5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-[4-(3-amino-1-oxo-1,4,5,6,6a,7-hexahydroimidazo[1,5-f]pteridin-8(9H)-yl)benzoyl]-L-glutamic acid | |
| Other names
5,10-CH2-THF, MTHF | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H23N7O6 | |
| Molar mass | 457.44 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
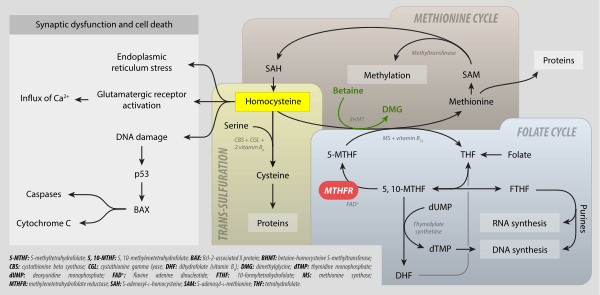
5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (N5,N10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-CH2-THF) is the substrate used by the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR)[1][2] to generate 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF, or levomefolic acid).
The diastereoisomer [6R]-5,10-methylene-THF is the key endogenous one-carbon donor and a co-substrate of the TS (thymidylate synthase) enzyme for methylation of 2-deoxy-uridine-5-monophosphate (dUMP) to 2-deoxy-thymidine-5-monophosphate (dTMP). The coenzyme is necessary for the biosynthesis of thymidine and is the C1-donor in the reactions catalyzed by TS and thymidylate synthase (FAD).
[6R]-5,10-methylene-THF is a biomodulator that has proven to enhance the desired cytotoxic antitumor effect of Fluorouracil (5-FU) and can bypass the metabolic pathway required by other folates (such as leucovorin) to achieve necessary activation.[3] The active metabolite is being evaluated in clinical trials for patients with colorectal cancer in combination with 5-FU.
It also acts as a cofactor in the synthesis of serine from glycine via the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
See also
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NAD(P)H)".
- ↑ Födinger M, Hörl WH, Sunder-Plassmann G (2000). "Molecular biology of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase.". J Nephrol. 13 (1): 20–33. PMID 10720211.
- ↑ Danenberg, Peter V.; Gustavsson, Bengt; Johnston, Patrick; Lindberg, Per; Moser, Rudolf; Odin, Elisabeth; Peters, Godefridus J.; Petrelli, Nicholas (2016-10-01). "Folates as adjuvants to anticancer agents: Chemical rationale and mechanism of action". Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 106: 118–131. ISSN 1879-0461. PMID 27637357. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.08.001.