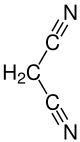
Malononitrile
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propanedinitrile[1] | |||
| Other names
Cyanoacetonitrile, Dicyanomethane, Malonic dinitrile[2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 773697 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.368 | ||
| EC Number | 203-703-2 | ||
| 1303 | |||
| MeSH | dicyanmethane | ||
| PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | OO3150000 | ||
| UN number | 2647 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H2N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 66.06 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless crystals or white powder[2] | ||
| Density | 1.049 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | 32 °C; 89 °F; 305 K | ||
| Boiling point | 220.1 °C; 428.1 °F; 493.2 K | ||
| 13% (20 °C)[2] | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 110.29 J K−1 mol−1 | |||
| Std molar entropy (S |
130.96 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
187.7–188.1 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−1.6540–−1.6544 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   | ||
| GHS signal word | DANGER | ||
| H301, H311, H331, H410 | |||
| P261, P273, P280, P301+310, P311 | |||
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LD50 (median dose) |
| ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[2] | ||
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 3 ppm (8 mg/m3)[2] | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related alkanenitriles |
|||
| Related compounds |
DBNPA | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Malononitrile, also propanedinitrile or malonodinitrile, is a nitrile with the formula CH2(CN)2.
Malononitrile is relatively acidic, with a pKa of 11 in water.[3] This allows it to be used in the Knoevenagel condensation, for example in the preparation of CS gas:

In related chemistry, malononitrile is a suitable starting material for the Gewald reaction, where the nitrile condenses with a ketone or aldehyde in the presence of elemental sulfur and a base to produce a 2-aminothiophene.[4]
Applications
Possible uses of malononitrile include in the synthesis of:
- Enloplatin
- triamterine
- Triap
- Milrinone
See also
References
- ↑ "dicyanmethane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0378". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Evans pKa table
- ↑ Sabnis, R.W.; Rangnekar, D.W.; Sonawane, N.D. (1999). "2-Aminothiophenes By The Gewald Reaction". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 36 (2): 333–345. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570360203. Retrieved 2007-07-18.
External links
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.

