ManKind Project
 | |
| Founded | 1984, Wisconsin, United States |
|---|---|
| Founder |
Rich Tosi,[1] Bill Kauth[2] Ron Hering |
| Type | 501(c)(3) |
| Focus | Men's movement |
| Location | |
| Product | Motivational training |
Key people | Board Chairmen: David Kaar, ManKind Project International; Robert Powell, MKP-USA |
Revenue | $1,938,132 for 2006[4] |
Employees | >5 |
Volunteers | >1000 |
| Slogan | Changing the world, one man at a time. also Men mentoring Men through the passages of their lives |
| Website |
mankindproject |
ManKind Project (MKP) is a global network of non-profit charitable and educational organizations, with the stated goal: "MKP supports men to "wake up, grow up, and show up" to build healthy male role models"[5]
The ManKind Project currently has 11 regions: Australia, Belgium, Canada, French Speaking Europe, New Zealand, Nordic (Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland), South Africa, Switzerland, The United Kingdom, Ireland, and the United States. There are also 7 developing regions: Costa Rica, Mexico, The Netherlands, China, Singapore, India, Central Africa (Cameroon, DRC).[6]
As of March 2017, MKP reports that over 60,000 men have participated in their flagship program, the New Warrior Training Adventure.[7]
History
MKP has its origins in the mythopoetic men's movement of the early 1980s, drawing heavily on the works of Robert Bly, Robert L. Moore, and Douglas Gillette. In 1984, Rich Tosi, a former Marine Corps officer; Bill Kauth, a social worker, therapist, and author; and university professor Ron Hering, Ph.D. (Curriculum Studies); created an experiential weekend for men called the "Wildman Weekend" (later renamed "The New Warrior Training"[8]). As the popularity of the training grew, they formed a New Warrior Network organization, which would later become The Mankind Project.[2][9]
New Warrior Training Adventure
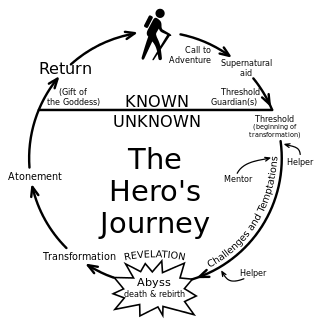
MKP states:
The New Warrior Training Adventure is a modern male initiation and self-examination... it is The Hero's Journey of classical literature and myth that has nearly disappeared in modern culture.[10]
MKP states that those who undertake this journey pass through three phases characteristic to virtually all historic forms of male initiation: descent, ordeal and return. Participants surrender all electronic devices (cell phones, watches, laptops, etc.), weapons (guns, knives, etc.) and jewelry for the weekend. This was explained as way of removing the "noise of a man's life", separating the man "from what he is comfortable with,"[11] and ensuring the safety of all participants.[12]
Participants agree to confidentiality of the NWTA processes, to create an experience "uncluttered by expectation" for the next man and to protect the privacy of all participants. MKP encourages participants to freely discuss what they learned about themselves with anyone.
Training courses usually involve 20 to 32 participants, and some 30 to 45 staff. The average cost of the weekend course is $650.[13] The course usually takes place at a retreat center, over a 48-hour period, with a one-to-one ratio of staff to participants.[11]
Integration Groups (I-Groups)
MKP co-founder Bill Kauth's 1992 book A Circle of Men: The Original Manual for Men's Support Groups details how groups of men can assemble to help one another emotionally and psychologically.[14] Men who have completed the NWTA are encouraged to consider joining such a group. An optional "Integration Group" training is offered shortly after each NWTA; a small fee is charged for training expenses (Fees vary by community and format). Some training courses are part of a small integration group on their own with qualified leaders, other training courses take place over an entire weekend and can cost between $100 and $250 depending on lodging, location, and number of men attending (See CoCreative Payment process, not yet written). Scholarships as well as a CCP (CoCreative Payment process) options are often available, making it more accessible to the financially less able.
The "I-Group" is for participants to engage in ongoing personal work and to apply the principles learned on the NWTA to their lives. I-Groups are available to all men who complete the NWTA, and sometimes to men who want to explore the Mankind Project. Many I-Groups meet one evening per week. A typical I-Group meeting includes conversation and sharing in a series of "rounds" that allow each man to be heard.[15]
Other training courses
MKP is affiliated with several similar training programs :
- Boys to Men, for adolescent boys[7]
- Inner King, for "initiating men into sovereign, kingly energy"[2]
- Inside Circle, for convicts in maximum security prisons[16]
- Inward Journey, for people of African descent
- Vets Journey Home (formerly "Bamboo Bridge"), for combat zone veterans[7]
- Warrior Monk, for "men and women who are in a transition phase of life"[2]
- Woman Within, for women[7]
Public reception
In an article by the magazine Pitchfork in 2013, musician Jim James thanked the ManKind Project for providing a place to “help men feel more OK with all the different sides of being a man.”.[17] Actor Wentworth Miller, in an address to the Human Rights Campaign during an event in 2013, describes his involvement with MKP as vital to his coming out process, and his introduction to being part of an accepting community.[18] In his letter rejecting an invitation to the Festival of Festivals, Saint Petersburg on grounds that he as a gay man could not support the event while Russian law prohibits homosexuality, Miller signed as a member of the ManKind Project as well as member of the HRC and GLAAD.[19]
Criticism
University chair and former therapist Norris Lang said that some of the groups' exercises that he attended were "fairly traumatic" and were "dangerous territory for an unprofessional". Some former MKP members have written negative material about MKP on public blogs and chat lists.[20]
Anti-cult advocate Rick Alan Ross of the Rick A. Ross Institute said that The ManKind Project appears to use coercive mind-control tactics. These include limiting participants' sleep and diet, cutting them off from the outside world, forcing members to keep secrets, and using intimidation.[20]
Wrongful death lawsuit
A 2007 wrongful death lawsuit filed by the parents of a Texas man charged that MKP was responsible for Michael Scinto's suicide.[20] The parents said that he had struggled with alcohol and cocaine addiction in the past. Scinto was a 29-year-old adult who had been clean and sober for a year and a half prior to his attending MKP's New Warrior Training Adventure in July 2005. Two days after Scinto returned from the NWTA retreat, he sought psychiatric help at Ben Taub Hospital. He subsequently began drinking and taking drugs again, and he then committed suicide.[20] MKP agreed to settle the case on June 4, 2008. The terms of the settlement are not disclosed.
Notes
- ↑ "About the Presenters". www.tosi.biz. Tosi and Associates. Archived from the original on October 10, 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
In 1985, Rich co-founded the ManKind Project...
- 1 2 3 4 Baer, Reid (May 2006). "May interview with Bill Kauth". A Man Overboard. MenStuff: The National Men's Resource. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
Bill Kauth is a co-founder of the New Warrior Training Adventure of the ManKind Project...
- ↑ Illinois Secretary of State; search for "Mankind Project"
- ↑ "Mankind Project Group Return". JustGive.org. GuideStar. Retrieved 2008-04-24.
- ↑ "The ManKind Project of Chicago". chicago.mkp.org. ManKind Project of Chicago. Retrieved 2017-03-21..
- ↑ "ManKind Project Regions and Communities". The ManKind Project. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- 1 2 3 4 "www.mankindproject.org". www.mankinkproject.org. Mankind Project. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- ↑ "MKP website". Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- ↑ "Interview with Bill Kauth". www.menweb.org. M.E.N. Magazine. Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ↑ "New Warrior Training Adventure". chicago.mkp.org. The ManKind Project of Chicago. Retrieved 2017-03-21.
- 1 2 Barry, Chris (2003-10-23). "Male transformer: Mankind Project uses mysterious rituals to help heal wounded men". Montreal, Quebec, Canada: Montreal Mirror. Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ↑ http://mankindproject.org/new-warrior-training-adventure
- ↑ "Frequently Asked Questions about the New Warrior Training Adventure". www.mkp.org. Mankind Project. Archived from the original on 2008-04-01. Retrieved 2008-04-24.
- ↑ Kauth, Bill (1992). A Circle of Men: The Original Manual for Men's Support Groups. New York: St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 0-312-07247-3. OCLC 24871074.
- ↑ Jackman, Michael (2006-11-29). "Band of brothers: The men's movement (still) want guys to open their hearts". Metro Times. Scranton, Pennsylvania: Times-Shamrock Communications. Retrieved 2008-04-23.
- ↑ "Missions of Service". www.mkp.org. Mankind Project. Archived from the original on 2008-04-01. Retrieved 2008-04-24.
- ↑ http://pitchfork.com/features/interviews/9053-jim-james/
- ↑ http://www.hrc.org/blog/entry/video-wentworth-miller-talks-about-coming-out-overcoming-struggles-at-hrc-d
- ↑ http://www.glaad.org/blog/wentworth-miller-rejects-russian-film-festival-invitation-gay-man-i-must-decline
- 1 2 3 4 Vogel, Chris (2007-10-04). "Naked Men: The ManKind Project and Michael Scinto.". Houston Press. Village Voice Media. Retrieved 2008-04-23.