Matchstick graph

| Harborth graph | |
|---|---|
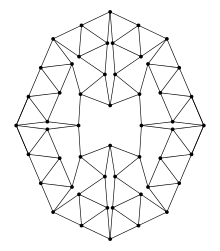 | |
| Vertices | 52 |
| Edges | 104 |
| Radius | 6 |
| Diameter | 9 |
| Girth | 3 |
In geometric graph theory, a branch of mathematics, a matchstick graph is a graph that can be drawn in the plane in such a way that its edges are line segments with length one that do not cross each other. That is, it is a graph that has an embedding which is simultaneously a unit distance graph and a plane graph. Informally, matchstick graphs can be made by placing noncrossing matchsticks on a flat surface, hence the name.[1]
Regular matchstick graphs
Much of the research on matchstick graphs has concerned regular graphs, in which each vertex has the same number of neighbors. This number is called the degree of the graph.
It is known that there are matchstick graphs that are regular of any degree up to 4. The complete graphs with one, two, and three vertices (a single vertex, a single edge, and a triangle) are all matchstick graphs and are 0-, 1-, and 2-regular respectively. The smallest 3-regular matchstick graph is formed from two copies of the diamond graph placed in such a way that corresponding vertices are at unit distance from each other; its bipartite double cover is the 8-crossed prism graph.[1]
In 1986, Heiko Harborth presented the graph that would bear his name, the Harborth Graph. With 104 edges and 52 vertices, is the smallest known example of a 4-regular matchstick graph.[2] It is a rigid graph.[3]
It is not possible for a regular matchstick graph to have degree greater than four.[4]
The smallest 3-regular matchstick graph without triangles (girth ≥ 4) has 20 vertices, as proved by Kurz and Mazzuoccolo.[5] Furthermore, they exhibit the smallest known example of a 3-regular matchstick graph of girth 5 (180 vertices).
Computational complexity
It is NP-hard to test whether a given undirected planar graph can be realized as a matchstick graph.[6][7] More precisely, this problem is complete for the existential theory of the reals.[8] Kurz (2014) provides some easily tested necessary criteria for a graph to be a matchstick graph, but these are not also sufficient criteria: a graph may pass Kurz's tests and still not be a matchstick graph.[9]
It is also NP-complete to determine whether a matchstick graph has a Hamiltonian cycle, even when the vertices of the graph all have integer coordinates that are given as part of the input to the problem.[10]
Combinatorial enumeration
The numbers of distinct (nonisomorphic) matchstick graphs are known for 1, 2, 3, ... up to ten edges; they are:
For instance the three different graphs that can be made with three matchsticks are a claw, a triangle graph, and a three-edge path graph.
Special classes of graphs
Uniformity of edge lengths has long been seen as a desirable quality in graph drawing,[13] and some specific classes of planar graphs can always be drawn with completely uniform edges.
Every tree can be drawn in such a way that, if the leaf edges of the tree were replaced by infinite rays, the drawing would partition the plane into convex polygonal regions, without any crossings. For such a drawing, if the lengths of each edge are changed arbitrarily, without changing the slope of the edge, the drawing will remain planar. In particular, it is possible to choose all edges to have equal length, resulting in a realization of an arbitrary tree as a matchstick graph.[14]

A similar property is true for squaregraphs, the planar graphs that can be drawn in the plane in such a way that every bounded face is a quadrilateral and every vertex either lies on the unbounded face or has at least four neighbors. These graphs can be drawn with all faces parallelograms, in such a way that if a subset of edges that are all parallel to each other are lengthened or shortened simultaneously so that they continue to all have the same length, then no crossing can be introduced. In particular it is possible to normalize the edges so that they all have the same length, and obtain a realization of any squaregraph as a matchstick graph.[15]
Related classes of graphs
Every matchstick graph is a unit distance graph. Penny graphs are the graphs that can be represented by tangencies of non-overlapping unit circles. Every penny graph is a matchstick graph, but not vice versa.
References
- 1 2 Weisstein, Eric W. "Matchstick graph". MathWorld.
- ↑ Harborth, Heiko (1994), "Match sticks in the plane", in Guy, R. K.; Woodrow, R. E., The Lighter Side of Mathematics: Proceedings of the Eugéne Strens Memorial Conference of Recreational Mathematics and its History, Calgary, Canada, 1986, Washington, D.C.: Mathematical Association of America, pp. 281–288. As cited in: Weisstein, Eric W. "Matchstick graph". MathWorld.
- ↑ Gerbracht, E. H.-A. (2006), Minimal polynomials for the coordinates of the Harborth graph, arXiv:math.CO/0609360

- ↑ Kurz, Sascha; Pinchasi, Rom (2011), "Regular matchstick graphs", American Mathematical Monthly, 118 (3): 264–267, MR 2800336, doi:10.4169/amer.math.monthly.118.03.264.
- ↑ Kurz, Sascha; Mazzuoccolo, Giuseppe (2010), "3-regular matchstick graphs with given girth", Geombinatorics, 19: 156–175, arXiv:1401.4360
 .
. - ↑ Eades, Peter; Wormald, Nicholas C. (1990), "Fixed edge-length graph drawing is NP-hard", Discrete Applied Mathematics, 28 (2): 111–134, doi:10.1016/0166-218X(90)90110-X.
- ↑ Cabello, Sergio; Demaine, Erik D.; Rote, Günter (2007), "Planar embeddings of graphs with specified edge lengths" (PDF), Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications, 11 (1): 259–276, doi:10.7155/jgaa.00145.
- ↑ Abel, Zachary; Demaine, Erik D.; Demaine, Martin L.; Eisenstat, Sarah; Lynch, Jayson; Schardl, Tao B. (2016), "Who needs crossings? Hardness of plane graph rigidity", in Fekete, Sándor; Lubiw, Anna, 32nd International Symposium on Computational Geometry (SoCG 2016), Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs), 51, Dagstuhl, Germany: Schloss Dagstuhl–Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik, pp. 3:1–3:15, ISBN 978-3-95977-009-5, doi:10.4230/LIPIcs.SoCG.2016.3.
- ↑ Kurz, Sascha (2014), Fast recognition of planar non unit distance graphs, arXiv:1401.4375
 .
. - ↑ Itai, Alon; Papadimitriou, Christos H.; Szwarcfiter, Jayme Luiz (1982), "Hamilton paths in grid graphs", SIAM Journal on Computing, 11 (4): 676–686, MR 677661, doi:10.1137/0211056.
- ↑ Salvia, Raffaele (2013), A catalog for matchstick graphs, arXiv:1303.5965

- ↑ Vaisse, Alexis (2015). "Matchstick graphs with up to 10 edges".
- ↑ Fruchterman, Thomas M. J.; Reingold, Edward M. (1991), "Graph Drawing by Force-Directed Placement", Software – Practice & Experience, Wiley, 21 (11): 1129–1164, doi:10.1002/spe.4380211102.
- ↑ Carlson, Josiah; Eppstein, David (2006), "Trees with convex faces and optimal angles", in Kaufmann, Michael; Wagner, Dorothea, Proc. 14th Int. Symp. Graph Drawing, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 4372, Springer-Verlag, pp. 77–88, MR 2393907, arXiv:cs.CG/0607113
 , doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70904-6_9.
, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-70904-6_9. - ↑ Eppstein, David; Wortman, Kevin A. (2011), "Optimal angular resolution for face-symmetric drawings", J. Graph Algorithms & Applications, 15 (4): 551–564, arXiv:0907.5474
 , doi:10.7155/jgaa.00238.
, doi:10.7155/jgaa.00238.