Sinus lift
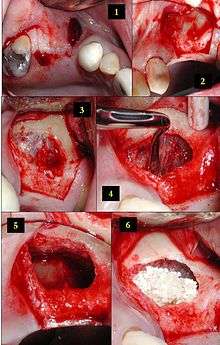
2) The soft tissue is flapped back to expose the underlying lateral wall of the left maxillary sinus.
3) The bone has been removed with a piezoelectric instrument, exposing the underlying Schneiderian membrane, which is the lining of the maxillary sinus cavity.
4) Through careful instrumentation, the membrane is carefully peeled from the inner aspect of the sinus cavity.
5) The membrane has been reflected from the internal aspect of the inferior portion of the sinus cavity; one can now visualize the bony floor of the sinus cavity without its lining membrane (note the triangular ridge of bone within the sinus, known as an Underwood's septum).
6) The newly formed space within the bony cavity of the sinus yet inferior to the intact membrane is grafted with human cadaver allograft bone. The floor of the sinus will now be roughly 10mm or so more superior than it was before, providing enough room to place dental implants into the edentulous site.
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation[1] (also termed sinus lift, sinus graft, sinus augmentation or sinus procedure) is a surgical procedure which aims to increase the amount of bone in the posterior maxilla (upper jaw bone), in the area of the premolar and molar teeth, by lifting the lower Schneiderian membrane (sinus membrane) and placing a bone graft.[2]
When a tooth is lost the alveolar process begins to remodel. The vacant tooth socket collapses as it heals leaving an edentulous (toothless) area, termed a ridge. This collapse causes a loss in both height and width of the surrounding bone. In addition, when a maxillary molar or premolar is lost, the floor of the maxillary sinus expands, which further diminishes the thickness of the underlying bone. Overall, this leads to a loss in volume of bone that is available for implantation of dental implants, which rely on osseointegration (bone integration), to replace missing teeth. The goal of the sinus lift is to graft extra bone into the maxillary sinus, so more bone is available to support a dental implant.[3]
Indications
While there may be a number of reasons for wanting a greater volume of bone in the posterior maxilla, the most common reason in contemporary dental treatment planning is to prepare the site for the future placement of dental implants.
Sinus augmentation (sinus lift) is performed when the floor of the sinus is too close to an area where dental implants are to be placed. This procedure is performed to ensure a secure place for the implants while protecting the sinus. Lowering of the sinus can be caused by: Long-term tooth loss without the required treatment, periodontal disease, trauma.[4]
Patients who have the following may be good candidates for sinus augmentation.[5]
- Lost more than one tooth in the posterior maxilla.
- Lost a significant amount of bone in the posterior maxilla.
- Missing teeth due to genetics or birth defect.
- Minus most of the maxillary teeth and need a strong sinus floor for multiple implants.
Technique
Prior to undergoing sinus augmentation, diagnostics are run to determine the health of the patient’s sinuses. Panoramic radiographs are taken to map out the patient's upper jaw and sinuses. In special instances, a computed tomography or CT scan is taken to measure the sinus’s height and width, and to rule out any sinus disease or pathology.[6]
There are several variations of the sinus lift technique.
Traditional Sinus Augmentation or Lateral Window Technique
There are multiple ways to perform sinus augmentation. The procedure is performed from inside the patient’s mouth where the surgeon makes an incision into the gum, or gingiva. Once the incision is made, the surgeon then pulls back the gum tissue, exposing the lateral boney wall of the sinus. The surgeon then cuts a "window" to the sinus, which is exposing the Schneiderian membrane. The membrane is separated from the bone, and bone graft material is placed into the newly created space. The gums are then sutured close and the graft is left to heal for 4–12 months.[7]
The graft material used can be either an autograft, an allograft, a xenograft, an alloplast (a growth-factor infused collagen matrix), synthetic variants, or combinations thereof.[8] Studies indicate that the mere lifting of the sinus membrane, creation of a void space and blood clot formation might result in new bone owing to the principles of guided bone regeneration.[9]
In some cases the dental implant is also inserted during the same sinus lift procedure.
Osteotome Technique
As an alternative, sinus augmentation can be performed by a less invasive osteotome technique. This technique is normally performed when the sinus floor needs to be lifted less than 4 mm. The osteotome technique is performed by flapping back gum tissue and making a socket in the bone within 1–2 mm short of the sinus membrane. The floor of the sinus is then lifted by tapping the sinus floor with the use of osteotomes. The amount of augmentation achieved with the osteotome technique is usually less than what can be achieved with the lateral window technique. A dental implant is normally placed in the socket formed at the time of the sinus lift procedure and left to integrate with bone. Bone integration normally lasts 4 to 8 months. The goal of this procedure is to stimulate bone growth and form a thicker sinus floor, in order to support dental implants for teeth replacement.
Hydraulic Sinus Condensing
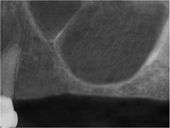
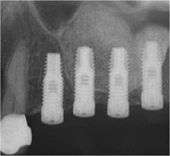
This technique was invented in 1996, by Dr. Leon Chen. There are other methods of this such as the Intralift(tm) from ACTEON that are also clinically proven.
Unlike the traditional methods of sinus lifts, which typically use an osteotomy of the lateral aspect of the maxilla, the Hydraulic Sinus Condensing, or HSC technique, uses an osteotomy on the lateral aspect of the ridge of the maxilla. The HSC technique has shown to have much shorter recovery times[10] than the traditional method. A dental implant is placed at the same time as the sinus lift, also reducing the healing time.
The gum tissue is flapped to access the underlying bone. An osteotomy (bone removal) is initiated along the ridge. Drilling ceases about 1mm short of the sinus floor. Hydraulic pressure is introduced to the surgical site at this stage, providing just enough force to begin atraumatically dissecting the membrane from the sinus floor. Once the membrane is loosened, the hydraulic pressure is ceased. The membrane at rest is slightly detached from the bone. A bone grafting mixture is then packed through the hole and pushed gently against the membrane. This pressure will slightly raise the sinus, resting it on the newly placed bone.
Once the initial lift is complete, the surgeon drills a socket in the bone that is sized to the new implant. Bone graft material is added again with pressure to further lift the sinus until it is raised to the proper height for implant placement. The surgeon then places the dental implant into the bone socket and sutures the gums back into place.
Over an 8-year study of 1,557 implants in 1,100 patients using the Hydraulic Sinus Condensing technique, only 8 implants failed, resulting in a 99.99% success rate.[10]
Complications
A major risk of a sinus augmentation is that the sinus membrane could be pierced or ripped. Remedies, should this occur, include stitching the tear or placing a patch over it; in some cases, the surgery is stopped altogether and the tear is given time to heal, usually three to six months. Often, the sinus membrane grows back thicker and stronger, making success more likely on the second operation.
Besides tearing of the sinus membrane, there are other risks involved in sinus augmentation surgery. Most notably, the close relationship of the augmentation site with the sinonasal complex can induce sinusitis, which may chronicize and cause severe symptoms. Sinusitis resulting from maxillary sinus augmentation is considered a Class 1 sinonasal complication according to Felisati classification and should be addressed surgically with a combined endoscopic endonasal and endoral approach.[11] Beside sinusitis, among other procedure related-risks include:
- Infection
- Inflammation
- Pain
- Itching
- Allergic reaction
- Tissue or nerve damage
- Scar formation
- Hematoma
- Graft failure
- Oro-antral communication / oro-antral fistula
- Tilting or loosening of implants
Recovery
It takes about three to six months for the sinus augmentation bone to become part of the patient's natural sinus floor bone. Up to six months of healing is sometimes left before implants are attempted. However, some surgeons perform both the augmentation and dental implant simultaneously, to avoid the necessity of two surgeries.[12]
History
The first maxillary sinus floor augmentation procedure was performed by Oscar Hilt Tatum, Jr. in 1974.
A sinus-lift procedure was first performed by Dr. Hilt Tatum Jr. in 1974 during his period of preparation to begin sinus grafting. The first sinus graft was done by Tatum in February, 1975 in Lee County Hospital in Opelika, Alabama. This was followed by the placement and successful restoration of two endosteal implants. Between 1975–1979, much of the sinus lining elevation was done using inflatable catheters. After this, suitable instruments had been developed to manage the lining elevation from the different anatomical surfaces encountered in sinuses. Tatum first presented the concept at The Alabama Implant Congress in Birmingham, Alabama in 1976 and presented the evolution of technique during multiple podium presentations each year until 1986 when he published an article describing the procedure. Dr. Philip Boyne was introduced to the procedure when he was invited, by Tatum, to be "The Discusser" of a presentation on sinus grafting given by Tatum at the annual meeting of The American Academy of Implant Dentistry in 1977 or 1978. Boyne and James authored the first publication on the technique in 1980 when they published case reports of autogenous grafts placed into the sinus and allowed to heal for 6 months, which was followed by the placement of blade implants. This sequence was confirmed by Boyne before the attendees at The Alabama Implant Congress in 1994.
Cost-effectiveness
The slightly higher effectiveness (implant survival) of the lateral sinus lift technique needs to be considered in relation to the substantially higher costs in comparison with the transalveolar sinus lift technique. From a patient perspective the higher invasiviness of the lateral technique will also be an important decision criterion. However, the transalveolar approach is unlikely to be effective in cases of advanced levels of bone reduction at the implant site.[13]
References
- ↑ Boyne, PJ. De novo bone induction by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) in maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005;63:1693-1707
- ↑ http://www.colgate.com/en/us/oc/oral-health/cosmetic-dentistry/implants/article/sinus-lift
- ↑ Esposito, M; Grusovin, MG; Rees, J; Karasoulos, D; Felice, P; Alissa, R; Worthington, HV; Coulthard, P (Mar 17, 2010). "Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews (3): CD008397. PMID 20238367. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008397.
- ↑ Brentwood Periodontists http://implantperiocenter.com/patient-education/sinus-augmentation-sinus-lift
- ↑ https://www.infusebonegraft.com/omf_sinus_lift.html
- ↑ "Sinus Lift". colgate.com.
- ↑ "Sinus Lift Surgery | Perio.org". www.perio.org. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ↑ Kumar, Prasanna; Vinitha, Belliappa; Fathima, Ghousia (2013-06-01). "Bone grafts in dentistry". Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences. 5 (Suppl 1): S125–S127. ISSN 0976-4879. PMC 3722694
 . PMID 23946565. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.113312.
. PMID 23946565. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.113312. - ↑ Hurley LA, Stinchfield FE, Bassett AL, Lyon WH (October 1959). "The role of soft tissues in osteogenesis. An experimental study of canine spine fusions". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 41–A: 1243–54. PMID 13852565.
- 1 2 Chen, Leon, & Cha, Jennifer, An 8-Year Retrospective Study: 1,100 Patients Receiving 1,557 Implants using the Minimally Invasive Hydraulic Sinus Condensing Technique, 'Innovations in Periodontics, Volume 76, Number 3, Page 482 March, 2005
- ↑ Felisati, Giovanni, Chiapasco, Matteo, Lozza, Paolo, Saibene, Alberto Maria, Pipolo, Carlotta, Zaniboni, Matteo, Biglioli, Federico & Borloni, Roberto, (July 2013). "Sinonasal complications resulting from dental treatment: outcome-oriented proposal of classification and surgical protocol". American Journal of Rhinology and Allergy. 27 (4): e101.
- ↑ "404 Not Found". atlantadentist.com.
- ↑ Listl S, Faggion CM (Aug 2010). "An economic evaluation of different sinus lift techniques.". J Clin Periodontol. 37: 777–87. PMID 20546083. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01577.x.
"Journal of Periodontology March 2005,". Journal of Periodontology. 76 (3): 482–491. doi:10.1902/jop.2005.76.3.482.
- Chen, Leon, & Cha, Jennifer, (March 2005). "An 8-Year Retrospective Study: 1,100 Patients Receiving 1,557 Implants using the Minimally Invasive Hydraulic Sinus Condensing Technique". Innovations in Periodontics. 76 (3): 490.
- Raghoebar GM, Timmenga NM, Reintsema H, Stegenga B, Vissink A (June 2001). "Maxillary bone grafting for insertion of endosseous implants: results after 12-124 months". Clin Oral Implants Res. 12: 279–86. PMID 11359486. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0501.2001.012003279.x.
- "Bilateral Sinus Lifts with SynthoGraft Using Floor Transport Technique with Sinus Lift Temporary Abutments, Two Stage Placements, and Restoration with Twelve Maxillary Full Arch Integrated Abutment Crowns".
- "Journal of Periodontology March 2005, Vol. 76, No. 3, Pages 482-491".
- Abrahams, James J. (2000). Sinus Lift Procedure of the Maxilla in Patients with Inadequate Bone for Dental Implants "American Journal of Roentgenology" Check
|url=value (help). 174 (=5): 1289–1292. - Boyne PJ, James RA (1980). "Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone". J Oral Surg. 38: 613–616.
- Tatum H Jr (1986). "Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions". Dent Clin North Am. 30: 207–229.
- Lazzara RJ. The sinus elevation procedure in endosseous implant therapy. Curr Opin Periodontol 1996; 3:178-183.
- Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: The osteotome technique. Compendium 1994;15:152, 154-156, 158 passim; quiz 162.
- Summers RB. The osteotome technique: Part 3 – Less invasive methods of elevating the sinus floor. Compendium 1994;15:698, 700, 702-694 passim; quiz 710.
- Zitzmann NU, Scharer P (1998). "Sinus elevation procedures in the resorbed posterior maxilla. Comparison of the crestal and lateral approaches". Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 85: 8–17. doi:10.1016/s1079-2104(98)90391-2.
- Rosen PS; Summers R; Mellado JR; et al. (1999). "The bone added osteotome sinus floor elevation technique: Multicenter retrospective report of consecutively treated patients". Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 14: 853–858.
- Felisati G; Chiapasco M; Lozza P; et al. (2013). "Sinonasal complications resulting from dental treatment: outcome-oriented proposal of classification and surgical protocol". Am J Rhinol Allergy. 27: e101–106. doi:10.2500/ajra.2013.27.3936.
External links
Educational Resources
- OsseoNews.com A detailed discussion on sinus lift procedures.
- Sonosurgery.it Documented cases on sinus lift procedures with sonical instruments.