Meralgia paraesthetica
| Meralgia paresthetica | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Innervation of lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh (shaded area) on right leg. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| ICD-10 | G57.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 355.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 31968 |
| eMedicine | neuro/590 orthoped/416, pmr/76 |
| Patient UK | Meralgia paraesthetica |
Meralgia paresthetica or meralgia paraesthetica (or Bernhardt-Roth syndrome[1]), is numbness or pain in the outer thigh not caused by injury to the thigh, but by injury to a nerve that extends from the spinal column to the thigh.
This chronic neurological disorder involves a single nerve—the lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh, which is also called the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (and hence the syndrome lateral femoral cutaneous neuropathy).[2] The term "meralgia paraesthetica" combines four Greek roots to mean "thigh pain with anomalous perception". The disorder has also been nicknamed skinny pants syndrome[3], in reference to a rise in teenagers wearing skin-tight pants.
Signs and symptoms
- Pain on the outer side of the thigh, occasionally extending to the outer side of the knee, usually constant.
- A burning sensation, tingling, or numbness in the same area
- Multiple bee-sting like pains in the affected area
- Occasionally, aching in the groin area or pain spreading across the buttocks
- Usually more sensitive to light touch than to firm pressure
- Hyper sensitivity to heat (warm water from shower feels like it is burning the area)
- Occasionally, patients may complain of itching or a bothersome sensation rather than pain in the affected area.
The entire distribution of the nerve is rarely affected. Usually, the unpleasant sensation(s) affect only part of the skin supplied by the nerve.
Cause
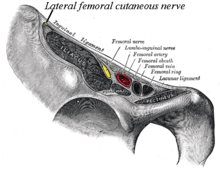
The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve most often becomes injured by entrapment or compression where it passes between the upper front hip bone (ilium) and the inguinal ligament near the attachment at the anterior superior iliac spine (the upper point of the hip bone). Less commonly, the nerve may be entrapped by other anatomical or abnormal structures, or damaged by diabetic or other neuropathy or trauma such as from seat belt injury in an accident.
The nerve may become painful over a period of time as weight gain makes underwear, belting or the waistband of pants gradually exert higher levels of pressure. Pain may be acute and radiate into the rib cage, and into the groin, thigh, and knee. Alternately, weight loss or aging may remove protective fat layers under the skin, so the nerve can compress against underwear, outer clothing, and—most commonly— by belting. Long periods of standing or leg exercise that increases tension on the inguinal ligament may also cause pressure.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is largely based on patient description and relevant details about recent surgeries, hip injuries, or repetitive activities that could irritate the nerve. Examination checks for sensory differences between the affected leg and the other leg. Accurate diagnosis may require an abdominal and pelvic examination to exclude problems in those areas.
Electromyographic (EMG) nerve-conduction studies may be required. X-rays may be needed to exclude bone abnormalities that might put pressure on the nerve; likewise CT or MRI scans to exclude soft tissue causes such as a tumor.
Treatment
Treatment varies. In most cases, the best treatment is to remove the cause of compression by modifying patient behavior, in combination with medical treatment to relieve inflammation and pain. Whatever the cause, typical treatment takes several weeks to months—depending on the degree of nerve damage. Typical treatment options include:
- Active Release Technique (ART) soft tissue treatment
- Wearing looser clothing and suspenders rather than belts
- Weight loss if obesity is present
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammatory pain if pain level limits motion and prevents sleep
- Reducing physical activity in relation to pain level. Acute pain may require absolute bed rest
- Deep tissue massage to reduce tension in the gluteal muscles, most commonly the gluteus maximus. The tensor fasciae latae may also be implicated.
The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh can occasionally be damaged during laparoscopic hernia repair, or scarring from the operation can lead to meralgia paraesthetica.[4]
For lower pain levels, treatment may involve having the patient:
- Seek appropriate physical therapy, such as stretching and massage, which plays a large role in the management of pain
- Learn to perform inguinal ligament stretching (from a physical therapist or from a YouTube video) which can rapidly relieve symptoms
- Use rest periods to interrupt long periods of standing, walking, cycling, or other aggravating activity
- Lose weight, and exercise to strengthen abdominal muscles[5]
- Wear clothing that is loose at the upper front hip area
- Apply heat, ice, or electrical stimulation[6]
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications for 7–10 days[5]
- Remove hair in affected area (shave)
- Lidocaine patches (must shave area first)
- Titanium dioxide patches to interfere with the electrostatic effect of the nerves on the surface of the skin
Pain may take significant time (weeks) to stop and, in some cases, numbness persists despite treatment. In severe cases, the physician might perform a local nerve block at the inguinal ligament, using a combination of local anaesthetic (lidocaine) and corticosteroids to provide relief that may last several weeks. Pain modifier drugs for neuralgic pain (such as amitriptyline, carbamazepine or gabapentin) may be tried,[6] but are often not as helpful in the majority of patients.[7]
Persistent and severe cases may require surgery to decompress the nerve[7] or, as a last resort, to resect the nerve.[6] The latter treatment leaves permanent numbness in the area.
See also
References
- ↑ Pearce, J M S (2006). "Meralgia paraesthetica (Bernhardt-Roth syndrome)". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 77: 84. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2005.072363.
- ↑ IASP, XXXI: LOCAL SYNDROMES IN THE LEG OR FOOT: PAIN OF NEUROLOGICAL ORIGIN, 2012
- ↑ "Make your pencil jeans less dangerous to your health". Vanguard. March 8, 2012.
- ↑ Ivins, Gregory K. (2000). "Meralgia Paresthetica, the Elusive Diagnosis". Annals of Surgery. 232 (2): 281–6. PMC 1421141
 . PMID 10903608. doi:10.1097/00000658-200008000-00019.
. PMID 10903608. doi:10.1097/00000658-200008000-00019. - 1 2 "Meralgia Paresthetica". Peripheral Nerve Diseases & Disorders. UCLA Neurosurgery. Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- 1 2 3 Meralgia Paresthetica orthoped/416 at eMedicine
- 1 2 Meralgia Paresthetica neuro/590 at eMedicine
External links
- Meralgia Paresthetica at eMedicine.com
- Meralgia Paresthetica at Chiroweb.com
- Curing Meralgia Paresthetica