Ibutamoren
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 4–6 hours (in beagles);[1] IGF-1 levels remain elevated in humans with a single oral dose for up to 24 hours[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
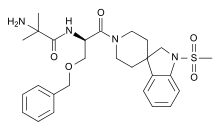
| Synonyms | 2-Amino-2-methyl-N-[1-(1-methylsulfonylspiro[2H-indole-3,4'-piperidine]-1'-yl)-1-oxo-3-(phenylmethoxy)propan-2-yl]propanamide |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.236.734 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H36N4O5S |
| Molar mass | 528.662 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ibutamoren (INN) (developmental code names MK-677, MK-0677, L-163,191) is a non-peptidic, potent, long-acting, orally-active, and selective agonist of the ghrelin receptor and a growth hormone secretagogue,[3][4] mimicking the growth hormone (GH)-stimulating action of the endogenous hormone ghrelin.[5][6] It has been demonstrated to increase the release of, and produces sustained increases in plasma levels of several hormones including GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), but without affecting cortisol levels.[7] MK677 has shown to sustain activation of GH-IGF-1 Axis and increase in lean body mass but no change in total fat mass or visceral fat. It is currently under development as a potential treatment for reduced levels of these hormones, such as in children or elderly adults with growth hormone deficiency,[8][9][10] and human studies have shown it to increase both muscle mass and bone mineral density,[11][12] making it a promising therapy for the treatment of frailty in the elderly.[13][14]
See also
- Anamorelin
- Capromorelin
- Examorelin (hexarelin)
- GHRP-6 (SKF-110679)
- Ipamorelin
- Macimorelin
- Pralmorelin (GHRP-2)
- Relamorelin
- SM-130,686
- Tabimorelin
References
- ↑ Roy G. Smith; Michael O. Thorner (28 January 2000). Human Growth Hormone: Research and Clinical Practice. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 45–. ISBN 978-1-59259-015-5.
- ↑ Smith, Roy G.; Ploeg, Lex H. T. Van der; Howard, Andrew D.; Feighner, Scott D.; Cheng, Kang; Hickey, Gerard J.; Wyvratt, Matthew J.; Fisher, Mike H.; Nargund, Ravi P.; Patchett, Arthur A. (1997). "Peptidomimetic Regulation of Growth Hormone Secretion". Endocrine Reviews. The Endocrine Society. 18 (5): 621–645. PMID 9331545. doi:10.1210/edrv.18.5.0316. Retrieved 2015-06-13.
- ↑ Patchett, AA; Nargund, RP; Tata, JR; Chen, MH; Barakat, KJ; Johnston, DB; Cheng, K; Chan, WW; Butler, B; Hickey, G; et al. (Jul 1995). "Design and biological activities of L-163,191 (MK-0677) a potent, orally active growth hormone secretagogue". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. 92 (15): 7001–5. PMC 41459
 . PMID 7624358. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.15.7001.
. PMID 7624358. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.15.7001. - ↑ Pong, SS; Chaung, LY; Dean, DC; Nargund, RP; Patchett, AA; Smith, RG (Jan 1996). "Identification of a new G-protein-linked receptor for growth hormone secretagogues". Molecular Endocrinology. 10 (1): 57–61. PMID 8838145. doi:10.1210/me.10.1.57.
- ↑ Cassoni P, Papotti M, Ghè C, Catapano F, Sapino A, Graziani A, Deghenghi R, Reissmann T, Ghigo E, Muccioli G. Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2001 Apr;86(4):1738–45. PMID 11297611
- ↑ Holst B, Frimurer TM, Mokrosinski J, Halkjaer T, Cullberg KB, Underwood CR, Schwartz TW. Overlapping Binding Site for the Endogenous Agonist, Small Molecule Agonists and Ago-allosteric Modulators on the Ghrelin Receptor. Molecular Pharmacology. 2008 Oct 15. PMID 18923064
- ↑ Copinschi G, Van Onderbergen A, L'Hermite-Balériaux M, Mendel CM, Caufriez A, Leproult R, Bolognese JA, De Smet M, Thorner MO, Van Cauter E. Effects of a 7-day treatment with a novel, orally active, growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, MK-677, on 24-hour GH profiles, insulin-like growth factor I, and adrenocortical function in normal young men. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1996 Aug;81(8):2776-82. PMID 8768828
- ↑ Chapman IM, Bach MA, Van Cauter E, Farmer M, Krupa D, Taylor AM, Schilling LM, Cole KY, Skiles EH, Pezzoli SS, Hartman ML, Veldhuis JD, Gormley GJ, Thorner MO. Stimulation of the growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor I axis by daily oral administration of a GH secretogogue (MK-677) in healthy elderly subjects. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1996 Dec;81(12):4249-57. PMID 8954023
- ↑ Thorner, MO; Chapman, IM; Gaylinn, BD; Pezzoli, SS; Hartman, ML (1997). "Growth hormone-releasing hormone and growth hormone-releasing peptide as therapeutic agents to enhance growth hormone secretion in disease and aging". Recent Progress in Hormone Research. 52: 215–46. PMID 9238854.
- ↑ Chapman, IM; Pescovitz, OH; Murphy, G; Treep, T; Cerchio, KA; Krupa, D; Gertz, B; Polvino, WJ; Skiles, EH; Pezzoli, SS; Thorner, MO (Oct 1997). "Oral administration of growth hormone (GH) releasing peptide-mimetic MK-677 stimulates the GH/insulin-like growth factor-I axis in selected GH-deficient adults". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 82 (10): 3455–63. PMID 9329386. doi:10.1210/jc.82.10.3455.
- ↑ Murphy, MG; Bach, MA; Plotkin, D; Bolognese, J; Ng, J; Krupa, D; Cerchio, K; Gertz, BJ (Jul 1999). "Oral administration of the growth hormone secretagogue MK-677 increases markers of bone turnover in healthy and functionally impaired elderly adults. The MK-677 Study Group". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 14 (7): 1182–8. PMID 10404019. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1182.
- ↑ Murphy MG, Weiss S, McClung M, Schnitzer T, Cerchio K, Connor J, Krupa D, Gertz BJ; MK-677/Alendronate Study Group. Effect of alendronate and MK-677 (a growth hormone secretagogue), individually and in combination, on markers of bone turnover and bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2001 Mar;86(3):1116–25. PMID 11238495
- ↑ Smith RG, Sun Y, Jiang H, Albarran-Zeckler R, Timchenko N. Ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1A) agonists show potential as interventive agents during aging. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2007 Nov;1119:147-64. PMID 18056963
- ↑ An Anti-frailty Pill For Seniors? New Drug Increases Muscle Mass In Arms And Legs Of Older Adults. ScienceDaily November 5th, 2008