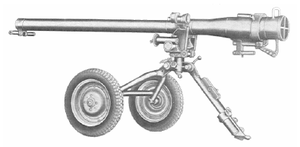
M60 recoilless gun
| M60 | |
|---|---|
|
82-mm M60 recoilless gun | |
| Type | Recoilless rifle |
| Place of origin |
|
| Service history | |
| Used by | See Users |
| Wars |
Yugoslav Wars Syrian Civil War[1][2] |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1960s |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 122 kg (269 lb) |
| Length | 2.20 m (7.2 ft) |
| Height | 0.83 m (2.7 ft) |
| Crew | 5 |
|
| |
| Shell | HEAT |
| Elevation | -20 to +35°[3] |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 4 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 388 m/s (1,270 ft/s) |
| Effective firing range | 500 m (1,600 ft) |
| Maximum firing range | 4,500 m (2.8 mi) |
| Sights | Optical |
The M60 recoilless gun is an 82-mm antitank recoilless gun developed in the former Yugoslavia. It entered service with the Yugoslav People's Army in the 1960s.
Description
The M60 is mounted on a towing carriage with wheels for transport and firing. Aiming is done with an optical sight. Ammunition for the M60 includes two fin-stabilized HEAT rounds. The first HEAT projectile for the M60 had an effective range of 500 meters. The second was an improved version that used a rocket booster to increase the effective range to 1,000 meters.[4]
The maximum range of the piece is 4,700 meters. Direct fire is limited to 1,500 meters against stationary targets and 1,000 meters against moving targets. The M60 is credited with a 220mm penetration of armor with its HEAT round.[5]
Users
 Yugoslavia: It was used by the Yugoslav People's Army.
Yugoslavia: It was used by the Yugoslav People's Army. Serbia
Serbia Croatia
Croatia Republic of Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia Syrian National Coalition: It is being used in the Syrian Civil War.[6]
Syrian National Coalition: It is being used in the Syrian Civil War.[6]
References
Notes
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BvBVX_hmIS4
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EMnB8pDqPSg
- ↑ JIW, p. 746.
- ↑ WEG, p. 62.
- ↑ JIW, p. 747. Sources from post-Yugoslavian republics claim later rounds increased armor penetration to 300 - 400mm.
- ↑ http://atwar.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/02/25/weapons-from-the-former-yugoslavia-spread-through-syrias-war/?_r=0
Bibliography
- (JIW) Hogg, Ian. Jane's Infantry Weapons 1984-85, London: Jane's Publishing Company Ltd., 1984.
- (WEG) U.S. Army. Worldwide Equipment Guide 2001, Training and Doctrine Command, 2001.