Glossary of astronomy
This page is a glossary of astronomy. This scientific study is concerned with celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth. The field of astronomy has an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.
A

Syrtis Major (center) is a prominent dark albedo feature on Mars
- Absolute magnitude is a measure of a star's absolute brightness. It is defined as the apparent magnitude the star would show if it were located at a distance of 10 parsecs, or 32.6 light years.
- Accretion disk is a roughly circular mass of diffuse material in orbit around a central object, such as a star or black hole. The material has been acquired from a source external to the central object.
- Active galactic nucleus is a compact region in the middle of a galaxy displaying a higher than normal luminosity over some part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Albedo feature is a large area on the surface of a reflecting object that shows a contrast in brightness or darkness (albedo) with adjacent areas.
- Am star is a chemically peculiar star belonging to the more general class of A-type stars. The spectrum of the Am stars shows abnormal enhancements and deficiencies of certain metals. (See metallicity below.)
- Apoapsis is the point of furthest excursion, or separation, between two orbiting objects.
- Apparent magnitude is a measure of the brightness of a celestial body as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere. The brighter the object appears, the lower the value of its magnitude.
- Appulse is the closest approach of one celestial object to another, as viewed from a third body.
- Asterism is a pattern of stars recognized on Earth's night sky. It may form part of an official constellation, or be composed of stars from more than one.
- Astrometric binary is a type of binary system where evidence for an unseen orbiting companion is revealed by its periodic gravitational perturbation of the visible component. See also spectroscopic binary.
- Astronomical unit, or AU, is the approximate distance between the midpoints of the Earth and the Sun.
- Autumnal equinox is the point in the year when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, while generally trending southward at each zenith passage. It represents the moment when the North Pole of the Earth begins to tilt away from the Sun.
- Azimuth is an angular measurement of an object's orientation along the horizon of the observer, relative to the direction of true north. When combined with the altitude above the horizon, it defines an object's current position in the spherical coordinate system.
B
- Black hole is a concentration of mass so compact that it creates a region of space from which not even light can escape. The outer boundary of this region is called the event horizon.
- Break-up velocity, critical velocity, or critical rotation of a rapidly spinning star is the surface velocity at which the centrifugal force just matches the force of Newtonian gravity. Beyond this point, the star would begin to eject matter from its surface.[1]
- Brown dwarf is a substellar object that is too low in mass to sustain the nuclear fusion of hydrogen-1 in its core, which is a characteristic of stars on the main sequence. Brown dwarfs can still generate energy from gravitational contraction and by the fusion of deuterium.
C
- Celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere that covers the entire sky and is stationary with respect to the background stars. It is used as a tool for spherical astronomy.
- Chromospheric activity index is a parameter indicating the magnetic activity in a star's chromosphere. One measure of this activity is log R′HK, where R′HK is the ratio of the equivalent width of a star's singly-ionized Calcium H and K lines, after correction for photospheric light, to the bolometric flux.[2]
- Color index is a numeric value that is used to compare the brightness of a star measured from different frequency bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Because the energy output of a star varies by frequency as a function of temperature, the color index can be used to indicate the star's temperature.
- Comets are relatively small, icy bodies that display extended features when they approach the Sun. The energy from the Sun vaporizes volatiles on a comet's surface, producing a visible coma around the cometary body. Sometimes a comet can produce a long tail radiating away from the Sun.
- Commensurability is the property of two objects orbiting the same body whose periods are in a rational proportion. For example, the orbital period of Saturn around the Sun is very nearly 5/2 the orbital period of Jupiter.
- Common proper motion is used to indicate two or more stars that share the same motion through space, within the margin of observational error. That is, they have nearly the same proper motion and radial velocity parameters. This may suggest that they are gravitationally bound or share a common origin.[3]
- Constellation is a region on the celestial sphere surrounding a grouping of stars. The names of constellations are assigned by tradition and often have an associated folklore based in mythology, while the modern demarcation of their borders are established by the International Astronomical Union in 1930.
D
- Declination, in the equatorial coordinate system, is the celestial equivalent of terrestrial latitude. Coordinates north of the celestial equator are measured in positive degrees from 0° to 90°, while coordinates to the south use coordinates in negative degrees.
- Decretion disk is a circumstellar disk formed from gas ejected from the central star that now follows a near Keplerian orbit around it. This type of disk can be found around many Be stars.[4]
- Double star is a pair of stars that appear near each other on the celestial sphere. This can happen because, by chance, the pair lie along nearly the same line of sight from the Earth. If the two are located in physical proximity to each other, they may form a co-moving pair or a binary star system.
- Dwarf star is the category of ordinary main sequence stars like the Sun, in contrast to evolved giant stars like Betelgeuse and Antares. Confusingly, the term dwarf has also came to include stellar remnants known as white dwarfs plus low mass, sub-stellar objects called brown dwarfs.
E
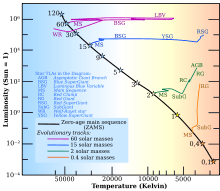
Sample evolutionary tracks for stars of different mass
- Early-type star is a hotter and more massive star, in contrast to late-type stars that are cooler and less massive. The term originated from historical stellar models that assumed stars began their early life at a high temperature then gradually cooled off as they aged. It can be used to refer to the higher temperature members of any particular population or category of stars, rather than just all stars in general.
- Eccentricity is a parameter that determines how much an orbit deviates from a perfect circle. For an elliptical orbit, the eccentricity ranges from greater than zero to less than one.
- Ecliptic plane, or plane of the ecliptic, is the plane defined by the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Hence, the position of the Sun as viewed from Earth defines the intersection of this plane with the celestial sphere. The ecliptic plane is used as a reference plane for describing the position of other Solar System bodies. It differs from the celestial equator because of the axial tilt of the Earth.
- Effective temperature of a star or planet is the temperature of an ideal black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation.
- Evolutionary track is a curve on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram that a solitary star, of a particular mass and composition, is expected to follow during the course of its evolution. This curve predicts the combination of temperature and luminosity that a star will have during part or all of its lifetime.[5]
- Extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by matter (dust and gas) between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Atmospheric extinction varies by the wavelength of the radiation, with the attenuation being greater for blue light than for red.
F
- A field galaxy is a galaxy that does not belong to a larger cluster of galaxies, but is gravitationally alone.
- A field star is a randomly situated star that lies along the line of sight to a group of physically associated stars under study, such as a star cluster. These field stars can contaminate the results for a study and so they need to be identified.[6]
G
- Galactic tide is the tidal force experienced by objects subject to the gravitational field of a galaxy such as the Milky Way.
- Geometric albedo is the ratio of the brightness of an astronomical body at a phase angle of zero to an idealized flat, fully reflecting, diffusively scattering (Lambertian) disk with the same cross-section. It is a measure of how much of the incoming illumination is being scattered back toward an observer and has a value between zero and one.
H
- H II region is a luminous region of space that is emitting the spectrum of ionized hydrogen. It is generated by an interstellar cloud near a source of ultraviolet energy, such as hot, massive stars. Typically H II regions are found among areas of star formation in spiral galaxies.
I
- Inferior planet is an archaic term that is sometimes used to refer to the planets Mercury and Venus. The name originated from the fact that they orbit closer to the Sun than the Earth and hence, in the geocentric cosmology of Ptolemy, both appeared to travel with the Sun across the sky. This is in contrast to so-called superior planets, such as Mars, that appeared to move independently of the Sun.
- Interstellar medium is the matter that exists in the space between the stars in a galaxy. This medium mainly consists of hydrogen and helium, but it is enhanced by traces of other elements contributed by matter expelled from stars.
- Interstellar reddening is an effect produced by the incremental absorption and scattering of electromagnetic energy from interstellar matter, an effect known as extinction. This effect causes the more distant objects such as stars to appear redder and dimmer than expected. It is not to be confused with the separate phenomenon of red shift.
- Isochrones are curves on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram that represent the evolutionary positions of stars having the same age but differing masses. This is in contrast to an evolutionary track, which is a plot of stars having the same mass but differing ages. In fact, multiple evolutionary tracks can be used to build isochrones by putting curves through equal-age points along the tracks. When the mass of a star can be determined, an isochrone can be used to estimate the star's age.
J
- Jeans instability is a physical state in which an interstellar cloud of gas will begin to undergo collapse and form stars. A cloud can become unstable against collapse when it cools sufficiently or has perturbations of density, allowing gravity to overcome the gas pressure.
M
- Magnetosphere is a mostly convex region formed when a plasma, such as the solar wind, interacts with the magnetic field of a body, such as a planet or star.
- Main sequence is a category of stars that form a continuous and distinctive band on plots of stellar temperature versus brightness. These stars are characterized by being in hydrostatic equilibrium and undergoing nuclear fusion of hydrogen-1 in their core region. For example, the Sun is a main sequence star.
- Meteor is the ionization trail produced by a meteoroid as it enters the Earth's atmosphere.
- Meteoroid is a small rock or boulder that has entered a planetary atmosphere. If it survives to reach the ground, it is then termed a meteorite.
- Meteor shower is a series of meteors that seemingly radiate from a point on the night sky. These are produced by debris left over from a larger body, such as a comet, and hence they follow roughly the same orbit. This makes many meteor showers predictable events as they reoccur every year.
- Metallicity is the abundance of elements other than hydrogen and helium. Note that these 'metals' include elements that are not typically considered metallic.
- Microvariable is a stellar object such as a variable star that undergoes very small variations in luminosity. Detecting microvariability will typically require sufficient observations to rule out random error as a source.[7]
- Minor planet is an object in direct orbit around the Sun that is neither a dominant planet nor originally classified as a comet. A moon is not a minor planet because it is orbiting another body.
- Molecular clouds are interstellar clouds where the conditions allow molecules to form, including molecular hydrogen.
- Morning width or rise width is the horizontal angular distance between the rise azimuth of a celestial body and the East direction.
- Moving group or stellar association is a loose grouping of stars that are traveling together through space. Although the members were formed together in the same molecular cloud, they have since moved too far apart to be gravitationally bound as a cluster.
N
- Nebula refers to a region of indistinct nebulosity. In modern terms, it means an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Historically, it was also used to refer to extended sources of luminosity that could not be resolved into their individual components, such as star cluster and galaxies.
- Neutron star is a type of stellar remnant that is composed almost entirely of neutrons, which is a type of subatomic particle with no electrical charge. Typically, a neutron star has a mass between 1.35 and about 2.0 times the mass of the Sun, but with a radius of only 12 km (7.5 mi).
- Number density is the quantity of some specified particle or object class per unit volume. For atoms, molecules or subatomic particles, the volume is typically in cm−3 or m−3. With stars, cubic parsecs (pc−3) are often used.
O
- OB association is a group of massive stars that are not gravitationally bound to each other, but move together through space in a loose association. The OB in the name is a reference to stars of stellar classification O and B.
- Opacity is a measure of the resistance of a medium to the radiative transmission of energy. Within a star, it is an importance factor in determining whether convection occurs.
- Open cluster is a gravitationally-bound group of up to a thousand stars that formed together in the same molecular cloud.
- Opposition occurs when two celestial objects are on opposite sides of the sky. This occurs, for example, when a planet makes its closest approach to the Earth, placing it in opposition to the Sun.
- Orbital elements are parameters that uniquely define an orbit.
P
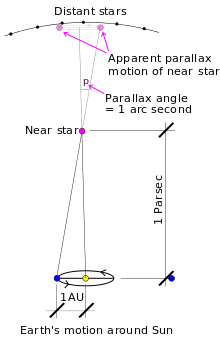
The parallax shift of a star at a distance of one parsec as seen from the Earth. Not to scale
- Parsec is a portmanteau of the words parallax and second. This is the distance at which a star would show a parallax shift of exactly one arcsecond as observed from Earth's orbit. It is equal to 3.2616 light years or 206,265 Astronomical Units.
- Periapsis is the point of closest approach between two orbiting objects.
- Phase angle is the elongation or angle between an orbiting body and the Sun as viewed from a particular perspective such as the Earth. It determines the amount of a planet or moon's visible surface that lies in shadow. Inferior planets such as Venus generally have a low phase angle as seen from Earth, so they are often viewed as a crescent. Superior planets such as Mars and Jupiter usually have a high phase angle, so little of the shadowed side is visible.
- Planetary differentiation is the process of separating out different constituents of a planetary body, causing it to develop compositionally distinct layers (such as a metallic core).
- Precession can refer to a slow change in the orientation of an object's axis of rotation. For the Earth, this is referred to as the precession of the equinoxes. Apsidal precession means a steady change in the orientation of an orbit, such as the precession in the orbit of Mercury that was explained by the theory of general relativity.
- Projected separation is the minimum physical separation of two astronomical objects, as determined from their angular separation and estimated distance.[8] For planets and double stars, this distance is usually given in Astronomical Units. The actual separation of the two objects depends on the angle of the line between the two objects to the line-of-sight of the observer.
- Proper motion is the rate of angular motion of an object over an interval of time, usually years. For stars, this is typically given in milliarcseconds per year.
- Protostar is a concentration of mass formed out of the contraction of a collapsing interstellar cloud. Once sufficient mass has fallen onto this central core, it becomes a pre-main-sequence star.
Q
- Quadratic field strength is a method of computing the mean strength of a varying stellar magnetic field. It is determined by taking the root mean square of a series of longitudinal magnetic field strength measurements taken at different time periods.[9]
R
- Radial velocity is the velocity of an object along the line of sight to the observer. Positive values are used to indicate a receding object. An object such as a star can undergo changes in its radial velocity because of the gravitational perturbation of another body, or because of radial pulsations of its surface. The latter, for example, occurs with a Beta Cephei variable star.
- Right ascension, in the equatorial coordinate system, is the celestial equivalent of terrestrial longitude. It divides the celestial equator into 24 hours, each of 60 minutes.
- Roche limit is the distance from an astronomical object where the tidal force matches an orbiting body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside this limit, the tidal forces will cause the orbiting body to disintegrate, usually to disperse and form a ring. Outside this limit, loose material will tend to coalesce.
- Rosseland optical depth (τR) is an extinction coefficient of an atmosphere, which describes the net opacity to radiation at a given depth. See optical depth.[10]
- Rotational modulation causes the luminosity of a star to vary as rotation carries star spots or other localized activity across the line of sight. Examples include RS CVn and BY Dra variables.[11]
S
- Semi-major axis is half the maximum length of an ellipse. It is used to give a physical dimension to a two-body Keplerian orbit, such as for a binary star system. However, when the distance to the system is unknown, the semi-major axis may be given as an angle.
- Spectroscopic binary is a type of binary star system where the individual components have not been resolved with a telescope. Instead, the evidence for the binarity comes from shifts observed in the spectrum. This is caused by the Doppler effect as the radial velocity of the components change over the course of each orbit.
- Starfield or star field refers to a set of stars visible in an arbitrarily-sized field of view of a telescope, usually in the context of some region of interest within the celestial sphere.
- Stellar atmosphere, or stellar envelope, is the outermost region of a star. Although it forms only a small portion of the star's mass, for some evolved stars the stellar envelope can form a significant fraction of the radius.
- Stellar classification is the categorization of stars based upon their spectrum. The modern MK spectral classification scheme is a two-dimensional classification based on temperature and luminosity.
- Superior planet is an archaic term that is sometimes used to refer to planets that orbit further from the Sun than the Earth, such as Saturn. The name originated from geocentric cosmology of Ptolemy.
- Synodic period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object, as calculated respect to the background stars.
- Syzygy is the straight-line configuration of three celestial bodies in a gravitational system.
T
- Telluric stars have nearly featureless continuum spectra that can be used to correct for the effect of telluric contamination of the Earth's atmosphere on the spectra of other stars. For example, water vapor in the atmosphere creates significant telluric absorption bands at wavelengths above 6800 Å. These features need to be corrected for in order to reach a more accurate spectrum.[12]
- Thin disk population refers to the layer of the Milky Way galaxy where the spiral arms are found and where most of the star formation takes place. It is about 300–400 parsecs (980–1,300 light-years) deep and centered on the galactic plane. Stars belonging to this population generally follow orbits that lie close to this plane.[13] This is in contrast to members of the thick disk population and halo stars.
- Tidal braking or tidal acceleration is the transfer of momentum between an astronomical body and an orbiting satellite as the result of tidal forces. This can cause changes in the rotation periods for both bodies as well as modification of their mutual orbit. A satellite in a prograde orbit will gradually recede from the primary body, while slowing the rotation rate of both bodies.
- Tidal locking is a net result of continued tidal braking wherein such that, over the course of an orbit, there is no net transfer of angular momentum between an astronomical body and its gravitational partner. When the orbital eccentricity is low, the result is that the satellite orbits with the same face always pointed toward its primary.[14] The Moon is tidally locked with the Earth.
- Tidal stream refers to the streams of stars and gas that are stripped from gas clouds and star clusters because of interaction with the gravitational field of a galaxy such as the Milky Way.[15]
- Tilt erosion is the gradual reduction of the obliquity of an orbiting satellite due to tidal interactions.[16]
- Transit is an astronomical event where an object passes across the face of a much larger body. An example of this event is the transit of Venus across the face of the Sun in 2004. Because a transit results in a decrease in the net luminosity from the two objects, the transit method is used to detect extrasolar planets as they pass in front of their host stars. Transits by objects that appear roughly the same size or larger than the body they are transiting are called occultations.
V
- Vernal equinox is the point in the year when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, while generally trending northward at each zenith passage. It represents the moment when the North Pole of the Earth begins to tilt toward the Sun.
W
- Weak-line star is a reference to the faintness of the spectral lines for a star compared to standard stars with the same stellar classification. Since most absorption lines are caused by elements other than hydrogen and helium—what astronomers refer to as "metals"—these are sometimes called metal weak stars.[17]
- White dwarf is a type of stellar remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf lacks the mass needed to continue the nuclear fusion process with its constituent atoms, so the object's energy output normally comes from radiative cooling. (But see nova and Type Ia supernova.)
Z
- Zenith is the point on the sky that is directly overhead, from the perspective of a particular location on the Earth.
See also
| For a list of words relating to astronomy, see the en:Astronomy category of words in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- List of astronomical catalogues
- List of astronomy acronyms
- List of common astronomy symbols
- List of glossaries
- Modern constellations
References
- ↑ Maeder, Andre (2008), Physics, Formation and Evolution of Rotating Stars, Astronomy and Astrophysics Library, Springer Science & Business Media, ISBN 3540769498.
- ↑ Noyes, R. W.; et al. (April 15, 1984), "Rotation, convection, and magnetic activity in lower main-sequence stars", Astrophysical Journal, Part 1, 279: 763–777, Bibcode:1984ApJ...279..763N, doi:10.1086/161945.
- ↑ Perryman, Michael (2009), Astronomical Applications of Astrometry: Ten Years of Exploitation of the Hipparcos Satellite Data, Cambridge University Press, p. 80, ISBN 0521514894.
- ↑ Silaj, J.; Jones, C. E.; Tycner, C.; Sigut, T. A. A.; Smith, A. D. (March 2010), "A Systematic Study of Hα Profiles of Be Stars", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement, 187 (1): 228−250, Bibcode:2010ApJS..187..228S, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/187/1/228
- ↑ Salaris, Maurizio; Cassisi, Santi (2005), Evolution of stars and stellar populations, John Wiley and Sons, p. 110, ISBN 0-470-09220-3, retrieved 2012-02-29
- ↑ Ridpath, Ian (2012), A Dictionary of Astronomy, OUP Oxford, p. 163, ISBN 0199609055, retrieved 2016-10-15.
- ↑ Rufener, F.; Bartholdi, P. (June 1982), "List of 333 variable, microvariable or suspected variable stars detected in the Geneva photometry", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, 48: 503−511, Bibcode:1982A&AS...48..503R.
- ↑ MacEvoy, Bruce; Tirion, Wil (2015), The Cambridge Double Star Atlas, Cambridge University Press, p. 4, ISBN 1107534208.
- ↑ Bychkov, V. D.; et al. (April 2009), "Catalogue of averaged stellar effective magnetic fields - II. Re-discussion of chemically peculiar A and B stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 394 (3): 1338–1350, Bibcode:2009MNRAS.394.1338B, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14227.x.
- ↑ Schrijver, C. J.; Zwaan, C. (2008), Solar and Stellar Magnetic Activity, Cambridge Astrophysics, 34, Cambridge University Press, p. 25, ISBN 1139425420.
- ↑ Rodono, M.; et al. (September 1986), "Rotational modulation and flares on RS CVn and BY Dra-type stars. I - Photometry and SPOT models for BY Dra, AU Mic, AR Lac, II Peg and V 711 Tau (= HR 1099)", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 165 (1−2): 135−156, Bibcode:1986A&A...165..135R.
- ↑ Husser, Tim-Oliver (2012), 3D-Spectroscopy of Dense Stellar Populations, Universitätsverlag Göttingen, pp. 54–59, ISBN 3863950925
- ↑ "Components of the Milky Way", Galaxies, Center for Computational Physics in Hawaii, retrieved 2012-02-27
- ↑ Barnes, Rory, ed. (2010), Formation and Evolution of Exoplanets, John Wiley & Sons, p. 248, ISBN 3527408967.
- ↑ Sanders, Jason (2015), Dynamics of the Milky Way: Tidal Streams and Extended Distribution Functions for the Galactic Disc, Springer Theses, Springer, p. 9, ISBN 3319187724.
- ↑ Heller, R.; et al. (April 2011), "Tidal obliquity evolution of potentially habitable planets", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 528: 16, Bibcode:2011A&A...528A..27H, arXiv:1101.2156
 , doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015809, A27.
, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015809, A27. - ↑ Jaschek, Carlos; Jaschek, Mercedes (1990), The Classification of Stars, Cambridge University Press, p. 257, ISBN 0-521-38996-8
External links
| Look up Appendix:List of astronomical terms in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- "Astronomical Glossary", A Knowledgebase for Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology, NASA/IPAC, January 10, 2006, retrieved 2012-02-19
- "ESO Astronomical Glossary", Public Outreach, European Southern Observatory, retrieved 2012-02-21
- "Glossary of (comet and) astronomical terms", International Comet Quarterly, Harvard University, retrieved 2012-02-20
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.