Royal Canadian Navy
| Royal Canadian Navy | |
|---|---|
| Marine royale canadienne | |
 | |
| Founded | 4 May 1910 |
| Country | Canada |
| Type | Navy |
| Size | 13,600 personnel, 30 ships (63 including auxiliaries) |
| Part of | Canadian Armed Forces |
| Headquarters | National Defence Headquarters |
| Motto(s) | Latin: Parati vero parati (Ready aye ready) |
| March | "Heart of Oak" |
| Mascot(s) | SONAR (Newfoundland dog) |
| Engagements | |
| Website |
navy-marine |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-chief | Elizabeth II, Queen of Canada, represented by Governor General, David Johnston |
| Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy | Vice-Admiral Ron Lloyd CMM CD |
| Insignia | |
| Naval Ensign |
 |
| Naval Jack |
 |
| Auxillary Jack |
 |
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) (French: Marine royale canadienne) is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the unified Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2017 Canada's navy operates 12 frigates, 4 patrol submarines, 12 coastal defence vessels and 8 unarmed patrol/training vessels, as well as several auxiliary vessels. The Royal Canadian Navy consists of 8,500 Regular Force and 5,100 Primary Reserve sailors, supported by 5,300 civilians.[a 1] Vice-Admiral Ron Lloyd is the current Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy and Chief of the Naval Staff.[a 2]
Founded in 1910 as the Naval Service of Canada and given royal sanction on 29 August 1911,[1] the Royal Canadian Navy was amalgamated with the Royal Canadian Air Force and the Canadian Army to form the unified Canadian Armed Forces in 1968, after which it was known as "Maritime Command" until 2011.
In 2011, its historical title of "Royal Canadian Navy" (RCN) was restored. Over the course of its history, the RCN has served in the First and Second World Wars, the Korean War, the Persian Gulf War, the War in Afghanistan and numerous United Nations peacekeeping missions and NATO operations.
History

1910–1968
Established following the introduction of the Naval Service Bill by then Prime Minister Sir Wilfrid Laurier, the Naval Service of Canada (NSC) was intended as a distinct naval force for the Dominion, that, should the need arise, could be placed under British control. The bill received royal assent on 4 May 1910. Initially equipped with two former Royal Navy vessels, HMCS Niobe and HMCS Rainbow, King George V granted permission for the service to be known as the Royal Canadian Navy on 29 August 1911.[2]

During the first years of the First World War, the RCN's six-vessel naval force patrolled both the North American west and east coasts to deter the German naval threat, with a seventh ship, HMCS Shearwater joining the force in 1915. Just before the end of the war in 1918, the Royal Canadian Naval Air Service was established with the purpose of carrying out anti-submarine operations; however, it was disbanded after the armistice of 11 November.[3]
After the war, the Royal Canadian Navy took over certain responsibilities of the Department of Transport's Marine Service, and slowly started to build its fleet, with the first warships specifically designed for the RCN being commissioned in 1932.[4] At the outbreak of the Second World War, the Navy had 11 combat vessels, 145 officers and 1,674 men.[5] During the Second World War, the Royal Canadian Navy expanded significantly, ultimately gaining responsibility for the entire Northwest Atlantic theatre of war. By the end of the war, the RCN had become the fifth-largest navy in the world after the United States Navy, the Royal Navy, the Imperial Japanese Navy, and the Soviet Navy, with over 900 vessels and 375 combat ships.[6] During the Battle of the Atlantic, the RCN sank 31 U-boats and sank or captured 42 enemy surface vessels, while successfully completing 25,343 merchant crossings. The Navy lost 24 ships and 1,797 sailors in the war.[7]
In 1940–41, the Royal Canadian Navy Reserves scheme for training yacht club members developed the first central registry system.[8]
From 1950 to 1955, during the Korean War, Canadian destroyers maintained a presence off the Korean peninsula, engaging in shore bombardments and maritime interdiction. During the Cold War, the Navy developed an anti-submarine capability to counter the growing Soviet naval threat.[9][10] In the 1960s, the Royal Canadian Navy retired most of its Second World War vessels, and further developed its anti-submarine warfare capabilities by acquiring the Sikorsky CH-124 Sea King, and successfully pioneered the use of large maritime helicopters on small surface vessels. At that time, Canada was also operating an aircraft carrier, HMCS Bonaventure, flying the McDonnell F2H Banshee fighter jet until 1962, as well as various other anti-submarine aircraft.[3]
1968–present
_is_shown_underway_in_close_formation_with_the_Nimitz-class_aircraft_carrier_USS_John_C._Stennis_(CVN_74)_and_the_guided_missile_frigate_USS_Ford_(FFG_54.jpg)
In 1968, under the Liberal government of Lester B. Pearson, the Royal Canadian Navy, Royal Canadian Air Force and Canadian Army were amalgamated to form the unified Canadian Forces. This process was overseen by then–Defence Minister Paul Hellyer. The controversial merger resulted in the abolition of the Royal Canadian Navy as a separate legal entity. All personnel, ships, and aircraft became part of Maritime Command (MARCOM), an element of the Canadian Armed Forces. The traditional naval uniform was eliminated and all naval personnel were required to wear the new Canadian Armed Forces rifle green uniform, adopted also by former Royal Canadian Air Force and Canadian Army personnel. Ship-borne aircraft continued to be under the command of MARCOM, while shore-based patrol aircraft of the former Royal Canadian Air Force were transferred to MARCOM. In 1975 Air Command was formed and all maritime aircraft were transferred to Air Command's Maritime Air Group. The unification of the Canadian Forces in 1968 was the first time that a nation with a modern military combined its formerly separate naval, land and air elements into a single service.
The 1970s saw the addition of four Iroquois-class destroyers, which were later updated to air-defence destroyers, and in the late 1980s and early 1990s the construction of twelve Halifax-class frigates. In 1990, Canada deployed three warships to support the Operation Friction. Later in the decade, ships were deployed to patrol the Adriatic Sea during the Yugoslav Wars and the Kosovo War. More recently, Maritime Command provided vessels to serve as a part of Operation Apollo and to combat piracy off the coast of Somalia.
On 16 August 2011, the government renamed the Canadian Forces' three environmental services: Maritime Command became the "Royal Canadian Navy", Air Command the "Royal Canadian Air Force," and Land Force Command the "Canadian Army."
As of August 2015, with the loss of command-and-control and resupply capabilities, the RCN is classified as a Rank 5 navy (offshore regional coastal defence) on the Todd-Lindberg classification system of naval strength, dropping from Rank 3 (multiregional power projection) in 2005.[11]
Structure
The Royal Canadian Navy is headquartered at National Defence Headquarters (NDHQ) in Ottawa, Ontario. Since 1968, the Royal Canadian Navy has been an environmental command of the Canadian Armed Forces and since 2012 it has been charged with maintaining and generating forces for the Canadian Joint Operations Command.[a 1]
Maritime Forces Atlantic

The Royal Canadian Navy's Atlantic Fleet, known as Canadian Fleet Atlantic is co-located with Maritime Forces Atlantic (MARLANT), with headquarters at CFB Halifax in Halifax, Nova Scotia. It is supported by CFS St. John's in Newfoundland. Attached to MARLANT and CFB Halifax is the Royal Canadian Air Force's 12 Wing Shearwater, based at Shearwater Heliport, which provides shipborne air support for the Atlantic Fleet. The RCAF's 14 Wing Greenwood provides fixed-wing air support for MARLANT through 404 Maritime Patrol and Training Squadron and 405 Maritime Patrol Squadron. Other Atlantic Fleet facilities are CFAD Bedford, an ammunition depot, and two radio stations, Naval Radio Section (NRS) Newport Corner and NRS Mill Cove.[a 3]
The Atlantic Fleet, with 18 warships and a number of auxiliary vessels, is responsible for Canada's exclusive economic zone on the East Coast, as well as Canada's area of responsibility in the Atlantic Ocean and the eastern Arctic Ocean.
Maritime Forces Pacific
The Royal Canadian Navy's Pacific Fleet, known as Canadian Fleet Pacific is co-located with Maritime Forces Pacific (MARPAC), with headquarters at CFB Esquimalt in British Columbia, in the Greater Victoria region. MARPAC consists of over 4,000 naval personnel and 2,000 civilian personnel.[a 4]
Comprising 15 warships and several auxiliary vessels homeported in Esquimalt, the Pacific Fleet is responsible for Canada's exclusive economic zone on the West Coast and Canada's area of responsibility in the Pacific Ocean and the western Arctic Ocean. Fleet Naval Facility Cape Breton provides repair and maintenance services to the Pacific Fleet. The Royal Canadian Air Force's 443 Maritime Helicopter Squadron, based at Patricia Bay Heliport but under the control of 12 Wing Shearwater, provides shipborne helicopter support for the Pacific Fleet, while 19 Wing Comox provides fixed-wing maritime air support for MARPAC through 407 Long Range Patrol Squadron. Other Pacific Fleet facilities are CFAD Rocky Point, an ammunition depot, and Naval Radio Section Aldergrove.
Reserve
The Naval Reserve Headquarters (NAVRESHQ), located at the Pointe-à-Carcy Naval Complex in Quebec City, is responsible for 24 naval reserve divisions across the country. The base is also home to Canadian Forces Fleet School Quebec and HMCS Montcalm. The Naval Reserve is composed of 4,000 reservists.[a 5]
Fleet
Warships

The Navy operates twelve frigates, four patrol submarines, twelve coastal-defence vessels and eight unarmed patrol/training vessels. The surface ships, which carry the designation Her Majesty's Canadian Ship (HMCS), consist of twelve Halifax-class multi-role patrol frigates and twelve Kingston-class coastal-defence vessels. In addition to the surface vessels, the RCN operates four Victoria-class submarines that were acquired from the Royal Navy in 1998. These warships carry the designation Her Majesty's Canadian Submarine. The Royal Canadian Navy also maintains and operates HMCS Oriole, a historic sailing ship commissioned in 1952 as a sail-training ship. Oriole is the oldest commissioned ship in the RCN and carries the royal designation and the battle honour Dunkirk, 1940.
On September 19, 2014, the Navy announced the decommissioning of its two resupply ships (HMCS Protecteur and HMCS Preserver), along with two destroyers (HMCS Algonquin and HMCS Iroquois).
Auxiliary vessels
The RCN operates auxiliary vessels to support the Canadian Forces. These vessels are not warships and do not carry the HMCS designation. Among the auxiliary ships operated by the Navy are eight Orca-class patrol class training tenders, five Ville-class harbour tugs, five Glen-class harbour tugs, and two fireboats of the Fire class.
Aircraft


Since 1975, all aircraft supporting the RCN are operated by the Royal Canadian Air Force through 1 Canadian Air Division. Since 1995, all CH-124 Sea King helicopters have been operated by squadrons under 12 Wing (from Shearwater Heliport and Patricia Bay Heliport). Similarly, all CP-140 Aurora and CP-140A Arcturus anti-submarine, ship surveillance and maritime patrol aircraft have been operated by squadrons under 14 Wing at CFB Greenwood and 19 Wing at CFB Comox. There are currently 27 CH-124 Sea King helicopters configured for ship-borne anti-submarine warfare, 18 CP-140 Aurora fixed wing aircraft for land-based anti-submarine warfare and area surveillance (of which 14 are being modernized and retained for active operations), and 1 CP-140A Arcturus for land-based maritime surveillance.
Squadrons
Future procurement
During the past several years, the following major projects have been announced by the Government of Canada to modernize the Canadian Navy:
- The Queenston-class Joint Support Ship Project is a program to replace the previous Protecteur-class replenishment vessels with two to three new joint support ships, providing support to naval task forces, a limited sealift capability and limited theatre command and control.[a 6] The JSS project dates back to 2002–2003 and plans were advanced enough at the time to begin construction, though with the change in government in 2006 that project was cancelled and replaced with a less capable and smaller planned acquisition. The RCN has decided to move forward with 2–3 Berlin-class replenishment ships under JSS, replacing the two Protecteur-class AORs. As part of the National Shipbuilding Procurement Strategy (NSPS), the ships will be built by Seaspan Marine Corporation at the Vancouver Shipyards facility located in North Vancouver, British Columbia. These Berlin class ships will displace approximately 22,250 tonnes in Canadian service.[12] Under the NSPS, the two JSS are sequenced to start building following on two classes of ships which are currently being built at the Seaspan yard for the Department of Fisheries and Oceans. Construction is therefore expected to begin in 2017 with projected service entry in the early 2020s. They will be named for battles of the War of 1812. HMCS Queenston is the lead ship, followed by HMCS Châteauguay.[13][14]
- The Harry DeWolf-class Arctic Patrol Ship Project, announced in 2007, is a program to build five to six Arctic patrol ships capable of operating with polar class 5 (PC-5) and to establish the Nanisivik Naval Facility, a deep water port in Arctic Bay, Baffin Island, Nunavut that would support RCN operations in the Northwest Passage and adjacent waters.[a 7] The lead ship began construction at the Irving Shipyard in Halifax in September 2015. Projected service entry for the lead ship of the class is in 2018. In September 2014, Prime Minister Stephen Harper announced that the name of the first ship in the class would be Her Majesty’s Canadian Ship Harry DeWolf, named in honour of wartime Canadian naval hero Harry DeWolf, and that the class would be named the Harry DeWolf class.[15]
- The Halifax-class frigates underwent a mid-life extension program that began in 2010 and was completed in November 2016 [a 8] and it was revealed in the October 2011 announcement of the National Shipbuilding Procurement Strategy that the RCN would be procuring up to 15 vessels under the Single Class Surface Combatant Project to replace the 12 Halifax-class frigates. This class of ship is currently in the design phase with construction anticipated to begin in around 2021.

- The Maritime Helicopter Project is an RCAF procurement project that will replace the CH-124 Sea Kings with 28 CH-148 Cyclone shipborne anti-submarine warfare helicopters that will operate from RCN warships.[a 9] This project has been delayed by several years for a variety of developmental challenges. However, deliveries of the Block 1 airframe began in June 2015 and so far nine have been delivered. Delivery of the fully operational "Block 2" airframes are projected to begin in 2018.
- In August 2015, the Conservative Government announced that a Letter of Intent was signed with Davie Shipbuilding in Quebec to convert a commercial vessel to provide interim refueling and support services to the Royal Canadian Navy while the Queenston-class vessels are constructed.[16][17] The commercial vessel Asterix, which is to be converted to provide this service, arrived in Canada in October 2015 and preliminary work started.[18] Initially the newly elected Liberal Government decided to delay decision on whether to proceed with the project until 2016.[19] However, that decision was then reversed and final approval of the project was given on 30 November 2015.[20]
Personnel
Commissioned officers

Commissioned officers of the Canadian Armed Forces have ranks ranging from the NATO standard ranks of OF-1 to OF-9. The only OF-9 position in the Canadian Forces is the Chief of the Defence Staff, who can be from any of the service elements. The highest position occupied in the current Royal Canadian Navy structure is OF-8, a vice-admiral who serves as the Commander of the Royal Canadian Navy and Chief of the Naval Staff. OF-6 (commodore) to OF-9 (admiral) are referred to as flag officers, OF-3 (lieutenant-commander) to OF-5 (captain (N)) are referred to as senior officers, while OF-2 (lieutenant (N)) and OF-1 (sub-lieutenant) are referred to as junior officers. Naval cadets are referred to as subordinate officers.[a 10] All except subordinate officers of the Canadian Forces receive a commission from the Queen of Canada as Commander-in-Chief of the Canadian Armed Forces. The commissioning scroll issued in recognition of the commission is signed by the Governor General of Canada as the Queen of Canada's representative, and countersigned by the serving Minister of National Defence. Subordinate officers are promoted to acting sub-lieutenant upon receiving their commissions.
Naval officers are trained at the Royal Military College of Canada in Kingston, Ontario, the Royal Military College Saint-Jean in Saint-Jean, Quebec, Naval Officer Training Centre (NOTC) Venture and Naval Fleet School (Pacific) in Esquimalt, British Columbia, and Naval Fleet School (Atlantic) in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Some specialized candidates may be commissioned without attending the Royal Military College; the plan is known as Direct-Entry Officer (DEO) Plan. Senior NCOs may also be offered commissions on the basis that their training and experience gives them a comparable basis of knowledge; this is referred to as the Commission-from-the-Ranks (CFR) Plan. NCOs who are offered such promotions are typically petty officer 1st class or higher, with 20 or more years of service.
Officers
The Royal Canadian Navy rank structure is shown below.
| Commander-in-Chief |
|---|
 |
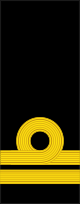
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | Student officer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Edit) |
No equivalent | _OF-9.svg.png) 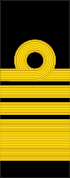 |
_OF-8.svg.png)  |
_OF-7.svg.png)  |
_OF-6.svg.png)  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | .svg.png) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Admiral | Vice-admiral | Rear-admiral | Commodore | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant-commander | Lieutenant | Sub-lieutenant | Acting sub-lieutenant | Naval cadet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amiral | Vice-amiral | Contre-amiral | Commodore | Capitaine de vaisseau | Capitaine de frégate | Capitaine de corvette | Lieutenant de vaisseau | Enseigne de vaisseau de 1re classe | Enseigne de vaisseau de 2e classe | Aspirant de marine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-commissioned members
Non-commissioned members of the Royal Canadian Navy have pay grades ranging from OR-2 to OR-9. OR-9 (chief petty officer 1st class), OR-8 (chief petty officers 2nd class) and OR-7 (petty officer 1st class) are known as petty officers, and together with OR-6 (petty officer 2nd class, referred to as senior non-commissioned officer) form the senior cadre of the non-commissioned (enlisted) members of the military. OR-5 (master seaman) and OR-4 (leading seaman) are referred to as junior non-commissioned officers, while OR-3 (able seaman) and OR-2 (ordinary seaman) are referred to as junior ranks.
All Regular Force non-commissioned members of the Canadian Forces undergo basic training at the Canadian Forces Leadership and Recruit School in Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu. Recruits then attend occupation-specific training at various locations across Canada.
| Senior non-commissioned appointments of the Royal Canadian Navy | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian Forces Chief Warrant Officer | Chief Petty Officer of the Navy | Formation Chief Petty Officer | |||||
 |
 |
 | |||||
| Non-commissioned member rank structure of the Royal Canadian Navy | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chief Petty Officer 1st class | Chief Petty Officer 2nd class | Petty Officer 1st class | Petty Officer 2nd class | Master Seaman | Leading Seaman | Able Seaman | Ordinary Seaman |
| OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| CPO1 | CPO2 | PO1 | PO2 | MS | LS | AB | OS |
Traditions
Colours


The queen's or king's colours (also referred to as the sovereign's colour) for the navy have been consecrated and presented four times: in 1939 by King George VI in Esquimalt, in 1959 by Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Phillip in Halifax, in 1979 by Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother in Halifax and in 2009 by the Governor General of Canada and Commander-in-Chief Michaëlle Jean in Halifax.[21] On each occasion two identical colours were presented, one for the Atlantic fleet and one for the Pacific fleet. The current colours consist of a ceremonial standard with the Maple Leaf flag in the top left canton, the monarch's royal cypher for Canada (a capital E on a blue background, surrounded by a circlet of gold Tudor roses and laurels, surmounted by a crown) and an anchor (from the Canadian Naval Ensign) on the lower right fly. These elements are found on the 1979 and 2009 colours. The colours from 1959 and 1939 consisted of a White Ensign with the queen's or king's cypher in the middle.[21]
The use of the service colours of the Royal Navy were granted to the RCN in 1925. Two service colours were sent to Halifax and Esquimalt. In 1937 they were retired, and new colours sent. The official presentation of the king's colour was not completed until 1939.[21] The Royal Canadian Navy's retired colours are laid up at Beechwood Cemetery in Ottawa, Ontario.[21]
Badge of the Royal Canadian Navy
The badge of the Royal Canadian Navy consists of:[22]
- St. Edward's Crown
- Maple leaf compartment
- a fouled anchor, within a circlet
- Motto "Ready aye ready" in Latin
Heritage
This history of Royal Canadian Navy is preserved and presented at the Maritime Command Museum in Halifax, the Canadian War Museum, the Naval Museum of Alberta and naval museums at Naval Reserve Headquarters in Quebec City and at CFB Esquimalt as well as the Maritime Museum of British Columbia. Several Royal Canadian Navy ships and submarines have been preserved including the destroyer HMCS Haida, the hydrofoil HMCS Bras d'Or and the submarines Ojibwa and Onondaga. The corvette HMCS Sackville serves as Canada's Naval Memorial. The Royal Canadian Navy Monument is located on the banks of the Ottawa River in Ottawa. A monument at Point Pleasant Park in Halifax commemorates members of Royal Canadian Navy who have died in peacetime and there are valour memorials in Halifax, Quebec City and Esquimalt.
Memorials


- "Royal Canadian Naval Association Naval Memorial (1995)" by André Gauthier (sculptor) was erected on the shore of Lake Ontario in Spencer Smith Park in Burlington, Ontario. The 6 ft 4 in (1.93 m) high cast bronze statue depicts a Second World War Canadian sailor in the position of attention saluting his lost shipmates. The model for the statue was a local Sea Cadet wearing Mike Vencel's naval service uniform.[23] On the black granite base, the names of Royal Canadian Navy and Canadian Merchant Navy ships sunk during the Second World War are engraved.[24]
- A commemorative plaque in SS Point Pleasant Park, Halifax, Nova Scotia unveilled in 1967, "When the United Kingdom declared war on Germany in 1914, Canada and Newfoundland's participation was virtually unquestioned. With the onset of the Second World War in 1939 Canadians and Newfoundlanders once more rushed to enlist and were a major factor in the Allied victories in both conflicts. During two world wars the main duty of the Royal Canadian Navy was to escort convoys in the Atlantic and guard merchant vessels against the threat of attack by German submarines. In the Second World War, it also escorted ships in the Mediterranean and to Russia and supported the Allied landings in Sicilian, Italian and Normandy campaigns as well as in the Pacific. The Canadian Merchant Navy's duties included the transportation of troops and supplies to the Allied armies and food for the United Kingdom, extremely dangerous work which resulted in considerable losses."
- At the Maritime Museum of the Atlantic in Halifax, Nova Scotia. "In memory of 2200 known Canadian Merchant Seamen and 91 Canadian vessels lost by enemy action and those who served in the cause of freedom – World War I 1914–1918; World War II 1939–1945; Korean Conflict 1950–1953"

 Halifax Memorial, Point Pleasant Park dedicated to the Canadian servicemen and women who died at sea during both World Wars and includes the Korean War
Halifax Memorial, Point Pleasant Park dedicated to the Canadian servicemen and women who died at sea during both World Wars and includes the Korean War
See also
References
- Notes
- The Department of National Defence and the Canadian Forces
- 1 2 "Canada’s Navy at a Glance". National Defence and the Canadian Forces. 16 August 2011. Archived from the original on 17 August 2011.
- ↑ "Senior Officer Biography: Vice-Admiral Norman M.A.G. , CMM, CD". Royal Canadian Navy. 2013-06-25. Retrieved 2013-07-13.
- ↑ Maritime Forces Atlantic, Royal Canadian Navy, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Rear-Admiral Nigel S. Greenwood, Royal Canadian Navy, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Canada Begins Joint Support Ships Procurement for the Canadian Forces, National Defence and the Canadian Forces, 14 July 2010, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Arctic/Offshore Patrol Ships, National Defence and the Canadian Forces, 5 August 2011, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Halifax-Class Modernization And Life Extension, National Defence and the Canadian Forces, 1 October 2010, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Maritime Helicopter Project, National Defence and the Canadian Forces, 26 July 2010, archived from the original on 17 August 2011
- ↑ Royal Canadian Navy Rank and Appointment Insignia, Royal Canadian Navy, 16 August 2011, archived from the original on 19 August 2011
- Other references
- ↑ Gilbert Norman Tucker The Naval Service of Canada: Its Official History Ottawa, 1952
- ↑ Tucker, Gibert Norman. The Naval Service of Canada: Volume I: Origins and Early Years. Ottawa: King's Printer, 1952, p. 137.
- ↑ Milner, Marc. "Walter Hose To The Rescue: Navy, Part 13." Legion Magazine, 1 January 2006. Retrieved: 2 May 2010.
- ↑ Schull, Joseph. Far Distant Ships: An Official Account of Canadian Naval Operations in World War II. Ottawa: King's Printer, 1952 – reprinted by Stoddart Publishing, Toronto, 1987, p. 1. ISBN 0-7737-2160-6.
- ↑ Personnel, Government of Canada, National Defence, Chief Military. "Official Histories". www.cmp-cpm.forces.gc.ca. Retrieved 2016-02-21.
- ↑ Schull, Joseph, p.430-1
- ↑ Royal Canadian Naval Reserve – Scheme for Training Yacht Club Members
- ↑ Thorgrimsson, Thor and E.C. Russell. Canadian Naval Operations in Korean Waters, 1950–1955. Ottawa: Queen's Printer, 1965. Retrieved: 9 May 2010.
- ↑ Milner. Marc. Canada's Navy: The First Century. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1999, pp. 207–209. ISBN 0-8020-4281-3.
- ↑ Gilmore, Scott. "The Sinking of the Canadian Navy". Maclean's. Maclean's. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "Canada Taps German Design for Navy's Support Ships". DefenseNews. 11 June 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ↑ "Names chosen for the Royal Canadian Navy's new Joint Support Ships". Royal Canadian Navy. Government of Canada. 25 October 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ↑ "Names chosen for the Royal Canadian Navy's new Joint Support Ships". navyrecognition.com. 30 November 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ↑ "PM announces the name of the first of the Royal Canadian Navy’s Arctic/Offshore Patrol Ships". Prime Minister of Canada. 18 September 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2014.
- ↑ Rosamond, Joe (4 October 2015). "Canada turns to Asterix for stop gap at-sea support". janes.com. Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ↑ Pugliese, David (27 October 2015). "Royal Canadian Navy to be given option to purchase interim supply ship". Ottawa Citizen. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ↑ Lavoie, Raphaël (9 October 2015). "Davie : le MS Asterix arrive à Lévis". Le Journal de Lévis (in French). Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ↑ Cudmore, James (20 November 2015). "Davie interim supply ship $700M deal delayed by Liberals". CBC News. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
- ↑ Cudmore, James (30 November 2015). "Davie Shipyard's $700M deal for navy supply ship retrofit to go ahead". CBC News. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Queen's Colours (Canada)". Flagspot. Retrieved 4 March 2011.
- ↑ "Royal Canadian Navy". Public Register of Arms, Flags and Banners. Governor General of Canada. Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ Royal Canadian Naval Association Naval Memorial
- ↑ "Public Art Inventory". 25 May 2010.
Further reading
- Armstrong, John Griffith. The Halifax Explosion and the Royal Canadian Navy: Inquiry and Intrigue (Vol. 1. UBC Press, 2002)
- Auchterlonie, Lieutenant Commander JR Bob. "Meeting the Challenge: The Canadian Navy in the New Strategic Environment." (Toronto: Canadian Forces College Command and Staff Course Masters Thesis Paper, 2004). online
- Douglas, W. A. B. and Michael Whitby. A Blue Water Navy: The Official Operational History of the Royal Canadian Navy in the Second World War, 1943–1945.
- German, Tony. The sea is at our gates: the history of the Canadian navy (McClelland & Stewart, 1990)
- Gimblett, Richard H., and Michael L. Hadley, eds. Citizen Sailors: Chronicles of Canada's Naval Reserve, 1910–2010 (Dundurn, 2010)
- Hadley, Michael L (1996), A nation's navy: in quest of Canadian naval identity, McGill-Queen's University Press, ISBN 0-7735-1506-2
- Huebert, Rob. "Submarines, Oil Tankers, and Icebreakers: Trying to Understand Canadian Arctic Sovereignty and Security." International Journal 66 (2010): 809.
- Milner, Marc (2010), Canada's Navy: The First Century, Univ. of Toronto Press
- Milner, Marc. North Atlantic run: the Royal Canadian Navy and the battle for the convoys (University of Toronto Press, 1985)
- Morton, Desmond. A military history of Canada (Random House LLC, 2007)
- Parker, Mike. Running the Gauntlet: An Oral History of Canadian Merchant Seamen in World War II (Nimbus, 1994)
- Pritchard, James. A Bridge of Ships: Canadian Shipbuilding During the Second World War (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2011)
- Rawling, William. "The Challenge of Modernization: The Royal Canadian Navy and Antisubmarine Weapons, 1944–1945." Journal of Military History 63 (1999): 355–378. in JSTOR
- Schull, Joseph. Lointoins navires: compte rendu official des operations de la Marine canadienne au cours de la seconde Grande Guerre. Ottawa, Ont.: E. Cloutier, 1953. N.B.: "Publié d'ordre du ministre de la Défense nationale."
- Tracy, Nicholas. Two-Edged Sword: The Navy as an Instrument of Canadian Foreign Policy (McGill-Queen's Press-MQUP, 2012)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Royal Canadian Navy. |
- Official website
- Royal Canadian Navy photographs taken by sailors in action.

