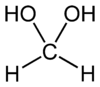
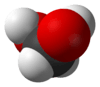
Methanediol
| |||
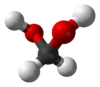 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methanediol[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | MADOL | ||
| 1730798 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.673 | ||
| EC Number | 207-339-5 | ||
| PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 48.04 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.199 g cm−3 | ||
| Boiling point | 194 °C (381 °F; 467 K) at 101 kPa | ||
| Vapor pressure | 16.1 Pa | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.29[2] | ||
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.401 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 99.753 °C (211.555 °F; 372.903 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest geminal diol, and formally the second simplest carbohydrate (after formaldehyde).
Methanediol is a product of the hydration of formaldehyde H2C=O, and predominates in water solution: the equilibrium constant being about 103,[3] and in a 5% by weight solution of formaldehyde in water, 80% is in the methanediol form.
The compound is of some relevance to astrochemistry.[4]
Methanediol is listed as one of the main ingredients of "Brazilian blowout", a hair-straightening formula marketed in the US.[5] The equilibrium with formaldehyde may cause some concern as formaldehyde in hair straighteners is a health hazard.[6] However the assumption of chemical and toxicological equivalence between formaldehyde (a reactive gas) and methylene glycol (a stable reaction product that forms in an aqueous solution forming the main portion of formalin preparations) is disputed as a conservative assumption (mostly due to the methods of testing that are unable to differentiate the forms) instead of based on empirical toxicological data. According to Golden and Valentini the use of hair products containing less than 3% methelene glycol under controlled conditions should be considered safe from formaldehyde dangers.[7]
See also
- Orthoformic acid (methanetriol)
- Orthocarbonic acid (methanetetrol)
References
- ↑ "Methanediol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
- ↑ Bell, R. P.; McTigue, P. T. (1960). "603. Kinetics of the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2983. doi:10.1039/JR9600002983.
- ↑ Eric V. Anslyn, Dennis A. Dougherty (2006), Modern physical organic chemistry. University Science Books. ISBN 1-891389-31-9. 1095 pages
- ↑ A theoretical study of the conversion of gas phase methanediol to formaldehyde Kent DR, Widicus SL, Blake GA, Goddard WA The Journal of Chemical Physics -- September 8, 2003 -- Volume 119, Issue 10, pp. 5117-5120 doi:10.1063/1.1596392
- ↑ "Brazilian blowout on natural hair". 2017-02-22. Retrieved 2017-03-14.
- ↑ https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/formaldehyde/hazard_alert.html
- ↑ Golden, R.; Valentini, M. (July 2014). "Formaldehyde and methylene glycol equivalence: Critical assessment of chemical and toxicological aspects". Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 69 (2): 178–186. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.03.007. Retrieved 25 May 2017.