Maniwa
| Maniwa 真庭市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
View of Hiruzen Plateau | |||
| |||
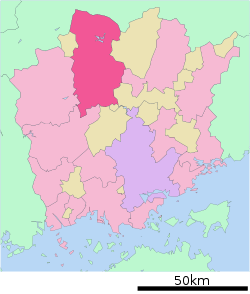 Location of Maniwa in Okayama Prefecture | |||
 Maniwa Location in Japan | |||
| Coordinates: 35°5′N 133°41′E / 35.083°N 133.683°ECoordinates: 35°5′N 133°41′E / 35.083°N 133.683°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Chūgoku (San'yō) | ||
| Prefecture | Okayama Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Koichiro Ide (since April 2005) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 828.43 km2 (319.86 sq mi) | ||
| Population (April 1, 2017) | |||
| • Total | 46,854 | ||
| • Density | 57/km2 (150/sq mi) | ||
| Symbols | |||
| • Tree | Chamaecyparis obtusa | ||
| • Flower | Cherry blossom | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| City hall address |
2927-2 Kuse, Maniwa-shi, Okayama-ken 719-3292 | ||
| Website |
www | ||

Maniwa (真庭市 Maniwa-shi) is a city located in north-central Okayama Prefecture, Japan.
The modern city of Maniwa was established on March 31, 2005, from the merger of the town of Hokubō (from Jōbō District); the towns of Katsuyama, Ochiai, Yubara and Kuse, and the villages of Mikamo, Kawakami, Yatsuka and Chūka (all from Maniwa District).
On April 1, 2017, Maniwa has an area of 828.43 km², the largest area of any municipality in the prefecture. Its population was 46,854, with 17,828 households.[1] The city is known for Mount Hiruzen (1,202 m (3,944 ft)) and the Hiruzen Plateau. Mount Hiruzen is also the source of the Asahi River (142 kilometres (88 mi)), which flows through much of Okayama Prefecture.[2][3][4][5][6]
Geography
Maniwa is located in approximately the center of the Chūgoku Mountains. The mountainous part of the city is dominated by Mount Hiruzen. The Asahi River, a Class 1 river under the Rivers Act of 1964, emerges from Mount Hiruzen in Maniwa, and its upper reaches are located within the town. The river has approximately 146 tributaries. Major tributaries of the Asahi in Maniwa include the Bitchū, Nakazui, Kōchi, Meki, and the Shinjō rivers.[6]
- Lakes
- Lake Yubara
- Dams
Adjoining municipalities
Transport
Railways
The main station is Chūgoku-Katsuyama.
Road
- Expressways:
- Chūgoku Expressway
- Mimasaka-Oiwake Parking Area - Ochiai Junction - Ochiai Interchange - Maniwa Parking Area - Hokubō Junction - Hokubō Interchange
- Okayama Expressway
- Hokubō Junction
- Yonago Expressway
- Ochiai Junction - Kuse Interchange - Ueno Parking Area - Yubara Interchange - Hiruzen-Kōgen Service Area - Hiruzen Interchange
- Chūgoku Expressway
- National highways:
- Main prefectural roads:
- Okayama Prefectural Route 30 (Ochiai-Takebe)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 32 (Niimi-Katsuyama)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 55 (Yubara-Mikamo)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 56 (Yubara-Okutsu)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 58 (Hokubō-Kawakami)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 65 (Kuse-Chūka)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 66 (Ochiai-Kamogawa)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 82 (Kagamino-Kuse)
- Okayama Prefectural Route 84 (Katsuyama-Kurihara)
- Roadside Station
- Hiruzen Plateau (蒜山高原 Hiruzen Kōgen)
- Windy House (風の家 Kaze no Ie)
- Village of Daigo (醍醐の里 Daigo no Sato)
Sister and Friendship cities
 Victor Harbor, Australia - Sister city agreement concluded on May 26, 2000
Victor Harbor, Australia - Sister city agreement concluded on May 26, 2000 Ruijin, China - Friendship city agreement concluded in January 16, 2001
Ruijin, China - Friendship city agreement concluded in January 16, 2001
Notable places and events
- The old castle town of Mimasaka-Katsuyama
- Kanba Waterfall (Japan's Top 100 Waterfalls)
- Former Senkyō Elementary School Building (Important Cultural Properties)
- Hiruzen Area
- Mount Hiruzen
- Hiruzen Plateau
- Hiruzen Kōgen Center / Joyful Park (Amusement park)
- Hiruzen Jersey Land
- Ski resort
Festivals
- Katsuyama Festival (October 19–20)
- Kuse Festival (October 25–26)
Onsens
- Yubara Onsen[2]
 The old castle town of Mimasaka-Katsuyama
The old castle town of Mimasaka-Katsuyama- Kanba Waterfall
 Yubara Onsen
Yubara Onsen
References
- ↑ "Official website of Maniwa city" (in Japanese). Japan: Maniwa City. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- 1 2 "真庭" [Maniwa]. Dijitaru Daijisen (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. OCLC 56431036. Archived from the original on 2007-08-25. Retrieved 2012-09-04.
- ↑ "Asahi-gawa". Dijitaru daijisen (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. Archived from the original on 2007-08-25. Retrieved 2012-05-24.
- ↑ "Hiruzen". Nihon Daihyakka Zensho (Nipponika) (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. Archived from the original on 2007-08-25. Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- ↑ "真庭" [Maniwa]. Nihon Kokugo Daijiten (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. OCLC 56431036. Archived from the original on 2007-08-25. Retrieved 2012-09-04.
- 1 2 "真庭" [Maniwa]. Nihon Daihyakka Zensho (Nipponika) (in Japanese). Tokyo: Shogakukan. 2012. OCLC 153301537. Archived from the original on 2007-08-25. Retrieved 2012-09-04.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Maniwa. |
- Maniwa City official website (in Japanese)
