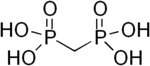
Medronic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
methanediylbis(phosphonic acid) | |
| Other names
methanediphosphonic acid; methylenebis(phosphonic acid); methylene diphosphonate; medronate; phosphonomethylphosphonic acid; MDP | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.229 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6O6P2 | |
| Molar mass | 176.00 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 199 to 200 °C (390 to 392 °F; 472 to 473 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
45-50 mg/kg (i.v., mice, rabbits)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Medronic acid (conjugate base, medronate) is the smallest bisphosphonate. Its complex with radioactive technetium, 99mTc medronic acid, is used in nuclear medicine to detect bone abnormalities, including metastases.
References
- 1 2 Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996), The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.), Merck, ISBN 0911910123
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.