest of Ranger Station, West Thumb, Teton, WY at HABS, also , , , , , , and