Longitudinal fissure
| Longitudinal fissure | |
|---|---|
 The human brain as viewed from above. Medial longitudinal fissure visible in red, running top to bottom. | |
 longitudinal fissure shown in red (animation) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fissura longitudinalis cerebri, fissura cerebri longitudinalis |
| NeuroNames | hier-16 |
| NeuroLex ID | Longitudinal fissure |
| TA | A14.1.09.007 |
| FMA | 83727 |
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, medial longitudinal fissure, or interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two hemispheres of the vertebrate brain.
The medial surfaces of the two hemispheres are as similarly convoluted by gyri and sulci as is the outer surface of the brain.
The falx cerebri, a dural brain covering, lies within the longitudinal fissure.
The corpus callosum crosses between the two hemispheres at the bottom of the longitudinal fissure.
Additional images
 facies dorsalis cerebri gyri
facies dorsalis cerebri gyri- Cerebrum. Medial face. Dissection of corpus callosum etc.
- Human brain - left and right hemispheres - superior-lateral view
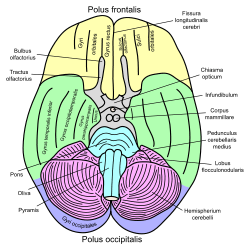 Basal view of a human brain
Basal view of a human brain- Cerebrum. Optic and olfactory nerves. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Meninges and superficial cerebral veins. Deep dissection. Superior view.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Longitudinal fissure. |
- Anatomy image: nerv/brainsup2 at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University
- Diagram at nih.gov
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.