Mass (mass spectrometry)
The mass recorded by a mass spectrometer can refer to different physical quantities depending on the characteristics of the instrument and the manner in which the mass spectrum is displayed.
Units
The unified atomic mass unit (symbol: u) is the standard unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale (atomic mass). The dalton (symbol: Da) is equivalent to the unified atomic mass unit. One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one a single proton or neutron.[1] The unified atomic mass unit has a value of 1.660538921(73)×10−27 kg.[2] The amu without the "unified" prefix is an obsolete unit based on oxygen, which was replaced in 1961.
Molecular mass
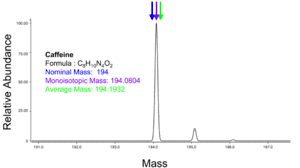
The molecular mass (abbreviated Mr) of a substance, formerly also called molecular weight and abbreviated as MW, is the mass of one molecule of that substance, relative to the unified atomic mass unit u (equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of 12C). Due to this relativity, the molecular mass of a substance is commonly referred to as the relative molecular mass, and abbreviated to Mr.
Average mass
The average mass of a molecule is obtained by summing the average atomic masses of the constituent elements. For example, the average mass of natural water with formula H2O is 1.00794 + 1.00794 + 15.9994 = 18.01528.
Mass number
The mass number, also called the nucleon number, is the number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. The mass number is unique for each isotope of an element and is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, carbon-12 (12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
Nominal mass
The nominal mass for an element is the mass number of its most abundant naturally occurring stable isotope, and for an ion or molecule, the nominal mass is the sum of the nominal masses of the constituent atoms.[3][4] Isotope abundances are tabulated by IUPAC:[5] for example carbon has two stable isotopes 12C at 98.9% natural abundance and 13C at 1.1% natural abundance, thus the nominal mass of carbon is 12. The nominal mass is not always the lowest mass number, for example iron has isotopes 54Fe, 56Fe, 57Fe, and 58Fe with abundances 6%, 92%, 10%, and 2%, respectively, and a nominal mass of 56. For a molecule, the nominal mass is obtained by summing the nominal masses of the constituent elements, for example water has two hydrogen atoms with nominal mass 1 and one oxygen atom with nominal mass 16, therefore the nominal mass of H2O is 18.
In mass spectrometry, the difference between the nominal mass and the monoisotopic mass is the mass defect.[6] This differs from the definition of mass defect used in physics which is the difference between the mass of a composite particle and the sum of the masses of its constituent parts.[7]
Accurate mass
The accurate mass (more appropriately, the measured accurate mass[8]) is an experimentally determined mass that allows the elemental composition to be determined.[9] For molecules with mass below 200 u, 5 ppm accuracy is often sufficient to uniquely determine the elemental composition.[10]
Exact mass
The exact mass of an isotopic species (more appropriately, the calculated exact mass[8]) is obtained by summing the masses of the individual isotopes of the molecule. For example, the exact mass of water containing two hydrogen-1 (1H) and one oxygen-16 (16O) is 1.0078 + 1.0078 + 15.9949 = 18.0105. The exact mass of heavy water, containing two hydrogen-2 (deuterium or 2H) and one oxygen-16 (16O) is 2.0141 + 2.0141 + 15.9949 = 20.0229.
When an exact mass value is given without specifying an isotopic species, it normally refers to the most abundant isotopic species.
Monoisotopic mass
The monoisotopic mass is the sum of the masses of the atoms in a molecule using the unbound, ground-state, rest mass of the principal (most abundant) isotope for each element.[11][4] The monoisotopic mass of a molecule or ion is the exact mass obtained using the principal isotopes. Monoisotopic mass is typically expressed in unified atomic mass units.
For typical organic compounds, where the monoisotopic mass is most commonly used, this also results in the lightest isotope being selected. For some heavier atoms such as iron and argon the principal isotope is not the lightest isotope. The mass spectrum peak corresponding to the monoisotopic mass is often not observed for large molecules, but can be determined from the isotopic distribution.[12]
Most abundant mass
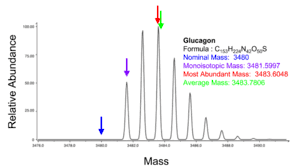
This refers to the mass of the molecule with the most highly represented isotope distribution, based on the natural abundance of the isotopes.[13]
Isotopomer and isotopologue
Isotopomers (isotopic isomers) are isomers having the same number of each isotopic atom, but differing in the positions of the isotopic atoms.[14] For example, CH3CHDCH3 and CH3CH2CH2D are a pair of structural isotopomers.
Isotopomers should not be confused with isotopologues, which are chemical species that differ in the isotopic composition of their molecules or ions. For example, the water molecule has three isotopologues with different isotopic composition of hydrogen: HOH, HOD and DOD, where D stands for deuterium (2H).
Kendrick mass
The Kendrick mass is a mass obtained by multiplying the measured mass by a numeric factor. The Kendrick mass is used to aid in the identification of molecules of similar chemical structure from peaks in mass spectra.[15][16] The method of stating mass was suggested in 1963 by the chemist Edward Kendrick.
According to the procedure outlined by Kendrick, the mass of CH2 is defined as 14.000 Da, instead of 14.01565 Da.[17][18]
The Kendrick mass for a family of compounds F is given by[19]
- .
For hydrocarbon analysis, F=CH2.
Nitrogen rule
The nitrogen rule states that organic compounds containing exclusively hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, and the halogens either have an odd nominal mass that indicates an odd number of nitrogen atoms are present or an even nominal mass that indicates an even number of nitrogen atoms are present in the molecular ion.[20][21]
Prout's hypothesis and the whole number rule

The whole number rule states that the masses of the isotopes are integer multiples of the mass of the hydrogen atom.[24] The rule is a modified version of Prout's hypothesis proposed in 1815, to the effect that atomic weights are multiples of the weight of the hydrogen atom.[25]
See also
References
- ↑ Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg; John L. Tymoczko; Lubert (2007). "2". Biochemistry (3rd print, 6th ed.). New York: Freeman. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-7167-8724-2.
- ↑ Fundamental Physical Constants from NIST
- ↑ Jürgen H Gross (14 February 2011). Mass Spectrometry: A Textbook. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-3-642-10709-2.
- 1 2 J. Throck Watson; O. David Sparkman (9 July 2013). Introduction to Mass Spectrometry: Instrumentation, Applications, and Strategies for Data Interpretation. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 385–. ISBN 978-1-118-68158-9.
- ↑ Berglund, Michael; Wieser, Michael E. (2011). "Isotopic compositions of the elements 2009 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 83 (2). ISSN 1365-3075. doi:10.1351/PAC-REP-10-06-02.
- ↑ Sleno, Lekha (2012). "The use of mass defect in modern mass spectrometry". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 47 (2): 226–236. ISSN 1076-5174. doi:10.1002/jms.2953.
- ↑ Imma Ferrer; E. M. Thurman (6 May 2009). Liquid Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 18–22. ISBN 978-0-470-42995-2.
- 1 2 O. David Sparkman. Mass Spec Desk Reference (2nd. ed.). p. 60. ISBN 0-9660813-9-0.
- ↑ Grange AH; Winnik W; Ferguson PL; Sovocool GW (2005), "Using a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer in accurate mass mode and an ion correlation program to identify compounds", Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 19 (18): 2699–715, PMID 16124033, doi:10.1002/rcm.2112.
- ↑ Gross, M. L. (1994), "Accurate Masses for Structure Confirmation", J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom, 5 (2): 57, doi:10.1016/1044-0305(94)85036-4.
- ↑ "Monoisotopic mass spectrum". IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the Gold Book). IUPAC. 2009. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M04014.
- ↑ Senko, Michael W.; Beu, Steven C.; McLaffertycor, Fred W. (1995). "Determination of monoisotopic masses and ion populations for large biomolecules from resolved isotopic distributions". Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 6 (4): 229–233. ISSN 1044-0305. doi:10.1016/1044-0305(95)00017-8.
- ↑ Goraczko AJ (2005), "Molecular mass and location of the most abundant peak of the molecular ion isotopomeric cluster", Journal of molecular modeling, 11 (4–5): 271–7, PMID 15928922, doi:10.1007/s00894-005-0245-x.
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "isotopomer".
- ↑ Kendrick, Edward (1963), "A mass scale based on CH2 = 14.0000 for high resolution mass spectrometry of organic compounds", Anal. Chem., 35 (13): 2146–2154, doi:10.1021/ac60206a048, retrieved 2010-01-25.
- ↑ Marshall AG; Rodgers RP (January 2004), "Petroleomics: the next grand challenge for chemical analysis", Acc. Chem. Res., 37 (1): 53–9, PMID 14730994, doi:10.1021/ar020177t.
- ↑ Mopper, Kenneth; Stubbins, Aron; Ritchie, Jason D.; Bialk, Heidi M.; Hatcher, Patrick G. (2007), "Advanced Instrumental Approaches for Characterization of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter: Extraction Techniques, Mass Spectrometry, and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy", Chemical Reviews, 107 (2): 419–42, PMID 17300139, doi:10.1021/cr050359b
- ↑ Meija, Juris (2006), "Mathematical tools in analytical mass spectrometry", Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 385 (3): 486–99, PMID 16514517, doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0298-4
- ↑ Kim, Sunghwan; Kramer, Robert W.; Hatcher, Patrick G. (2003), "Graphical Method for Analysis of Ultrahigh-Resolution Broadband Mass Spectra of Natural Organic Matter, the Van Krevelen Diagram", Analytical Chemistry, 75 (20): 5336–44, PMID 14710810, doi:10.1021/ac034415p
- ↑ Tureček, František; McLafferty, Fred W. (1993). Interpretation of mass spectra. Sausalito, Calif: University Science Books. pp. 37–38. ISBN 0-935702-25-3.
- ↑ David O. Sparkman (2007). Mass Spectrometry Desk Reference. Pittsburgh: Global View Pub. p. 64. ISBN 0-9660813-9-0.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1922". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-04-14.
- ↑ Squires, Gordon (1998). "Francis Aston and the mass spectrograph". Dalton Transactions (23): 3893–3900. doi:10.1039/a804629h. Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ Budzikiewicz H; Grigsby RD (2006). "Mass spectrometry and isotopes: a century of research and discussion". Mass spectrometry reviews. 25 (1): 146–57. PMID 16134128. doi:10.1002/mas.20061.
- ↑ Prout, William (1815). "On the relation between the specific gravities of bodies in their gaseous state and the weights of their atoms.". Annals of Philosophy. 6: 321–330. Retrieved 2007-09-08.