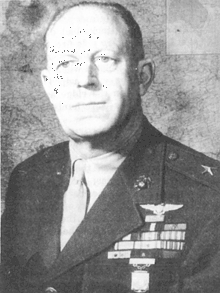
Merritt A. Edson
| Merritt Austin Edson | |
|---|---|
  "Red Mike" Edson | |
| Nickname(s) | Red Mike |
| Born |
April 25, 1897 Chester, Vermont |
| Died |
August 14, 1955 (aged 58) Washington, D.C. |
| Place of burial | Arlington National Cemetery |
| Allegiance |
|
| Service/branch |
|
| Years of service |
1917–1947 |
| Unit |
4th Marine Regiment 2nd Marine Division |
| Commands held |
1st Marine Raider Battalion 5th Marine Regiment |
| Battles/wars | |
| Awards |
Medal of Honor Navy Cross (2) Silver Star Legion of Merit (2) Distinguished Service Order (United Kingdom) |
| Other work |
Commissioner of the Vermont State Police Executive Director of the National Rifle Association |
Major General Merritt Austin Edson (April 25, 1897 – August 14, 1955), known as "Red Mike", was a general in the United States Marine Corps. Among the decorations he received were the Medal of Honor, two Navy Crosses, the Silver Star, and two Legions of Merit. He is best known by Marines for the defense of Lunga Ridge during the Guadalcanal Campaign in World War II.
He received a commission as a second lieutenant in the Marines in October 1917, and served in France and Germany in World War I. After the war he held several positions until going to flight school in 1922. After graduating flight school and being designated a Naval Aviator, he performed several assignments in Central America and China. It was in Central America where he received his first Navy Cross and the Nicaraguan Medal of Merit with Silver Star.
When World War II started Edson was sent as the Commanding officer of the Marine Raiders and earned his second Navy Cross on Tulagi. When his unit was sent to fight on Guadalcanal, Edson led his men in fighting for which he would later receive the Medal of Honor.
After World War II Edson held several commands until retiring from the Marine Corps August 1, 1947. After retirement he had several jobs including the Director of the National Rifle Association.
Early years
Edson was born in Rutland, Vermont but grew up in Chester, Vermont and after graduating from high school he attended the University of Vermont for two years. On June 27, 1916 he left college as a member of the First Vermont National Guard Regiment and was sent to Eagle Pass, Texas, for duty on the Mexican border. He returned to the University in September 1916, but joined the Marine Corps Reserve on June 26, the following year.[1]
Early career
He was commissioned a second lieutenant in the Marine Corps on October 9, 1917[1] and in September of the next year he sailed for France with the 11th Marines. This regiment saw no combat, but during the last six months of his European tour, he commanded Company D, 15th Separate Marine Battalion, which had been organized for the express purpose of assisting in the holding of a plebiscite in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Owing to the failure of the United States to ratify the Treaty of Versailles, this mission, however, was never carried out.[1]
Following the end of World War I, he was assigned to several positions that would qualify him for the high commands he was to hold in later years. He was promoted to first lieutenant on June 4, 1920 and spent two years at Marine Barracks, Quantico, Virginia, as the Adjutant-Registrar of the Marine Corps Institute, after which he was sent on a short tour in Louisiana guarding the mail.[1] His interest in military aviation prompted him to apply for flight training at NAS Pensacola, Florida and he earned his gold wings as a Naval Aviator in 1922. Soon after, he was ordered to the Marine Air Station at Guam where he had his introduction to the semitropical islands of the Marianas with which his name was later to become so closely linked.[1]
Upon returning to the United States in 1925, he first took an extensive course in advanced aviation tactics with the U.S. Army Air Service at Kelly Field, Texas, and then attended the Company Officers' Course at Marine Corps Base Quantico, Virginia. He graduated with the highest grades ever attained by any student up to that time. For physical reasons, however, he had to give up his flying status in 1927 and continue his career as a ground officer. He was then assigned to duty as Ordnance Officer at the Philadelphia Navy Yard.[1]
Central America and China
Late in the same year, he was ordered to sea duty as Commanding Officer of the Marine Detachment on the USS Denver (CL-16) and was promoted to captain on December 21, 1927. During service in Central American waters, his detachment was ashore in Nicaragua during the period February 1928 - 1929. In command of 160 hand picked and specially trained Marines, he fought twelve separate engagements with the Sandino-led bandits and denied them the use of the Poteca and Coco River valleys. Here, he received his first Navy Cross for actions in which "his exhibition of coolness, intrepidity, and dash so inspired his men that superior forces of bandits were driven from their prepared positions and severe losses inflicted upon them." From a grateful Nicaraguan government, he was also awarded the Nicaraguan Medal of Merit with Silver Star.[1]
In September 1929, he returned to the United States and was assigned as tactics instructor to fledgling Marine lieutenants at The Basic School in Philadelphia. Upon detachment from that duty, he became Ordnance and War Plans Officer at the Philadelphia Depot of Supplies for the next four years.[1]
This ordnance duty was not new to him since he had been closely associated with the development of small arms marksmanship within the Marine Corps. In 1921, he had been a firing member of the winning Marine Corps Team at the National Matches at Camp Perry, Ohio. In 1927, 1930, and 1931, he served with the rifle and pistol teams as assistant coach. During the regional matches of 1932 and 1933, he acted as team coach and captain, respectively. Upon the resumption of the National Matches in 1935, he was captain of the Marine Corps national rifle and pistol teams of 1935 and 1936, winning the national trophies in both years.[1]
After short tours at Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island and Marine Corps Headquarters in Washington, D.C., he was enrolled in the Senior Officers' Course at the Marine Corps Schools, Quantico, Virginia in 1936. He was promoted to major on February 9, 1936. Foreign duty as operations officer with the 4th Marines in Shanghai, China from 1937 to 1939, enabled him to observe closely Japanese military operations.[1]
His second tour of duty at Marine Corps Headquarters began in May 1939 when, as Inspector of Target Practice, he was in a position to stress the importance of every Marine being highly skilled with his own individual arm. He was promoted to lieutenant colonel on April 1, 1940.[1]
World War II
Raider Battalion
In June 1941, he was again transferred to Quantico, to command the 1st Battalion, 5th Marines, which was redesignated the 1st Separate Battalion in January 1942. The training exercises which he conducted in the succeeding months with Navy high speed transports (APDs) led to the organization of the 1st Marine Raider Battalion in early 1942. This unit was the prototype of every Marine Raider battalion formed throughout the war. He was promoted to colonel on May 21, 1942.[1]

Colonel Edson's introduction to the Pacific theater of operations began with the overseas training of his raider command in American Samoa. On August 7, 1942, his raiders, together with the 2nd Battalion, 5th Marines, landed on Tulagi, British Solomon Islands. Two days of severe fighting secured this strategic island in the Battle of Tulagi. After his battalion relocated to Guadalcanal they conducted raids on Savo Island and at Tasimboko, on Guadalcanal. He was awarded a Gold Star in lieu of a second Navy Cross for his successful conduct of the Tulagi operation.[1]
Guadalcanal
The battle he is best known for was the defense of Lunga Ridge on Guadalcanal September 13–14, 1942. His Raider Battalion, with two companies of the 1st Parachute Battalion attached, were sent to a ridge line a short distance south of Henderson Field. Here, they were supposed to get a short rest but Japanese forces unexpectedly attacked the position on the first evening, penetrating the left center of his line of resistance, forcing a withdrawal to a reserve position.[1]
Approximately 800 Marines withstood the repeated assaults of more than 2,500 Japanese on the "Bloody Ridge", as it came to be called.[1] To the men of the 1st Raider Battalion, however, who sustained 256 casualties, it became "Edson's Ridge",[1] in high honor of the officer who "was all over the place, encouraging, cajoling, and correcting as he continually exposed himself to enemy fire."[1] His nickname, "Red Mike", originating from his red beard worn in Nicaragua days, was also his code name during this battle. From then on he was known by all as "Red Mike".[1] It was for this action—the Battle of Edson's Ridge—that he received the Medal of Honor.[1]
After Edson's Ridge, he was placed in command of the 5th Marine Regiment. In this capacity, he was one of the primary leaders in the Matanikau actions from September 23 to October 9, 1942. He also commanded the 5th Marines during the Battle for Henderson Field and until the regiment was withdrawn from Guadalcanal, along with the rest of the 1st Marine Division, in November 1942.[1] Shortly after, another officer stated "that officers and men would willingly follow him anywhere—the only problem was to keep up with him".[1] A combat correspondent testified that "he is not a fierce Marine. In fact he appears almost shy. Yet Colonel Edson is probably among the five finest combat commanders in all the United States armed forces."[1] It was also said that he was not readily given to a show of emotion but when his personal runner of several months' service was killed at the Matanikau River on Guadalcanal, witnesses said he "cried like a baby",[1] and later stated that the man could never be replaced.[1]
Higher commands & more battles

In August 1943, he was named Chief of Staff of the 2nd Marine Division, which was then preparing for the invasion of Tarawa. He prepared an estimate of the situation for this operation which proved to be surprisingly accurate and has since become a classic in Marine Corps military literature. For this action, he received the Legion of Merit and was promoted to brigadier general (December 1, 1943). Later, he was appointed Assistant Division Commander of the 2d Marine Division and participated in this capacity in the capture of Saipan and Tinian. The Silver Star was awarded him for these operations.[1]
Brigadier General Edson became Chief of Staff, Fleet Marine Force, Pacific and in October 1944 was awarded a Gold Star in lieu of a second Legion of Merit. Duty as Commanding General, Service Command, Fleet Marine Force, Pacific, rounded out 44 months of continuous service in the war zone. When a young officer asked him when he might expect to be rotated back to the United States, BGen Edson replied, "When the war's over; when the job's done."[1]
Retirement
In December 1945, he was assigned to the Office of the Chief of Naval Operations and, in February 1947, to Marine Corps Headquarters. Retirement from active duty came at the age of 50 years and after more than 30 years in the military service of his country. He was promoted to major general at the time of his retirement on August 1, 1947.[1]
Following retirement from the Marine Corps he became the first Commissioner of the Vermont State Police, organizing the force partially from an older organization of motor vehicle officers. He established the organization on a semi-military basis which has since been adopted by other states.[1] He served as president of the National Rifle Association 1949–1950.[2]
In July 1951, after returning to Washington, D.C. he became Executive Director of the National Rifle Association where his major efforts in that post were stimulating the interest of Americans in rifle marksmanship. Concurrently, he campaigned vigorously for a Marine Corps adequate both in size and strength for its many commitments.[1]
He died on August 14, 1955, in Washington, D.C., by his own hand, having committed suicide by carbon monoxide poisoning in the garage next to his Washington, D.C. home while serving in the NRA post.[3][4][5] At the time of his death, in addition to his duties at the Rifle Association, he was the Navy representative on the Defense Advisory Committee on Prisoner of War Problems. This group recommended the standards of conduct for American prisoners of war that were later adopted and issued as the Code of Conduct for all American servicemen.[1]
He was buried at Arlington National Cemetery.
Awards
Major General Edson's decorations included:[1]
 | |||
| Naval Aviator Badge | ||||||||||||
| 1st row | Medal of Honor | Navy Cross w/ 1 award star | Silver Star | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd row | Legion of Merit w/ 1 award star | Navy Presidential Unit Citation w/ 2 service stars | Mexican Service Medal | World War I Victory Medal w/ Maltese cross | ||||||||
| 3rd row | Nicaraguan Campaign Medal (1933) | China Service Medal w/ 1 service star | American Defense Service Medal w/ Fleet clasp | American Campaign Medal | ||||||||
| 4th row | Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal w/ 4 service stars | World War II Victory Medal | Distinguished Service Order | Nicaraguan Presidential Medal of Merit with star | ||||||||
Medal of Honor citation
The President of the United States takes pleasure in presenting the MEDAL OF HONOR to
COLONEL MERRITT A. EDSON
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS
for service as set forth in the following CITATION:
- For extraordinary heroism and conspicuous intrepidity above and beyond the call of duty as Commanding Officer of the 1st Marine Raider Battalion, with Parachute Battalion attached, during action against enemy Japanese forces in the Solomon Islands on the night of 13–14 September 1942. After the airfield on Guadalcanal had been seized from the enemy on August 8, Col. Edson, with a force of 800 men, was assigned to the occupation and defense of a ridge dominating the jungle on either side of the airport. Facing a formidable Japanese attack which, augmented by infiltration, had crashed through our front lines, he, by skillful handling of his troops, successfully withdrew his forward units to a reserve line with minimum casualties. When the enemy, in a subsequent series of violent assaults, engaged our force in desperate hand-to-hand combat with bayonets, rifles, pistols, grenades, and knives, Col. Edson, although continuously exposed to hostile fire throughout the night, personally directed defense of the reserve position against a fanatical foe of greatly superior numbers. By his astute leadership and gallant devotion to duty, he enabled his men, despite severe losses, to cling tenaciously to their position on the vital ridge, thereby retaining command not only of the Guadalcanal airfield, but also of the 1st Division's entire offensive installations in the surrounding area.
First Navy Cross citation
Citation:
The Navy Cross is presented to Merritt Austin Edson, Captain, U.S. Marine Corps, for extraordinary heroism on August 7, 1928, while in command of a Marine patrol on the Coco River, en route to Poteca. Captain Edson upon encountering a force of bandits entrenched upon both sides of the river, personally led his advance guard against the enemy, engaging in hand-to-hand conflict with them, and by his exhibition of coolness, intrepidity, and dash, so inspired his men that the superior force of bandits were driven from their prepared position, and severe losses inflicted upon them.[7]
Second Navy Cross citation
Citation:
The President of the United States takes pleasure in presenting a Gold Star in lieu of a Second Award of the Navy Cross to Merritt Austin Edson (0-257), Colonel, U.S. Marine Corps, for extraordinary heroism and devotion to duty while serving as Commanding Officer of the Tulagi Combat Group during the landing assault and seizure of enemy Japanese-held Tulagi Island, British Solomon Islands, 7 to August 9, 1942. In personal command of the FIRST Marine Raider Battalion during the initial operation, Colonel Edson advanced the attack of his Battalion and its supporting units with such skill, courage and aggressiveness that he was an inspiration to the entire Combat Group and was directly responsible for the capture of Tulagi Island. His gallant conduct throughout this hazardous action was in keeping with the highest traditions of the United States Naval Service.[7]
Other honors


In addition to the Medal of Honor and his other military awards, Edson also received several marksmanship awards including the Distinguished Rifleman Badge in 1927.
Edson Range
A part of Camp Pendleton’s Stuart Mesa area was named Edson Range in his honor in 1964. Edson range was built to replace the one at Camp Matthews in La Jolla. The range is used for teaching marksmanship training to recruits from Marine Corps Recruit Depot San Diego. On October 28, 2008 more than 200 volunteers unveiled a monument in honor of Major General Edson during a ceremony at Edson Range. The volunteers used rocks and recycled [ammunition] stripper clips and brass shells from throughout Edson Range in the cement when making the monument.[8]
USS Edson (DD-946)
The USS Edson (DD-946) was a Forrest Sherman-class destroyer of the United States Navy. The Edson was laid down December 3, 1956 by Bath Iron Works Corporation, Bath, Maine and launched January 4, 1958. The ship was sponsored by Mrs. M. A. Edson, widow of General Edson. It was commissioned November 7, 1958, with Commander Thomas J. Moriarty in command.[9]
Edson Hall
Edson hall, the location of the Communications School at Marine Corps Base Quantico in Virginia, is dedicated to Edson as a result of his role as a vocal proponent of the criticality of communications in combat.[10]See also
- List of Medal of Honor recipients for World War II
- List of military figures by nickname
- List of people from Vermont
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "Major General Merritt Austin Edson, USMC". Who's Who in Marine Corps History. History Division, United States Marine Corps. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
- ↑ Rodengen, Jeffrey L. (2002). NRA: An American Legend. Fort Lauderdale, Florida: Write Stuff Enterprises, Inc. 304 pp. ISBN 0-945903-81-2. ("The Presidents of NRA", p. 276).
- ↑ Hoffman, Jon T. 2000, p. 411-12
- ↑ Ronald J. Owens. Medal of Honor: Historical Facts & Figures. Turner Publishing Company, 2004. page 122.
- ↑ http://www.arlingtoncemetery.net/maedson.htm
- ↑ "Medal of Honor — Col. Merritt A. Edson (Medal of Honor citation)". Marines Awarded the Medal of Honor. History Division, United States Marine Corps. Archived from the original on March 5, 2007.
- 1 2 "Merritt Austin Edson, Major General, United States Marine Corps". Medal of Honor recipients buried at Arlington National Cemetery. Arlington National Cemeter.net. Retrieved June 16, 2009.
- ↑ Lance Corporal Michael Atchue (October 25, 2008). "Local non-profit dedicates monument in honor of Marine Corps Maj. Gen Merrit 'Red Mike' Edson". United States Marine Corps. Archived from the original on May 19, 2009. Retrieved July 19, 2009. Camp Pendelton News Article Archived 2014-03-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Delgado, James P. (January 8, 1990). "National Register of Historic Places Registration" (PDF). USS Edson (DD-946). National Park Service.
- ↑ "History of Communications School". United States Marine Corps. Retrieved February 18, 2010.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Marine Corps.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Marine Corps.- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
- Hoffman, Jon T. (2001). Once a Legend: Red Mike Edson of the Marine Raiders. Presidio Press. ISBN 0-89141-732-X.
External links
- "Merritt A. Edson". Hall of Valor. Military Times. Retrieved February 18, 2010.