Low Beskids
| Lower Beskids | |
|---|---|
| Polish: Beskid Niski Slovak: Nízke Beskydy | |
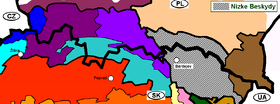 | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Busov (Slovakia) |
| Elevation | 1,002 m (3,287 ft) |
| Coordinates | 49°29′00″N 22°40′04″E / 49.48333°N 22.66778°ECoordinates: 49°29′00″N 22°40′04″E / 49.48333°N 22.66778°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 120 km (75 mi) west-east |
| Width | 50–70 km (30–40 mi) north-south |
| Area | 7,000 km2 (2,700 sq mi) |
| Geography | |
| Countries | Poland and Slovakia |
| Parent range | Outer Western Carpathians |
| Borders on |
Doły Jasielsko Sanockie, Bieszczady Mountains, Pogórze Bukowskie, Bukovské vrchy, Vihorlat Mountains, Eastern Slovak Lowland, Slanské vrchy, Čergov, Ľubovnianska vrchovina |
| Geology | |
| Type of rock | granite, gneiss, limestone |

The Low Beskids or Lower Beskids (Polish: Beskid Niski, Slovak: Nízke Beskydy), are one of the Beskids mountain ranges in the Outer Eastern Carpathians in southeastern Poland and northeastern Slovakia. Is a hilly region in Prešov Region, Sanok County and Jasło County, between Busov, Ondavská vrchovina, Laborecká vrchovina, Beskydské predhorie in Slovakia, Beskid Sądecki, Pogórze Bukowskie and Bieszczady near the river Wisłoka, Wisłok and Osława in Poland. The mountain has two separate summits, one of 1,002 (Busov) and one of 997 metres (Lackowa). The Low Beskids separating the East from the Western Carpathians.
Original flora and fauna was preserved because of the area's remoteness. The mountain range is covered with beech forests. The area is protected by Magurski National Park and Jaśliski Park Krajobrazowy. Animals living in this reserve are, amongst others, black storks, deers and wolves.
Division
Since there exist many variants of divisions of the mountain ranges and names for the Beskids, several divisions are given in the following:
- Busov (Slovakia),
- Ondavská vrchovina (Slovakia),
- Laborecká vrchovina Slovakia),
- Beskydské predhorie (Slovakia),
- Góry Grybowskie - near rivers Kamienica and Biała (Poland),
- Góry Hańczowskie - near rivers Biała, Ropa and Zdynia, (Poland),
- Beskid Gorlicki - near river Biała, villages : Radocyna, Bartne, Wołowiec,
- Pasmo Magurskie - mountains ranges Magura Wątkowska and Małastowskie,
- Beskid Dukielski - between rivers Wisłoka and Tabor, (Poland),
- Gniazdo Jawornika - between rivers Jasiołki i Wisłoka, (Poland),
- Pasmo Bukowicy and Kamieni Peak - between rivers Wisłok and Osławica,
- Pasmo graniczne - near river Bełcza, (Poland),
- Wzgórza Rymanowskie - near river Tabor,(Poland),
History
Poland
The region then became a site of contention between Poland, Kievan Rus and Hungary starting in at least the 9th century. The population was primarily Slavic but with contentions over nationality. Germans and town dwelling Lemkos were Polonized and the countryside remained primarily Lemko/Ukrainian. Up until 1947, the majority of the population was Lemko (Rusin). The Lemkos are sometimes considered the westernmost of the Ukraininans. They were forcibly removed in a Polinization plan agreed between the Soviet Union and the Polish communist government. Many were killed or forcibly sent to Soviet Ukraine. Those not sent to Ukraine were dispersed among towns and villages in the new western Polish territory taken from Germany.
Slovakia
The Lower Beskids on the territory of present-day Slovakia has attracted settlers since the Stone Age. The Slavic forefathers of the Slovaks gradually moved to the basin of Humenné and Bardejov during the great migration of peoples, starting in the 5th century. An intensive and organized settlement of this area started as late as in the middle of the 13th century, after the Mongol raids. However, the first written reference to the town dates back to the 1240s, when monks from Bardejov complained to the King Béla IV about a violation of the town’s borders by Prešov.
Rural landscape pictures
Towns and villages
Important towns and villages of this region include:
- Bardejov
- Humenné
- Svidník
- Medzilaborce
- Stropkov
- Giraltovce
- Bukowsko
- Grybów
- Gorlice
- Iwonicz Zdrój
- Rymanów-Zdrój
Ethnic groups
Hiking trails

- Somár - sedlo Baba - Dolná Rakova - Končini - Brezová pod Bradlom - Polianka - Myjava - Veľká Javorina - Nové Mesto nad Váhom - Machnáč - Trenčín - Košecké Rovné - Fačkovské sedlo - Kunešov - Kraľová studňa - Donovaly - Chopok - Čertovica - Telgárt - Skalisko - Štós-kúpele - Skalisko - Chata Lajoška - Košice - Malý Šariš - Prešov - Miháľov - Kurimka - Dukla - Iwonicz-Zdrój – Rymanów-Zdrój - Puławy – Tokarnia (778 m) – Kamień (717 m) – Komańcza - Cisna - Ustrzyki Górne -Tarnica - Wołosate.
Literature
- Prof. Jerzy Kondracki. Geografia fizyczna Polski Warszawa : Państ. Wydaw. Naukowe, 1988, ISBN 83-01-02323-6.
- Prof. Jadwiga Warszyńska. Karpaty Polskie : przyroda, człowiek i jego działalność ; Uniwersytet Jagielloński. Kraków, 1995 ISBN 83-233-0852-7.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Low Beskids in Poland. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to The Beskids. |



_and_Przemy%C5%9Bl_area_Ukrainians_in_original_goral_folk-costumes..jpg)
