Micah 1
| Micah 1 | |
|---|---|
|
← Jonah 4 | |
|
In this Bible from about 1270, an initial V introduces the Old Testament book of Micah. The scene inside the letter illustrates the following text: "The word of the Lord that came to Micah the Morasthite . . ." The illuminator added details not mentioned in the text to his representation of the scene, showing the prophet Micah in bed while an angel, its hand raised in a gesture of speech, delivers the "word of the Lord" represented by a scroll. Although he appears in bed, it is clear that Micah is not dreaming; his eyes are open and he glances toward the angel at the side of the bed. | |
| Book | Book of Micah |
| Bible part | Old Testament |
| Order in the Bible part | 33 |
| Category | Nevi'im |
Micah 1 is the first chapter of the Book of Micah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible.[1][2] This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Micah, and is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.[3][4]
Text
- The original text is written in Hebrew language.
- This chapter is divided into 16 verses.
Textual versions
Some most ancient manuscripts containing this chapter in Hebrew language:
Ancient translations in Koine Greek:
- Septuagint (3rd century BC)
- Dead Sea Scrolls: (2nd century BC)[5]
- Naḥal Ḥever (8ḤevXIIgr): extant: verses 1-8[5]
- Theodotion version (~AD 180)
Structure
NKJV groups this chapter into:
- Micah 1:1 = Title
- Micah 1:2-7 = The Coming Judgment on Israel
- Micah 1:8-16 = Mourning for Israel and Judah
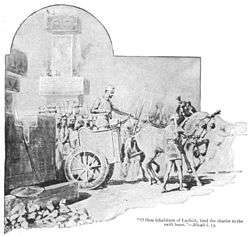
An illustration of Micah 1:13: "O thou inhabitant of Lachish, bind the chariot to the swift beast." (www.ordination.org).
Verse 1
- The word of the Lord that came to Micah the Morasthite
- in the days of Jotham, Ahaz, and Hezekiah, kings of Judah,
- which he saw concerning Samaria and Jerusalem.[7]
- The inscription, or heading of the book, conveying the prophet's authority. The word of the Lord. The expression applies to the whole contents of the book, as in Hosea 1:1 and Zephaniah 1:1. It is often used for some particular message to a prophet, as Jeremiah 1:4, 11; Jeremiah 2:1; Ezekiel 3:16.[8]
- "Micah the Morasthite"; i.e. Micah of Moresheth-Gath (verse 14), a village in the lowland of Judaea, near Eleutheropolis,[9] some twenty miles southwest of Jerusalem,[8] on the border of the Philistine country; so called to distinguish it from Moresheth of Judah.[10] Micah omits all mention of his father. His great predecessor was known as Micaiah son of Imlah. Micah, a villager, would be known only by the name of his native village.[11]
- "Jotham": It is not said what year of Jotham this prophet begun, it is probable it was about the beginning of Jotham's reign, A.M. 3190, of which we have this character, 2 Kings 15:34,35, He did right, &c., yet the high places were not removed. Religion was not wholly corrupted as in Israel, yet was it exceedingly abased with their own mixtures.[10]
- "Kings of Judah": Micah dates his prophetic office from kings of Judah only, as the only kings of the line appointed by God. Kings of Israel are mentioned in addition, only by prophets of Israel. He names Samaria first, because, its iniquity being most nearly full, its punishment was the nearest.[11]
- "Samaria and Jerusalem": in the vision of prophecy; Samaria was the metropolis of the ten tribes of Israel, and is put for them all; as Jerusalem was of the tribes of Judah and Benjamin, and is put for them Samaria is mentioned first, because it was the head of the greatest body of people; and as it was the first in transgression, it was the first in punishment.[12]
See also
- Related Bible parts: 1 Kings 22, Isaiah 1, Jeremiah 26, Hosea 1
Notes and references
- ↑ Collins 2014.
- ↑ Hayes 2015.
- ↑ Metzger, Bruce M., et al. The Oxford Companion to the Bible. New York: Oxford University Press, 1993.
- ↑ Keck, Leander E. 1996. The New Interpreter's Bible: Volume: VII. Nashville: Abingdon.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dead sea scrolls - Micah
- ↑ Timothy A. J. Jull; Douglas J. Donahue; Magen Broshi; Emanuel Tov (1995). "Radiocarbon Dating of Scrolls and Linen Fragments from the Judean Desert". Radiocarbon. 38 (1): 14. Retrieved 26 November 2014.
- ↑ Micah 1:1
- 1 2 Joseph S. Exell; Henry Donald Maurice Spence-Jones (Editors). The Pulpit Commentary. 23 volumes. First publication: 1890.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Jerome. Prolog. in Mic.
- 1 2 Robert Jamieson, Andrew Robert Fausset; David Brown. Jamieson, Fausset, and Brown's Commentary On the Whole Bible. 1871.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 Barnes, Albert. Notes on the Old Testament. London, Blackie & Son, 1884. Reprint, Grand Rapids: Baker Books, 1998.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ John Gill. John Gill's Exposition of the Entire Bible. Exposition of the Old and New Testament. Published in 1746-1763.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
Bibliography
- Collins, John J. (2014). Introduction to the Hebrew Scriptures. Fortress Press.
- Hayes, Christine (2015). Introduction to the Bible. Yale University Press.
External links
Jewish
Christian
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
