Sweet potato
| Sweet potato | |
|---|---|
_Flower.jpg) | |
| Sweet potato in flower in Hong Kong | |
| | |
| Sweet potato roots | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Ipomoea |
| Species: | I. batatas |
| Binomial name | |
| Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. | |
The sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the family Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting, tuberous roots are a root vegetable.[1][2] The young leaves and shoots are sometimes eaten as greens. The sweet potato is only distantly related to the potato (Solanum tuberosum) and does not belong to the nightshade family, Solanaceae, but both families belong to the same taxonomic order, the Solanales.
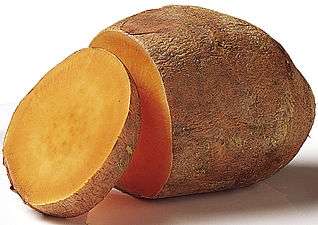
The plant is a herbaceous perennial vine, bearing alternate heart-shaped or palmately lobed leaves and medium-sized sympetalous flowers. The edible tuberous root is long and tapered, with a smooth skin whose color ranges between yellow, orange, red, brown, purple, and beige. Its flesh ranges from beige through white, red, pink, violet, yellow, orange, and purple. Sweet potato cultivars with white or pale yellow flesh are less sweet and moist than those with red, pink or orange flesh.[3]
Ipomoea batatas is native to the tropical regions in the Americas.[4][5] Of the approximately 50 genera and more than 1,000 species of Convolvulaceae, I. batatas is the only crop plant of major importance—some others are used locally (e.g. I. aquatica "kangkong"), but many are poisonous. The genus Ipomoea that contains the sweet potato also includes several garden flowers called morning glories, though that term is not usually extended to Ipomoea batatas. Some cultivars of Ipomoea batatas are grown as ornamental plants under the name tuberous morning glory, used in a horticultural context.

Naming
Although the soft, orange sweet potato is often called a "yam" in parts of North America, the sweet potato is botanically very distinct from a genuine yam (Dioscorea), which is native to Africa and Asia and belongs to the monocot family Dioscoreaceae. To add to the confusion, a different crop plant, the oca (Oxalis tuberosa, a species of wood sorrel), is called a "yam" in many parts of Polynesia, including New Zealand. The United States Department of Agriculture requires that the label "yam" always be accompanied by "sweet potato" in U.S. retail sales of sweet potato.[6]
Although the sweet potato is not closely related botanically to the common potato, they have a shared etymology. The first Europeans to taste sweet potatoes were members of Christopher Columbus's expedition in 1492. Later explorers found many cultivars under an assortment of local names, but the name which stayed was the indigenous Taino name of batata. The Spanish combined this with the Quechua word for potato, papa, to create the word patata for the common potato.
In Argentina, Venezuela, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic the sweet potato is called batata. In Mexico, Peru, Chile, Central America, and the Philippines, the sweet potato is known as camote (alternatively spelled kamote in the Philippines), derived from the Nahuatl word camotli.[7]
In Peru, the Quechua name for a type of sweet potato is kumar, strikingly similar to the Polynesian name kumara and its regional Oceanic cognates (kumala, umala, 'uala, etc.), which has led some scholars to suspect an instance of pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact.
In New Zealand, the most common cultivar is the red (purple) cultivar called kumara, a name derived from the Māori name kūmara, but orange ('Beauregard') and gold cultivars are also available.[8] Kumara is particularly popular as a roasted food, or in contemporary cuisine as kumara chips, often served with sour cream and sweet chili sauce. Occasionally, shops in Australia will label purple cultivars as "purple sweet potato" to denote the difference to the other cultivars. About 95% of Australia's production is of the orange cultivar named 'Beauregard', originally from North America, known simply as "sweet potato". A reddish-purple cultivar, 'Northern Star', is 4% of production and is sold as "kumara".
Origin, distribution and diversity
The origin and domestication of sweet potato is thought to be in either Central America or South America.[9] In Central America, sweet potatoes were domesticated at least 5,000 years ago.[10] In South America, Peruvian sweet potato remnants dating as far back as 8000 BC have been found.
One author postulated that the origin of I. batatas was between the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico and the mouth of the Orinoco River in Venezuela.[11] The 'cultigen' had most likely been spread by local people to the Caribbean and South America by 2500 BC.[12] Strong supporting evidence was provided that the geographical zone postulated by Austin is the primary center of diversity.[11] The much lower molecular diversity found in Peru–Ecuador suggests this region should be considered as a secondary center of sweet potato diversity.
The sweet potato was grown in Polynesia before western exploration. Sweet potato has been radiocarbon-dated in the Cook Islands to 1000 AD, and current thinking is that it was brought to central Polynesia around 700 AD, possibly by Polynesians who had traveled to South America and back, and spread across Polynesia to Hawaii and New Zealand from there.[13][14] It is possible, however, that South Americans brought it to the Pacific, although this is unlikely as it was the Polynesians who had a strong maritime tradition and not the Native South Americans. The theory that the plant could spread by floating seeds across the ocean is not supported by evidence. Another point is that the sweet potato in Polynesia is the cultivated Ipomoea batatas, which is generally spread by vine cuttings and not by seeds.[15]
Sweet potatoes are cultivated throughout tropical and warm temperate regions wherever there is sufficient water to support their growth.[16] Due to a major crop failure, sweet potatoes were introduced to Fujian province of China in about 1594 from Luzon. The growing of sweet potatoes was encouraged by the Governor Chin Hsüeh-tseng (Jin Xuezeng).[17][18] Sweet potatoes were introduced as a food crop in Japan, and by 1735 were planted in Shogun Tokugawa Yoshimune's private garden.[19] It was also introduced to Korea in 1764.[20]
Sweet potatoes became popular very early in the islands of the Pacific Ocean, spreading from Polynesia to Japan and the Philippines. One reason is that they were a reliable crop in cases of crop failure of other staple foods because of typhoon flooding. They are featured in many favorite dishes in Japan, Taiwan, the Philippines, and other island nations. Indonesia, Vietnam, India, and some other Asian countries are also large sweet potato growers. Sweet potato, also known as kelang in Tulu, is part of Udupi cuisine in South India. Uganda (the second largest grower after China), Rwanda, and some other African countries also grow a large crop which is an important part of their peoples' diets. The New World, the original home of the sweet potato, grows less than three percent (3%) of the world's supply. Europe has only a very small sweet potato production, mainly in Portugal. In the Caribbean, a cultivar of the sweet potato called the boniato is popular. The flesh of the boniato is cream-colored, unlike the more popular orange hue seen in other cultivars. Boniatos are not as sweet and moist as other sweet potatoes, but many people prefer their fluffier consistency and more delicate flavor.
Sweet potatoes have been an important part of the diet in the United States for most of its history, especially in the Southeast. From the middle of the 20th century, however, they have become less popular. The average per capita consumption of sweet potatoes in the United States is only about 1.5–2 kg (3.3–4.4 lb) per year, down from 13 kg (29 lb) in 1920. Southerner Kent Wrench writes: "The Sweet Potato became associated with hard times in the minds of our ancestors and when they became affluent enough to change their menu, the potato was served less often."[21]
Transgenicity
A study published in 2015 by scientists from Ghent University and the International Potato Center found that the genome of cultivated sweet potatoes contains sequences of DNA from Agrobacterium, with genes being actively expressed by the plants. The discovery of the transgenes was made while performing metagenomic analysis of the sweet potato genome for viral diseases. Transgenes were observed both in the sweet potato's closely related wild relatives, and also were found in more distantly related wild species. This observation makes cultivated sweet potatoes the first known example of a naturally transgenic food crop.[22][23]
Cultivation
| Producers (in million tonnes)[24] Data for year 2011 | |
|---|---|
| China | 81.7 |
| Uganda | 2.8 |
| Nigeria | 2.8 |
| Indonesia | 2.0 |
| Tanzania | 1.4 |
| Vietnam | 1.3 |
| India | 1.1 |
| United States | 1.0 |
| World | 106.5 |
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 359 kJ (86 kcal) |
|
20.1 g | |
| Starch | 12.7 g |
| Sugars | 4.2 g |
| Dietary fiber | 3 g |
|
0.1 g | |
|
1.6 g | |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A equiv. |
(89%) 709 μg (79%) 8509 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(7%) 0.078 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(5%) 0.061 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(4%) 0.557 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(16%) 0.8 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(16%) 0.209 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(3%) 11 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(3%) 2.4 mg |
| Vitamin E |
(2%) 0.26 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(3%) 30 mg |
| Iron |
(5%) 0.61 mg |
| Magnesium |
(7%) 25 mg |
| Manganese |
(12%) 0.258 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(7%) 47 mg |
| Potassium |
(7%) 337 mg |
| Sodium |
(4%) 55 mg |
| Zinc |
(3%) 0.3 mg |
|
| |
| |
|
Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database | |
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 378 kJ (90 kcal) |
|
20.7 g | |
| Starch | 7.05 g |
| Sugars | 6.5 g |
| Dietary fiber | 3.3 g |
|
0.15 g | |
|
2.0 g | |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A equiv. |
(120%) 961 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(10%) 0.11 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(9%) 0.11 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(10%) 1.5 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(22%) 0.29 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(2%) 6 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(24%) 19.6 mg |
| Vitamin E |
(5%) 0.71 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(4%) 38 mg |
| Iron |
(5%) 0.69 mg |
| Magnesium |
(8%) 27 mg |
| Manganese |
(24%) 0.5 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(8%) 54 mg |
| Potassium |
(10%) 475 mg |
| Sodium |
(2%) 36 mg |
| Zinc |
(3%) 0.32 mg |
|
| |
| |
|
Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database | |
The plant does not tolerate frost. It grows best at an average temperature of 24 °C (75 °F), abundant sunshine and warm nights. Annual rainfalls of 750–1,000 mm (30–39 in) are considered most suitable, with a minimum of 500 mm (20 in) in the growing season. The crop is sensitive to drought at the tuber initiation stage 50–60 days after planting, and it is not tolerant to water-logging, as it may cause tuber rots and reduce growth of storage roots if aeration is poor.[25]
Depending on the cultivar and conditions, tuberous roots mature in two to nine months. With care, early-maturing cultivars can be grown as an annual summer crop in temperate areas, such as the northern United States and China. Sweet potatoes rarely flower when the daylight is longer than 11 hours, as is normal outside of the tropics. They are mostly propagated by stem or root cuttings or by adventitious shoots called "slips" that grow out from the tuberous roots during storage. True seeds are used for breeding only.
They grow well in many farming conditions and have few natural enemies; pesticides are rarely needed. Sweet potatoes are grown on a variety of soils, but well-drained, light- and medium-textured soils with a pH range of 4.5-7.0 are more favorable for the plant.[2] They can be grown in poor soils with little fertilizer. However, sweet potatoes are very sensitive to aluminum toxicity and will die about six weeks after planting if lime is not applied at planting in this type of soil.[2] Because they are sown by vine cuttings rather than seeds, sweet potatoes are relatively easy to plant. Because the rapidly growing vines shade out weeds, little weeding is needed. A commonly used herbicide to rid the soil of any unwelcome plants that may interfere with growth is DCPA, also known as Dacthal. In the tropics, the crop can be maintained in the ground and harvested as needed for market or home consumption. In temperate regions, sweet potatoes are most often grown on larger farms and are harvested before first frosts.
In the Southeastern United States, sweet potatoes are traditionally cured to improve storage, flavor, and nutrition, and to allow wounds on the periderm of the harvested root to heal.[21] Proper curing requires drying the freshly dug roots on the ground for two to three hours, then storage at 29–32 °C (85–90 °F) with 90 to 95% relative humidity from five to fourteen days. Cured sweet potatoes can keep for thirteen months when stored at 13–15 °C (55–59 °F) with >90% relative humidity. Colder temperatures injure the roots.[26][27]
Yields
In 2010, the world average annual yield for sweet potato crop was 13.2 tonnes per hectare. The most productive farms of sweet potato breeds were in Senegal, where the nationwide average annual yield was 33.3 tonnes per hectare.[28] Yields as high as 80 metric tonnes per hectare have been reported from farms of Israel.[29]
Diseases
Production
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) statistics, world production in 2004 was 127 million tonnes.[30] The majority comes from China, with a production of 105 million tonnes from 49,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi). About half of the Chinese crop is used for livestock feed.[10]
Per capita production is greatest in countries where sweet potatoes are a staple of human consumption, led by Papua New Guinea at about 500 kg (1,100 lb)[31] per person per year, the Solomon Islands at 160 kg (350 lb), Burundi and Rwanda[32] at 130 kg (290 lb) and Uganda at 100 kg (220 lb).
About 20,000 tonnes of sweet potatoes are produced annually in New Zealand, where sweet potato is known by its Māori name, kūmara. It was a staple food for Māori before European contact.[33]
In the United States, North Carolina, the leading state in sweet potato production, provided 38.5% of the 2007 U.S. production of sweet potatoes. In 2007, California produced 23%, Louisiana 15.9%, and Mississippi 19% of the U.S. total.[34][35]
Mississippi has about 150 farmers growing sweet potatoes on about 8,200 acres (30 km2), contributing $19 million to the state's economy. Mississippi's top five sweet-potato-producing counties are Calhoun, Chickasaw, Pontotoc, Yalobusha, and Panola. The National Sweet Potato Festival is held annually the entire first week in November in Vardaman (Calhoun County), which proclaims itself as "The Sweet Potato Capital".
Nutrient content
Besides simple starches, raw sweet potatoes are rich in complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber and beta-carotene (a provitamin A carotenoid), while having moderate contents of other micronutrients, including vitamin B5, vitamin B6 and manganese (table).[36] When cooked by baking, small variable changes in micronutrient density occur to include a higher content of vitamin C at 24% of the Daily Value per 100 g serving (right table).[37][38]
The Center for Science in the Public Interest ranked the nutritional value of sweet potatoes as highest among several other foods.[39]
Sweet potato cultivars with dark orange flesh have more beta-carotene than those with light-colored flesh, and their increased cultivation is being encouraged in Africa where vitamin A deficiency is a serious health problem. A 2012 study of 10,000 households in Uganda found that children eating beta-carotene enriched sweet potatoes suffered less vitamin A deficiency than those not consuming as much beta-carotene.[40]
Comparison to other food staples
The table below presents the relative performance of sweet potato to other food staples. While sweet potato provides less edible energy and protein per unit weight than cereals, it has higher nutrient density than cereals.[41]
| Nutrient component: | Maize / Corn[A] | Rice (white)[B] | Rice (brown)[I] | Wheat[C] | Potato[D] | Cassava[E] | Soybean (Green)[F] | Sweet potato[G] | Yam[Y] | Sorghum[H] | Plantain[Z] | RDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (g) | 10 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 79 | 60 | 68 | 77 | 70 | 9 | 65 | 3000 |
| Energy (kJ) | 1528 | 1528 | 1549 | 1369 | 322 | 670 | 615 | 360 | 494 | 1419 | 511 | 8368–10,460 |
| Protein (g) | 9.4 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.6 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 13.0 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 11.3 | 1.3 | 50 |
| Fat (g) | 4.74 | 0.66 | 2.92 | 1.54 | 0.09 | 0.28 | 6.8 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 3.3 | 0.37 | |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 74 | 80 | 77 | 71 | 17 | 38 | 11 | 20 | 28 | 75 | 32 | 130 |
| Fiber (g) | 7.3 | 1.3 | 3.5 | 12.2 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 4.2 | 3 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 30 |
| Sugar (g) | 0.64 | 0.12 | 0.85 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.18 | 0.5 | 0 | 15 | |
| Calcium (mg) | 7 | 28 | 23 | 29 | 12 | 16 | 197 | 30 | 17 | 28 | 3 | 1000 |
| Iron (mg) | 2.71 | 0.8 | 1.47 | 3.19 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 8 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 127 | 25 | 143 | 126 | 23 | 21 | 65 | 25 | 21 | 0 | 37 | 400 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 210 | 115 | 333 | 288 | 57 | 27 | 194 | 47 | 55 | 287 | 34 | 700 |
| Potassium (mg) | 287 | 115 | 223 | 363 | 421 | 271 | 620 | 337 | 816 | 350 | 499 | 4700 |
| Sodium (mg) | 35 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 14 | 15 | 55 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 1500 |
| Zinc (mg) | 2.21 | 1.09 | 2.02 | 2.65 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.99 | 0.3 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.14 | 11 |
| Copper (mg) | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.18 | - | 0.08 | 0.9 | |
| Manganese (mg) | 0.49 | 1.09 | 3.74 | 3.99 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.40 | - | - | 2.3 |
| Selenium (μg) | 15.5 | 15.1 | 70.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0 | 1.5 | 55 | |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.7 | 20.6 | 29 | 2.4 | 17.1 | 0 | 18.4 | 90 |
| Thiamin (B1)(mg) | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 1.2 |
| Riboflavin (B2)(mg) | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 1.3 |
| Niacin (B3) (mg) | 3.63 | 1.6 | 5.09 | 5.46 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 1.65 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 2.93 | 0.69 | 16 |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) (mg) | 0.42 | 1.01 | 1.49 | 0.95 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.80 | 0.31 | - | 0.26 | 5 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.3 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.29 | - | 0.30 | 1.3 |
| Folate Total (B9) (μg) | 19 | 8 | 20 | 38 | 16 | 27 | 165 | 11 | 23 | 0 | 22 | 400 |
| Vitamin A (IU) | 214 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 13 | 180 | 14187 | 138 | 0 | 1127 | 5000 |
| Vitamin E, alpha-tocopherol (mg) | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 0 | 0.14 | 15 |
| Vitamin K1 (μg) | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 0 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 0 | 0.7 | 120 |
| Beta-carotene (μg) | 97 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 8509 | 83 | 0 | 457 | 10,500 | |
| Lutein+zeaxanthin (μg) | 1355 | 0 | 220 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 | ||
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.14 | |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 1.25 | 0.21 | 1.05 | 0.2 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 1.28 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.03 | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 2.16 | 0.18 | 1.04 | 0.63 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 3.20 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 1.37 | 0.07 |
| A yellow corn | B raw unenriched long-grain white rice | ||||||||
| C hard red winter wheat | D raw potato with flesh and skin | ||||||||
| E raw cassava | F raw green soybeans | ||||||||
| G raw sweet potato | H raw sorghum | ||||||||
| Y raw yam | Z raw plantains | ||||||||
| I raw long-grain brown rice |
Culinary uses
Although the leaves and shoots are also edible, the starchy tuberous roots are by far the most important product. In some tropical areas, they are a staple food crop.
Africa
Amukeke (sun-dried slices of root) and inginyo (sun-dried crushed root) are a staple food for people in northeastern Uganda.[43] Amukeke is mainly served for breakfast, eaten with peanut sauce. Inginyo is mixed with cassava flour and tamarind to make atapa. People eat atapa with smoked fish cooked in peanut sauce or with dried cowpea leaves cooked in peanut sauce. Emukaru (earth-baked root) is eaten as a snack anytime and is mostly served with tea or with peanut sauce. Similar uses are also found in South Sudan.
The young leaves and vine tips of sweet potato leaves are widely consumed as a vegetable in West African countries (Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia, for example), as well as in northeastern Uganda, East Africa.[43] According to FAO leaflet No. 13 - 1990, sweet potato leaves and shoots are a good source of vitamins A, C, and B2 (riboflavin), and according to research done by A. Khachatryan, are an excellent source of lutein.
In Kenya, Rhoda Nungo of the home economics department of the Ministry of Agriculture has written a guide to using sweet potatoes in modern recipes.[44] This includes uses both in the mashed form and as flour from the dried tubers to replace part of the wheat flour and sugar in baked products such as cakes, chapatis, mandazis, bread, buns and cookies. A nutritious juice drink is made from the orange-fleshed cultivars, and deep-fried snacks are also included.
In Egypt, sweet potato tubers are known as "batata" (بطاطا) and are a common street food in winter, when street vendors with carts fitted with ovens sell them to people passing time by the Nile or the sea. The cultivars used are an orange-fleshed one as well as a white/cream-fleshed one. They are also baked at home as a snack or dessert, drenched with honey.
In Ethiopia, the commonly found cultivars are black-skinned, cream-fleshed and called "bitatis" or "mitatis". They are cultivated in the eastern and southern lower highlands and harvested during the rainy season (June/July). In recent years, better yielding orange-fleshed cultivars were released for cultivation by Haramaya University as a less sugary sweet potato with higher vitamin A content.[45] Sweet potatoes are widely eaten boiled as a favored snack providing calories and carbohydrates.
Asia

_2.jpg)
_2.jpg)




In East Asia, roasted sweet potatoes are popular street food. In China, sweet potatoes, typically yellow cultivars, are baked in a large iron drum and sold as street food during winter. In Korea, sweet potatoes, known as goguma, are roasted in a drum can, baked in foil or on an open fire, typically during winter. Roasted sweet potato is called gun-goguma and sold as street food. In Japan, a dish similar to the Korean preparation is called yaki-imo (roasted sweet potato), which typically uses either the yellow-fleshed "Japanese sweet potato" or the purple-fleshed "Okinawan sweet potato", which is known as beni-imo.
Sweet potato soup, served during winter, consists of boiling sweet potato in water with rock sugar and ginger. Sweet potato greens are a common side dish in Taiwanese cuisine, often boiled or sautéed and served with a garlic and soy sauce mixture, or simply salted before serving. They, as well as dishes featuring the sweet potato root, are commonly found at bento (Pe̍h-ōe-jī: piān-tong) restaurants. In northeastern Chinese cuisine, sweet potatoes are often cut into chunks and fried, before being drenched into a pan of boiling syrup.[46]
In some regions of India, fasts of religious nature are an occasion for a change in normal diet, and a total absence from cooking or eating is held as elective while a normal diet for a fasting day is a light feast consisting of different foods from usual, amongst which sweet potato is one of the prime sources of sustenance. Sweet potato – shakarkand, शक्करकंद – is eaten otherwise, too, and a popular variety of preparation in most parts is roasted slow over kitchen coals at night and eaten with some dressing—primarily salt, possibly yogurt—while the easier way in the south is simply boiling or pressure cooking before peeling, cubing and seasoning for a vegetable dish as part of the meal. In Indian state of Tamil Nadu, it is known as 'Sakkara valli Kilangu'. It is boiled and consumed as evening snack. In some parts of India, fresh sweet potato is chipped, dried and then ground into flour; this is then mixed with wheat flour and baked into chapattis (bread). Between 15 and 20 percent of sweet potato harvest is converted by some Indian communities into pickles and snack chips. A part of the tuber harvest is used in India as cattle fodder.[3]
In Sri Lanka, it is called 'Bathala' (බතල in sinhala language) and tubers are used mainly for breakfast (boiled sweet potato commonly with sambal or grated coconut) or as an supplementary curry dish for rice. There are many other culinary uses with sweet potato as well.
The tubers of this plant, known as kattala in Dhivehi, have been used in the traditional diet of the Maldives. The leaves were finely chopped and used in dishes such as mas huni.[47]
In Japan, both sweet potatoes (called "satsuma-imo") and true purple yams (called "daijo" or "beni-imo") are grown. Boiling and steaming are the most common cooking methods. Also, the use in vegetable tempura is common. Daigaku-imo is a baked sweet potato dessert. Because it is sweet and starchy, it is used in imo-kinton and some other traditional sweets, such as ofukuimo. Shōchū, a Japanese spirit normally made from the fermentation of rice, can also be made from sweet potato, in which case it is called imo-jōchū. Imo-gohan, sweet potato cooked with rice, is popular in Guangdong, Taiwan and Japan. It is also served in nimono or nitsuke, boiled and typically flavored with soy sauce, mirin and dashi. In Korean cuisine, sweet potato starch is used to produce dangmyeon (cellophane noodles). Sweet potatoes are also boiled, steamed, or roasted, and young stems are eaten as namul. Pizza restaurants such as Pizza Hut and Domino's in Korea are using sweet potatoes as a popular topping. Sweet potatoes are also used in the distillation of a variety of Soju.
In Malaysia and Singapore, sweet potato is often cut into small cubes and cooked with yam and coconut milk (santan) to make a sweet dessert called bubur caca or "bubu chacha". A favorite way of cooking sweet potato is deep frying slices of sweet potato in batter, and served as a tea-time snack. In homes, sweet potatoes are usually boiled. The leaves of sweet potatoes are usually stir-fried with only garlic or with sambal belacan and dried shrimp by Malaysians.
.jpg)
In the Philippines, sweet potatoes (locally known as camote or kamote) are an important food crop in rural areas. They are often a staple among impoverished families in provinces, as they are easier to cultivate and cost less than rice.[48] The tubers are boiled or baked in coals and may be dipped in sugar or syrup. Young leaves and shoots (locally known as talbos ng kamote or camote tops) are eaten fresh in salads with shrimp paste (bagoong alamang) or fish sauce. They can be cooked in vinegar and soy sauce and served with fried fish (a dish known as adobong talbos ng kamote), or with recipes such as sinigang.[48] The stew obtained from boiling camote tops is purple-colored, and is often mixed with lemon as juice. Sweet potatoes are also sold as street food in suburban and rural areas. Fried sweet potatoes coated with caramelized sugar and served in skewers (camote cue) are popular afternoon snacks.[49] Sweet potatoes are also used in a variant of halo-halo called ginatan, where they are cooked in coconut milk and sugar and mixed with a variety of rootcrops, sago, jackfruit and bilu-bilo (glutinous rice balls).[50] Bread made from sweet potato flour is also gaining popularity. Sweet potato is relatively easy to propagate, and in rural areas that can be seen abundantly at canals and dikes. The uncultivated plant is usually fed to pigs.
In Indonesia, sweet potatoes are locally known as ubi jalar (lit: spreading tuber) and are frequently fried with batter and served as snacks with spicy condiments, along with other kinds of fritters such as fried bananas, tempeh, tahu, breadfruits, or cassava. In the mountainous regions of West Papua, sweet potatoes are the staple food among the natives there. Using the bakar batu way of cooking (free translation: burning rocks), rocks that have been burned in a nearby bonfire are thrown into a pit lined with leaves. Layers of sweet potatoes, an assortment of vegetables, and pork are piled on top of the rocks. The top of the pile then is insulated with more leaves, creating a pressure of heat and steam inside which cooks all food within the pile after several hours.
Young sweet potato leaves are also used as baby food particularly in Southeast Asia and East Asia.[51][52] Mashed sweet potato tubers are used similarly throughout the world.[53]
North America

Candied sweet potatoes are a side dish consisting mainly of sweet potatoes prepared with brown sugar, marshmallows, maple syrup, molasses, orange juice, marron glacé, or other sweet ingredients. It is often served in America on Thanksgiving. Sweet potato casserole is a side dish of mashed sweet potatoes in a casserole dish, topped with a brown sugar and pecan topping.[54] Sweet potato pie is also a traditional favorite dish in Southern U.S. cuisine. Sweet potato slices are fried in bacon drippings and eaten with the bacon on toast. Sweet potato fries or chips are another common preparation, and are made by julienning and deep frying sweet potatoes, in the fashion of French fried potatoes. Sweet potato fries are served with a variety of condiments such as blue cheese salad dressing. Baked sweet potatoes are sometimes offered in restaurants as an alternative to baked potatoes. They are often topped with brown sugar and butter. Sweet potato butter can be cooked into a gourmet spread. Sweet potato mash is served as a side dish, often at Thanksgiving dinner or with barbecue. John Buttencourt Avila is called the "father of the sweet potato industry" in North America. Another variation on the typical sweet potato pie is the Okinawan (Sweet Potato) Haupie pie, which is made with purple sweet potatoes, native to the island of Hawaii and believed to have been originally cultivated as early as 500 AD.[55]
The town of Opelousas, Louisiana's "Yambilee" has been celebrated every October since 1946. The Frenchmen who established the first settlement at Opelousas in 1760 discovered the native Atakapa, Alabama, Choctaw, and Appalousa tribes eating sweet potatoes. The sweet potato became a favorite food item of the French and Spanish settlers and thus continued a long history of cultivation in Louisiana.[56]
The town of Benton, Kentucky, celebrates the sweet potato annually with its Tater Day Festival on the first Monday of April. The town of Gleason, Tennessee, celebrates the sweet potato on Labor Day weekend with its Tater Town Special. The town of Gilmer, Texas celebrates the East Texas Yamboree each year in October.
Sweet potatoes are recognized as the state vegetable of North Carolina.[57]
New Zealand
Before European contact, the Māori grew the small, yellow-skin, finger-sized kūmara known as taputini,[58] hutihuti and rekamaroa[59] that they had brought with them from east Polynesia. Modern trials have shown that the taputini was capable of producing well,[60] but when American whalers, sealers and trading vessels introduced larger cultivars in the early 19th century, they quickly predominated.[61][62][63][64]
In New Zealand, Māori traditionally cooked the kūmara in a hāngi earth oven. This is still a common practice when there are large gatherings on marae.
Currently there are three main cultivars or groups of cultivar (red, orange and gold) grown in the subtropical northern part of the North Island near Dargaville[65] and widely available throughout New Zealand year-round, where they are a popular alternative to potatoes.[66] The red cultivar has dull red skin and purple-streaked white flesh, and is the most popular. The orange cultivar is the same as the American 'Beauregard'. The gold kumara has pale, yellowish skin and flesh.
Kūmara are an integral part of roast meals in New Zealand. They are served alongside such vegetables as potatoes and pumpkin and, as such, are generally prepared in a savory manner. Kūmara are ubiquitous in supermarkets, roast meal takeaway shops and hāngi.
Other
Among the Urapmin people of Papua New Guinea, taro (known in Urap as ima) and the sweet potato (Urap: wan) are the main sources of sustenance, and in fact the word for "food" in Urap is a compound of these two words.[67]
In Spain, sweet potato is called boniato. On the evening of All Souls' Day, in Catalonia (northeastern Spain) it is traditional to serve roasted sweet potato and chestnuts, panellets and sweet wine. The occasion is called La Castanyada.[68] Sweet potato is also appreciated to make cakes or to eat roasted through the whole country.
In Peru, sweet potatoes are called 'camote' and are frequently served alongside ceviche. Sweet potato chips are also a commonly sold snack, be it on the street or in packaged foods.
Dulce de batata is a traditional Argentine, Paraguayan and Uruguayan dessert, which is made of sweet potatoes. It is a sweet jelly, which resembles a marmalade because of its color and sweetness but it has a harder texture, and it has to be sliced in thin portions with a knife as if it was a pie. It is commonly served with a portion of the same size of soft cheese on top of it.
In the Veneto (northeast Italy), sweet potato is known as patata mericana in the Venetian language (patata americana in Italian, meaning "American potato"), and it is cultivated above all in the southern area of the region;[69] it is a traditional fall dish, boiled or roasted.
Nonculinary uses

In South America, the juice of red sweet potatoes is combined with lime juice to make a dye for cloth. By varying the proportions of the juices, every shade from pink to black can be obtained.[70]
Purple sweet potato color is used as food coloring.[71]
All parts of the plant are used for animal fodder.
Sweet potatoes or camotes are often found in Moche ceramics.[72]
Several selections are cultivated in gardens as ornamental plants for their attractive foliage, including the dark-leafed cultivars 'Blackie' and 'Ace of Spades' and the chartreuse-foliaged 'Margarita'.
Cuttings of sweet potato vine, either edible or ornamental cultivars, will rapidly form roots in water and will grow in it, indefinitely, in good lighting with a steady supply of nutrients. For this reason, sweet potato vine is ideal for use in home aquariums, trailing out of the water with its roots submerged, as its rapid growth is fueled by toxic ammonia and nitrates, a waste product of aquatic life, which it removes from the water. This improves the living conditions for fish, which also find refuge in the vast root systems.
Researchers at North Carolina State University are breeding sweet potato cultivars that would be grown primarily for biofuel production.
Notes
- ↑ Purseglove, John Williams (1968). Tropical crops: Dicotyledons. Longman Scientific and Technical. New York: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 978-0-582-46666-1.
- 1 2 3 Woolfe, Jennifer A. (5 March 1992). Sweet Potato: An Untapped Food Resource. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press and the International Potato Center (CIP). ISBN 9780521402958.
- 1 2 Gad Loebenstein; George Thottappilly (2009). The sweetpotato. pp. 391–425. ISBN 978-1-4020-9475-0.
- ↑ "Ipomoea batatas". purdue.edu.
- ↑ "Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) Classification". uwlax.edu.
- ↑ "Sweet Potato or Yam? Which is which?". Foodreference.com. 20 March 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ↑ "Nahuatl Influences in Tagalog". El Galéon de Acapulco News, Embajada de México, Filipinas. Retrieved 16 February 2012.
- ↑ Yen, D. E. (1963). "The New Zealand Kumara or Sweet Potato". Economic Botany. 17 (1): 31–45. JSTOR 4252401. doi:10.1007/bf02985351.
- ↑ "Geneflow 2009". google.com.
- 1 2 Sweet Potato, Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research
- 1 2 Austin, Daniel F. (1988). "The taxonomy, evolution and genetic diversity of sweet potatoes and related wild species". In P. Gregory. Exploration, Maintenance, and Utilization of Sweet Potato Genetic Resources. First Sweet Potato Planning Conference, 1987. Lima, Peru: International Potato Center. pp. 27–60.
- ↑ Zhang, D.P.; Ghislain, M.; Huaman, Z.; Cervantes, J.C.; Carey, E.E. (1999). AFLP Assessment of Sweetpotato Genetic Diversity in Four Tropical American Regions (PDF). : International Potato Center (CIP) Program report 1997-1998. Lima, Peru: International Potato Center (CIP). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 April 2014.
- ↑ VAN TILBURG, Jo Anne. 1994. Easter Island: Archaeology, Ecology and Culture. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press
- ↑ "Gardening at the Edge: Documenting the Limits of Tropical Polynesian Kumara Horticulture in Southern New Zealand", University of Canterbury
- ↑ "Batatas, Not Potatoes". Botgard.ucla.edu. Archived from the original on 19 May 2008. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ↑ Stephen K. O'Hair (1990). "Tropical Root and Tuber Crops". In: J. Janick and J.E. Simon (eds.), Advances in new crops. Timber Press, Portland, OR. pp. 424–8. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ↑ Spence, Jonathan D. (1993). Chinese Roundabout: Essays in History and Culture (illustrated, reprint, revised ed.). W. W. Norton & Company. p. 167. ISBN 0393309940.
- ↑ Journal of Nanyang University, Volumes 5-6. Contributor 南洋大學. 新加坡南洋大學. 1971. p. 195.
- ↑ Takekoshi, Yosaburō. (1930). Economic Aspects of the History of the Civilization of Japan, p. 352.
- ↑ Kim, Jinwung. (2012). A History of Korea: From 'Land of the Morning Calm' to States in Conflict, p. 255.
- 1 2 North Carolina Sweet Potato Commission (NCSPC)
- ↑ Kyndt, Tina; Quispea, Dora; Zhaic, Hong; Jarretd, Robert; Ghislainb, Marc; Liuc, Qingchang; Gheysena, Godelieve; Kreuzeb, Jan F. (20 April 2015). "The genome of cultivated sweet potato contains Agrobacterium T-DNAs with expressed genes: An example of a naturally transgenic food crop". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112: 5844–5849. PMC 4426443
 . PMID 25902487. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419685112. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
. PMID 25902487. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419685112. Retrieved 23 April 2015. - ↑ "Sweet Potato Is a Natural GMO". genengnews.com. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Apr 22, 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ↑ FAO statistics (FAO)"Archived copy". Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ↑ Ahn, Peter (1993). Tropical soils and fertilizer use. Intermediate Trop. Agric. Series. UK: Longman Sci. and Tech. Ltd. ISBN 0-582-77507-8.
- ↑ "Sweetpotato: Organic Production - Publication Summary - ATTRA - National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service".
- ↑ US Davis Archived 5 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Crop Production, Worldwide, 2010 data". FAOSTAT, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2011. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015.
- ↑ James Duke (1983). "Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.". Purdue University.
- ↑ "Internet Archive Wayback Machine". fao.org.
- ↑ Bourke, R.M. and Vlassak, V.: Estimates of food crop production in Papua New Guinea, ANU Canberra, 2004
- ↑ "International Institute of Tropical Agriculture: Sweetpotato sub-sector market survey Rwanda, 2002" (PDF).
- ↑ WARDLE, P. 1991. The Vegetation of New Zealand. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press
- ↑ "Web Archives: View Archived Page" (PDF). cdlib.org.
- ↑ Top 10 Sweetpotato Growing Counties in North Carolina, ncsweetpotatoes.com
- ↑ "Sweet potato, raw, unprepared, includes USDA commodity food A230". Nutritiondata.com. Conde Nast. 2013. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- ↑ "Sweet potato, cooked, baked in skin, without salt". Nutritiondata.com. Conde Nast. 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ↑ Dincer, C; Karaoglan, M; Erden, F; Tetik, N; Topuz, A; Ozdemir, F (Nov 2011). "Effects of baking and boiling on the nutritional and antioxidant properties of sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] cultivars". Plant Foods for Human Nutrition. 66 (4): 341–7. PMID 22101780. doi:10.1007/s11130-011-0262-0.
- ↑ "Nutrition Action Health Letter: 10 Worst and Best Foods". Center for Science in the Public Interest. 2013. Archived from the original on 4 January 2014.
- ↑ Coghlan A (17 August 2012). "Nutrient-boosted foods protect against blindness". New Scientist, Health. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- ↑ Scott, Best, Rosegrant, and Bokanga (2000). "Roots and tubers in the global food system: A vision statement to the year 2020" (PDF). International Potato Center, and others. ISBN 92-9060-203-1.
- ↑ "Nutrient data laboratory". United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
- 1 2 Abidin, P.E. (2004). Sweetpotato breeding for northeastern Uganda: Farmer varieties, farmer-participatory selection, and stability of performance (PhD Thesis). The Netherlands: Wageningen University. p. 152 pp. ISBN 90-8504-033-7.
- ↑ Nutritious Kenyan Sweet Potato Recipes compiled by Rhoda A. Nungo, KARi, Kakamega 1994
- ↑ Tekalign Tsegaw and Nigussie Dechassa (2008). "Registration of Adu and Barkume: Improved Sweet Potato ( Ipomoea batatas ) Varieties for Eastern Ethiopia". East African Journal of Sciences. 2 (2): 189–191. doi:10.4314/eajsci.v2i2.40382.
- ↑ Chinese
- ↑ Xavier Romero-Frias, The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom. Barcelona 1999, ISBN 84-7254-801-5
- 1 2 "Fusion kamote". Editorials. The Manila Times (The Sunday Times), www.manilatimes.net. 16 March 2008. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ↑ Nicole J. Managbanag (25 October 2010). "Elections and banana cue". sunstar.com.ph/. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ↑ Susan G. Daluz. "A recipe that supported a brood of 12". Inquirer News Service. INQ7 Interactive, Inc. An INQUIRER and GMA Network Company. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ↑ South Pacific Commission (1990). Leaflet No. 13 : Sweet Potato. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISSN 1018-0966.
- ↑ Ma. Idelia G. Glorioso (January–December 2003). "10 Best Foods for Babies". Food and Nutrition Research Institute, Department of Science and Technology, Republic of the Philippines. Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ↑ Carol R. Ember; Melvin Ember, eds. (2004). Encyclopedia of Medical Anthropology: Cultures. Springer. p. 596. ISBN 9780306477546.
- ↑ Diana Rattray. "Sweet Potato Casserole Recipe with Crunchy Pecan Topping". About.com Food.
- ↑ Chung, H.L. (October 1923). "The Sweet Potato in Hawaii" (PDF). ctahr.hawaii.edu. United States Dept. of Agriculture.
- ↑ History of the Louisiana Yambilee, Yambilee.com
- ↑ "Sweet Potato - North Carolina State Vegetable". State of North Carolina. Retrieved 17 February 2014.
- ↑ "A Guide to Growing Pre-European Māori Kumara", Burtenshaw, M. (2009), The Open Polytechnic of New Zealand
- ↑ "Original Kumera", Enid Tapsell, TJPS
- ↑ Wilson, Dee (29 April 2009). "Heritage kumara shows its worth". The Marlborough Express. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ↑ "Waitangi tribunal and the kumara claim", Horticulture New Zealand
- ↑ Stokes, Jon (1 February 2007). "Kumara claim becomes hot potato". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ↑ "DNA analysis expected to solve kumara row". The New Zealand Herald. NZPA. 8 February 2007. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ↑ "KUMARA". teara.govt.nz.
- ↑ Barrington, Mike; Downey, Robyn (18 March 2006). "Ohakune has its carrot ... and Dargaville has its kumara". The Northern Advocate. Retrieved 24 July 2012.
- ↑ "How to cook with kumara". Taranaki Daily News. 3 March 2009. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ↑ Robbins, Joel (1995). "Dispossessing the Spirits: Christian Transformations of Desire and Ecology among the Urapmin of Papua New Guinea". Ethnology. 34 (3): 211–24. JSTOR 3773824. doi:10.2307/3773824.
- ↑ es:Castanyada#Casta.C3.B1ada
- ↑ Mondo agricolo veneto - la patata americana di Anguillara Archived 12 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Verrill, Alpheus Hyatt; Barrett, Otis Warren (1937). Foods America Gave the World: The Strange, Fascinating and Often Romantic Histories of Many Native American Food Plants, Their Origin and Other Interesting and Curious Facts Concerning Them. Boston: L.C. Page & Co. p. 47.
- ↑ "Purple sweet potatoes among ‘new naturals’ for food and beverage colors".
- ↑ Berrin, Katherine & Larco Museum. The Spirit of Ancient Peru:Treasures from the Museo Arqueológico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York: Thames and Hudson, 1997.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sweet potato. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Sweet Potato. |
- Edmond, Joseph Bailey; Ammerman, Gale Richard (1 November 1971). Sweet potatoes: production, processing, marketing. Major Feed and Food Crops in Agriculture and Food Series. Westport, Connecticut: The Avi Publishing Company.
- Hartemink, Alfred E; Poloma, S; Maino, M; Powell, K.S; Egenae, J; O'Sullivan, J.N (2000). "Yield decline of sweet potato in the humid lowlands of Papua New Guinea". Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. 79 (2–3): 259–269. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(00)00139-0.
External links
| Look up Sweet potato in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
