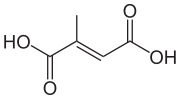
Mesaconic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2E)-2-Methyl-2-butenedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.146 |
| EC Number | 207-859-2 |
| KEGG | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 130.10 g/mol |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 204 to 205 °C (399 to 401 °F; 477 to 478 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (decomposes) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Mesaconic acid is one of several isomeric carboxylic acids obtained from citric acid. It is the trans-isomer of citraconic acid. It is used as a fire retardant.
History
This acid was studied for the first time by Dutch chemist Jacobus H. van 't Hoff in 1874. Later American biochemist Horace Albert Barker and his team successfully isolated this acid from fermenting bacterium Clostridium tetanomorphum in 1950s. Further studies led him to discover this organic compound was involved in vitamin B12 coenzymes synthesis.
Recent studies revealed this acid is a competitive inhibitor of fumarate reduction.
References
- "Mesaconic acid". Mesaconic acid. Archived from the original on November 17, 2005. Retrieved September 8, 2005.
- "Barker, Horace Albert". The Stadtman Way: The Story of Two Biochemists at NIH. Office of NIH History. Retrieved December 21, 2011.
- Switzer, Robert L.; Stadtman, Earl R.; Stadtman, Thressa C. (2004). "H.A. Barker". Biographical Memoirs. National Academies Press. 84: 3–22. Retrieved December 21, 2011.
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5806.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.