Opportunity (rover)
 | |
| Mission type | Mars rover |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 2003-032A |
| Website | JPL's Mars Exploration Rover |
| Mission duration |
Planned: 90 sols (92.5 days) Current: 4825 sols (4958 days) since landing |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | Rover |
| Dry mass | 185 kilograms (408 lb) (rover only) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | July 7, 2003 03:18 UTC[1][2] |
| Rocket | Delta II 7925H-9.5[2][3][4] |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17B |
| Contractor | Boeing |
| Mars rover | |
| Landing date |
January 25, 2004,[1] 05:05 UTC SCET MSD 46236 14:35 AMT |
| Landing site | 1°56′46″S 354°28′24″E / 1.9462°S 354.4734°E[5] |
| Distance covered | 43.79 km (27.21 mi)[6] (as of 17 January 2017) |
 The launch patch for Opportunity, featuring Duck Dodgers (Daffy Duck) | |
Opportunity, also known as MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B) or MER-1, is a robotic rover active on Mars since 2004.[1] Launched on July 7, 2003 as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover program, it landed in Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004, three weeks after its twin Spirit (MER-A) touched down on the other side of the planet.[7] With a planned 90 sol duration of activity (slightly more than 90 earth days), Spirit functioned until getting stuck in 2009 and ceased communications in 2010, while Opportunity remains active as of August 22, 2017, having already exceeded its operating plan by 13 years, 118 days (in Earth time). Opportunity has continued to move, gather scientific observations, and report back to Earth for over 50 times its designed lifespan. As of August 7, 2017, the rover had traveled 44.97 kilometers (27.94 miles).[6] This date was mission time of Sol 4793.
Mission highlights include the initial 90 sol mission, finding extramartian meteorites such as Heat Shield Rock (Meridiani Planum meteorite), and over two years studying Victoria crater. It survived dust-storms and reached Endeavour crater in 2011, which has been described as a "second landing site".[8]
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Exploration Rover project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
Objectives

The scientific objectives of the Mars Exploration Rover mission are to:[9]
- Search for and characterize a variety of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity. In particular, samples sought will include those that have minerals deposited by water-related processes such as precipitation, evaporation, sedimentary cementation or hydrothermal activity.
- Determine the distribution and composition of minerals, rocks, and soils surrounding the landing sites.
- Determine what geologic processes have shaped the local terrain and influenced the chemistry. Such processes could include water or wind erosion, sedimentation, hydrothermal mechanisms, volcanism, and cratering.
- Perform calibration and validation of surface observations made by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter instruments. This will help determine the accuracy and effectiveness of various instruments that survey Martian geology from orbit.
- Search for iron-containing minerals, identify and quantify relative amounts of specific mineral types that contain water or were formed in water, such as iron-bearing carbonates.
- Characterize the mineralogy and textures of rocks and soils and determine the processes that created them.
- Search for geological clues to the environmental conditions that existed when liquid water was present.
- Assess whether those environments were conducive to life.
During the next two decades, NASA will continue to conduct missions to address whether life ever arose on Mars. The search begins with determining whether the Martian environment was ever suitable for life. Life, as we understand it, requires water, so the history of water on Mars is critical to finding out if the Martian environment was ever conducive to life. Although the Mars Exploration Rovers do not have the ability to detect life directly, they are offering very important information on the habitability of the environment in the planet's history.
Mission overview
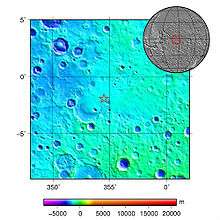
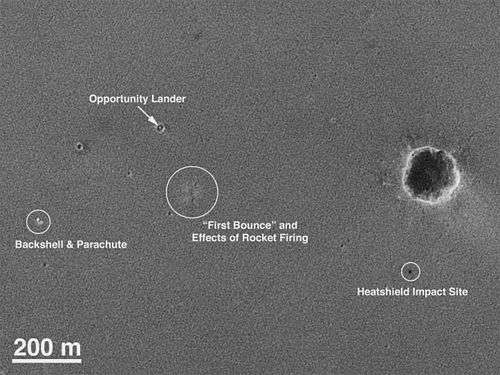
The primary surface mission for Opportunity was planned to last 90 sols (92 Earth days). The mission has received several extensions and has been operating for 4958 days since landing. An archive of weekly updates on the rover's status can be found at the Opportunity Update Archive.[10]
From its initial landing, by chance, into an impact crater amidst an otherwise generally flat plain, Opportunity has successfully investigated soil and rock samples and taken panoramic photos of its landing site. Its sampling allowed NASA scientists to make hypotheses concerning the presence of hematite and past presence of water on the surface of Mars. Following this, it was directed to travel across the surface of Mars to investigate another crater site, Endurance crater, which it investigated from June – December 2004. Subsequently, Opportunity examined the impact site of its own heat shield and discovered an intact meteorite, now known as Heat Shield Rock, on the surface of Mars.
From late April 2005 to early June of that year, Opportunity was perilously lodged in a sand dune, with several wheels buried in the sand. Over a six-week period Earth-based physical simulations were performed to decide how best to extract the rover from its position without risking a permanent immobilization of the valuable vehicle. Successful maneuvering a few centimeters at a time eventually freed the rover, which resumed its travels.
Opportunity was directed to proceed in a southerly direction to Erebus crater, a large, shallow, partially buried crater and a stopover on the way south towards Victoria crater, between October 2005 and March 2006. It experienced some mechanical problems with its robotic arm.
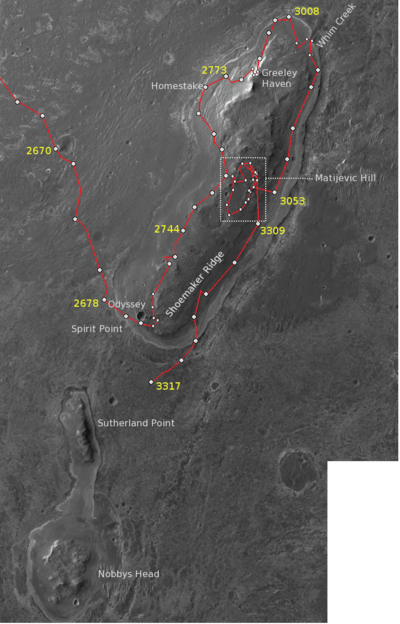
In late September 2006, Opportunity reached Victoria crater and explored along the rim in a clockwise direction. In June 2007 it returned to Duck Bay, its original arrival point; in September 2007 it entered the crater to begin a detailed study. In August 2008, Opportunity left Victoria crater for Endeavour crater, which it reached on August 9, 2011.[11]

Here at the rim of the Endeavour crater the rover moved around a geographic feature named Cape York. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter had detected phyllosilicates there, and the rover analyzed the rocks with its instruments to check this sighting on the ground. This structure was analyzed in depth until summer 2013. At May 2013 the rover was heading south to a hill named Solander Point.
Opportunity's total odometry as of June 27, 2016 (sol 4417) was 42.85 km (26.63 mi), while the dust factor is 0.725. [12] Since January 2013, the solar array dust factor (one of the determinants of solar power production) varied from a relatively dusty 0.467 on December 5, 2013 (sol 3507) to a relatively clean 0.964 on May 13, 2014 (sol 3662).[13]
In December 2014, NASA reported that Opportunity was suffering from "amnesia" events in which the rover fails to write data, e.g. telemetry information, to non-volatile memory. The hardware failure is believed to be due to an age-related fault in one of the rover's seven memory banks. As a result, NASA had aimed to force the rover's software to ignore the failed memory bank,[14] however amnesia events continued to occur which eventually resulted in vehicle resets. In light of this, on Sol 4027 (May 23, 2015), the rover was configured to operate in RAM-only mode, completely avoiding the use of non-volatile memory for storage.[15]
As of August 22, 2017, Opportunity is still roving the surface of Mars, and is slated for further scientific exploration.[16]
Design and construction
Opportunity (along with its twin, Spirit) is a six-wheeled, solar-powered robot standing 1.5 meters (4.9 ft) high, 2.3 meters (7.5 ft) wide, and 1.6 meters (5.2 ft) long and weighing 180 kilograms (400 lb). Six wheels on a rocker-bogie system enable mobility. Each wheel has its own motor, the vehicle is steered at front and rear and is designed to operate safely at tilts of up to 30 degrees. Maximum speed is 5 centimeters per second (2.0 in/s) although average speed is about a fifth of this (0.89 centimeters per second (0.35 in/s)). Both Spirit and Opportunity have pieces of the fallen World Trade Center's metal on them that were "turned into shields to protect cables on the drilling mechanisms".[17][18]
Solar arrays generate about 140 watts for up to fourteen hours per Martian day (sol) while rechargeable lithium ion batteries store energy for use at night. Opportunity's onboard computer uses a 20 MHz RAD6000 CPU with 128 MB of DRAM, 3 MB of EEPROM, and 256 MB of flash memory. The rover's operating temperature ranges from −40 to +40 °C (−40 to 104 °F) and radioisotope heaters provide a base level of heating, assisted by electrical heaters when necessary.[19] A gold film and a layer of silica aerogel provide insulation.
Communications depends on an omnidirectional low-gain antenna communicating at a low data rate and a steerable high-gain antenna, both in direct contact with Earth. A low gain antenna is also used to relay data to spacecraft orbiting Mars.
Fixed science/engineering instruments include:
- Panoramic Camera (Pancam) – examines the texture, color, mineralogy, and structure of the local terrain.
- Navigation Camera (Navcam) – monochrome with a higher field of view but lower resolution, for navigation and driving.
- Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer (Mini-TES) – identifies promising rocks and soils for closer examination, and determines the processes that formed them.
- Hazcams, two B&W cameras with 120 degree field of view, that provide additional data about the rover's surroundings.
The rover arm holds the following instruments:
- Mössbauer spectrometer (MB) MIMOS II – used for close-up investigations of the mineralogy of iron-bearing rocks and soils.
- Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) – close-up analysis of the abundances of elements that make up rocks and soils.
- Magnets – for collecting magnetic dust particles
- Microscopic Imager (MI) – obtains close-up, high-resolution images of rocks and soils.
- Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) – exposes fresh material for examination by instruments on board.
The cameras produce 1024-pixel by 1024-pixel images, the data is compressed with ICER, stored, and transmitted later.
The rover's name was chosen through a NASA sponsored student essay competition.
Power
Examples of watt-hours per sol collected by the rover.[20] The rover uses combination of solar cells and a rechargeable chemical battery.[21] This class of rover has two rechargeable lithium batteries with 8 amp-hour capacity.[21] At the start of the mission the solar panels could provide up to around 900 watt-hours to recharge the battery and power system in one Sol, but this can vary due to a variety of factors.[21] In Eagle crater the cells were producing about 840 watt-hours, but by Sol 319 in December 2004, it had dropped to 730 watt-hours.[22]
Like Earth, Mars has seasonal variations that reduce sunlight during Winter. However, since the Martian year is longer than that of the Earth, the seasons fully rotate roughly once every 2 Earth years.[23] By 2016, MER-B had endured seven Martian winters, during which times power levels drop which can mean the rover avoids doing activities that use a lot of power.[23] During its first winter power levels dropped to under 300 watt-hours per day for two months, but some later winters were not as bad.[23]
Another factor that can reduce received power is dust in the atmosphere, especially dust storms.[24] Dust storms have occurred quite frequently when Mars is closest to the Sun.[24] Global dust storms in 2007 reduced power levels for Opportunity and Spirit so much they could only run for a few minutes each day.[24] It was predicted that dust storms might hit later in 2016 as well.[24]
| Solar array energy production throughout mission graphs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Launch
Opportunity's launch was managed by NASA's Launch Services Program. This was the first launch of the Delta II Heavy. The launch period went from June 25 to July 15, 2003. The first launch attempt occurred on June 28, 2003, but the spacecraft launched nine days later on July 7, 2003 due to delays for range safety and winds, then later to replace items on the rocket (insulation and a battery). Each day had two instantaneous launch opportunities. On the day of launch, the launch was delayed to the second opportunity (11:18 p.m. EDT) in order to fix a valve.[25]
Scientific findings
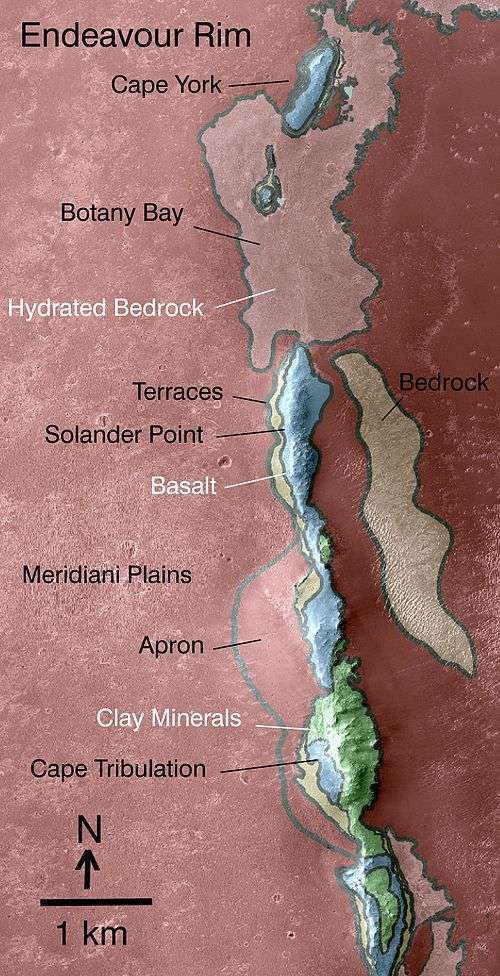
Opportunity has provided substantial evidence in support of the mission's primary scientific goals: to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity on Mars. In addition to investigating the water, Opportunity has also obtained astronomical observations and atmospheric data.
Honors
Honoring Opportunity's great contribution to the exploration of Mars, an asteroid was named Opportunity: 39382 Opportunity.[28] The name was proposed by Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld who, along with Cornelis Johannes van Houten and Tom Gehrels, discovered the asteroid on September 24, 1960. Opportunity's lander is Challenger Memorial Station.[29]
On July 28, 2014, it was announced that Opportunity, having traversed over 40 km (25 mi), had become the rover achieving the longest off-world distance, surpassing the previous record of 39 km (24 mi) on the Moon by Lunokhod 2.[26][27]
On March 24, 2015, NASA celebrated Opportunity having traveled the distance of a marathon race, 42.195 kilometers (26.219 mi), from the start of Opportunity's landing and traveling on Mars.[30]
Images
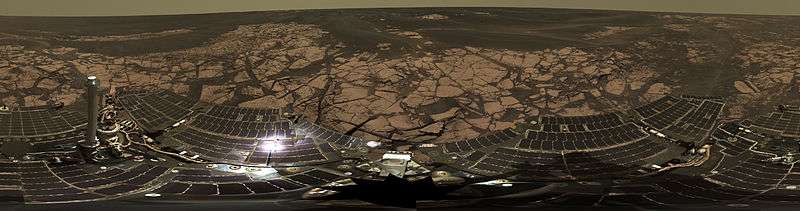
The rover can take pictures with its different cameras, but only the PanCam camera has the ability to photograph a scene with different color filters. The panorama views are usually built up from PanCam images. As of November 20, 2013, Opportunity had returned 186,246 pictures.[31]

Views
|
Panoramas
A selection of panoramas from the mission:
Microscopic images
|
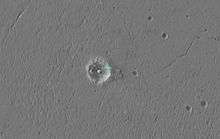
From orbit
|
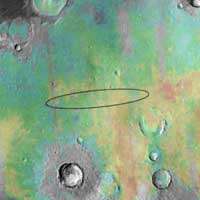
Maps
|
See also
|
References
- 1 2 3 Nelson, Jon. "Mars Exploration Rover – Opportunity". NASA. Retrieved February 2, 2014.
- 1 2 "Launch Event Details – When did the Rovers Launch?". Retrieved April 25, 2009.
- ↑ "Mars Exploration Rover project, NASA/JPL document NSS ISDC 2001 27/05/2001" (PDF). p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 27, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2003). "Jonathan's Space Report No. 504". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ↑ Staff. "Mapping the Mars Rovers' Landing Sites". Esri. Retrieved May 4, 2014.
- 1 2 "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: All Opportunity Updates". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 24, 2017.
- ↑ Spirit landed on January 4, 2004.
- ↑ "Opportunity on verge of new discovery". wustl.edu.
- ↑ "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: Science". nasa.gov.
- ↑ "Opportunity Update Archive". NASA/JPL. Retrieved May 4, 2009.
- ↑ "NASA – NASA Mars Rover Arrives at New Site on Martian Surface". Nasa.gov. Retrieved July 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: All Opportunity Updates". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Opportunity Updates". Retrieved November 20, 2014.
- ↑ O'Neill, Ian (29 December 2014). "Mars Rover Opportunity Suffers Worrying Bouts of 'Amnesia'". Web article. Discovery News. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ↑ "Opportunity Update Archive, sols 4024-4029, May 20, 2015-May 25, 2015".
- ↑ "NASA's Opportunity Rover to Explore Mars Gully". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ↑ Chang, Kenneth (November 7, 2004). "Martian Robots, Taking Orders From a Manhattan Walk-Up". The New York Times. Retrieved April 9, 2009.
- ↑ Squyres, Steve (2005). Roving Mars: Spirit, Opportunity, and the Exploration of the Red Planet. Hyperion Press. pp. 113–117. ISBN 978-1-4013-0149-1.
- ↑ "MER – Batteries and Heaters". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. NASA. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- ↑ "All Opportunity Status Updates". Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: Technology". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: All Opportunity Updates". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- 1 2 3 mars.nasa.gov. "Mars Rover Opportunity Busy Through Depth of Winter – Mars News". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 "Europe's ExoMars mission arrives in the middle of dust season". phys.org. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ↑ Harwood, William (July 8, 2003). "Opportunity launched to Mars". SPACEFLIGHT NOW. Retrieved 18 December 2015.
- 1 2 Webster, Guy; Brown, Dwayne (July 28, 2014). "NASA Long-Lived Mars Opportunity Rover Sets Off-World Driving Record". NASA. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- 1 2 Knapp, Alex (July 29, 2014). "NASA's Opportunity Rover Sets A Record For Off-World Driving". Forbes. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ↑ "Mars Exploration Rover Mission; "Like Rover, Like Asteroid"". Retrieved June 9, 2008.
- ↑ "Space Shuttle Challenger Crew Memorialized on Mars". Retrieved July 24, 2008.
- ↑ "The First Martian Marathon – NASA Science". science.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2015-05-15.
- ↑ Truong, Brian. "Mars Exploration Rover". nasa.gov.
- ↑ "Opportunity's View in 'Botany Bay' Toward 'Solander Point'". NASA.
- ↑ mars.nasa.gov. "Mars Exploration Rover Mission: Press Release Images: Opportunity". nasa.gov. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ↑ Webster, Guy; Cantillo, Laurie; Brown, Dwayne (June 16, 2017). "Martian Crater Provides Reminder of Apollo Moonwalk". NASA. Retrieved June 16, 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mars Exploration Rover. |
NASA links
MSSS and WUSTL links
- Finding Opportunity: high resolution images of landing site (Mars Global Surveyor – Mars Orbiter Camera)
- MER Analyst's Notebook, Interactive access to mission data and documentation
Other links
- Full-page, high-res spherical panorama of Opportunity in Erebus Crater, nasatech.net, Nov 23, to Dec 5, 2005 (long download, uses Java)
- Full-page, high-res spherical panorama of Opportunity in Victoria Crater, nasatech.net, October 23 to December 11, 2007 (long download, uses Java)
- Mars Exploration Rover Manual (Unofficial)
- High resolution video by Seán Doran of sol 4626 flyby of Opportunity
























.jpg)
.jpg)