Methyl yellow
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
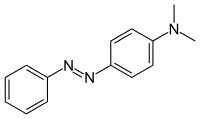
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dimethyl-4-(phenyldiazenyl)aniline | |
| Other names
4-Dimethylaminoazobenzene p-Dimethylaminoazobenzene DAB N,N-Dimethyl-4-phenylazoaniline N,N-Dimethyl-4-aminoazobenzene Butter Yellow Solvent Yellow 2 C.I. 11020 | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.414 |
| EC Number | 200-455-7 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | BX7350000 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H15N3 | |
| Molar mass | 225.30 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow crystals |
| Melting point | 111–116 °C (232–241 °F; 384–389 K) decomposes[1] |
| 13.6 mg/l | |
| log P | 4.58 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Carcinogen[2] |
| GHS pictograms |   [1] [1] |
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H301, H351[1] | |
| P281, P301+310[1] | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
OSHA-regulated carcinogen[2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
Ca[2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [N.D.][2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Methyl yellow, or C.I. 11020, is a organic compound with the formula C6H5N2C6H4N(CH3)2. It is an azo dye derived from dimethylaniline. It is a yellow solid. According to X-ray crystallography, the C14N3 core of the molecule is planar.[3]
It is used as a dye for plastics may be used as a pH indicator.
| Methyl yellow (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 2.9 | above pH 4.0 | |
| 2.9 | ⇌ | 4.0 |
In aqueous solution at low pH, methyl yellow appears red. Between pH 2.9 and 4.0, methyl yellow undergoes a transition, to become yellow above pH 4.0.
Safety
It is a possible carcinogen.[2] As "butter yellow", the agent had been used as a food additive before its toxicity was recognized.[4]
See also
Structurally similar compounds:
References
- 1 2 3 4 Dimethyl yellow
- 1 2 3 4 5 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0220". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ A. Whitaker (1992). "Crystal and molecular structure of C.I. Solvent Yellow 2, 1-Phenylazo-4 (N,N-dimethylamine)-phenyl". Journal of Crystallographic and Spectroscopic Research. 22: 151–155. doi:10.1107/S0108270188006791.
- ↑ Opie, E. L. (1944). "The Pathogenesis of Tumors of the Liver Produced by Butter Yellow" (pdf). The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 80 (3): 231–246. PMC 2135460
 . PMID 19871411. doi:10.1084/jem.80.3.231.
. PMID 19871411. doi:10.1084/jem.80.3.231.
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 1498
- "para-dimethylaminoazobenzene". Inchem.
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Chung, K. T.; Fulk, G. E.; Andrews, A. W. (1981). "Mutagenicity testing of some commonly used dyes" (pdf). Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 42 (4): 641–648. PMC 244076
 . PMID 7039509.
. PMID 7039509.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
