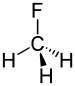
Fluoromethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Fluoromethane | |||
| Other names
Freon 41 Methyl fluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | R41 | ||
| 1730725 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.907 | ||
| EC Number | 209-796-6 | ||
| 391 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Fluoromethane | ||
| PubChem CID |
|||
| UN number | UN 2454 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3F | |||
| Molar mass | 34.03 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, odorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.4397 g/L 0.557 g/cm3 (liquid) at saturation pressure at 25 °C | ||
| Melting point | −137.8 °C (−216.0 °F; 135.3 K) [1] | ||
| Boiling point | −78.4 °C (−109.1 °F; 194.8 K) [1] | ||
| 1.66 L/kg (2.295 g/L) | |||
| Vapor pressure | 3.3 MPa | ||
| Hazards | |||
| EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
| ||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R12 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S9, S16, S23, S24/25, S26, S28, S33, S36/37/39, S60 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is made of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. The name stems from the fact that it is methane (CH4) with a fluorine atom substituted for one of the hydrogen atoms.
The compound is the lowest mass member of the hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) family, compounds which contain only hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon. These are related to the Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)s, but since they do not contain chlorine, are not destructive to the ozone layer.[2]
It is used in the manufacture of semiconductor and electronic products. In the presence of an RF field fluoromethane will dissociate into fluoride ions that selectively etch silicon compound films (reactive-ion etching).
Fluoromethane has an agreeable ether-like odor and is also narcotic in high concentrations. Fluoromethane is highly flammable and burns in air with evolution of highly toxic hydrogen fluoride. The flame is colorless, similar to alcohol.
The C-F bond energy is 552 kJ/mol and its length is 0.139 nm (typically 0.14 nm). Its molecular geometry is tetrahedral.
Its specific heat capacity (Cp) is 38.171 J·mol−1·K−1 at 25 °C. The critical point of fluoromethane is at 44.9 °C (318.1 K) and 6.280 MPa.
References
- 1 2 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ Fluoromethane CH3F
See also
External links
- MSDS at Chemblink.com
- Data at Airliquide Encyclopedia
- Thermochemical data at chemnet.ru
- CAS DataBase List METHYL FLUORIDE at ChemicalBook