Homotopy group
In mathematics, homotopy groups are used in algebraic topology to classify topological spaces. The first and simplest homotopy group is the fundamental group, which records information about loops in a space. Intuitively, homotopy groups record information about the basic shape, or holes, of a topological space.
To define the n-th homotopy group, the base-point-preserving maps from an n-dimensional sphere (with base point) into a given space (with base point) are collected into equivalence classes, called homotopy classes. Two mappings are homotopic if one can be continuously deformed into the other. These homotopy classes form a group, called the n-th homotopy group, πn(X), of the given space X with base point. Topological spaces with differing homotopy groups are never equivalent (homeomorphic), but the converse is not true.
The notion of homotopy of paths was introduced by Camille Jordan.[1]
Introduction
In modern mathematics it is common to study a category by associating to every object of this category a simpler object that still retains sufficient information about the object of interest. Homotopy groups are such a way of associating groups to topological spaces.


That link between topology and groups lets mathematicians apply insights from group theory to topology. For example, if two topological objects have different homotopy groups, they can't have the same topological structure—a fact that may be difficult to prove using only topological means. For example, the torus is different from the sphere: the torus has a "hole"; the sphere doesn't. However, since continuity (the basic notion of topology) only deals with the local structure, it can be difficult to formally define the obvious global difference. The homotopy groups, however, carry information about the global structure.
As for the example: the first homotopy group of the torus T is
- π1(T)=Z2,
because the universal cover of the torus is the complex plane C, mapping to the torus T ≅ C / Z2. Here the quotient is in the category of topological spaces, rather than groups or rings. On the other hand, the sphere S2 satisfies
- π1(S2)=0,
because every loop can be contracted to a constant map (see homotopy groups of spheres for this and more complicated examples of homotopy groups).
Hence the torus is not homeomorphic to the sphere.
Definition
In the n-sphere Sn we choose a base point a. For a space X with base point b, we define πn(X) to be the set of homotopy classes of maps
- f : Sn → X
that map the base point a to the base point b. In particular, the equivalence classes are given by homotopies that are constant on the basepoint of the sphere. Equivalently, we can define πn(X) to be the group of homotopy classes of maps g : [0,1]n → X from the n-cube to X that take the boundary of the n-cube to b.
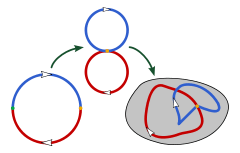
For n ≥ 1, the homotopy classes form a group. To define the group operation, recall that in the fundamental group, the product f ∗ g of two loops f and g is defined by setting
The idea of composition in the fundamental group is that of traveling the first path and the second in succession, or, equivalently, setting their two domains together. The concept of composition that we want for the n-th homotopy group is the same, except that now the domains that we stick together are cubes, and we must glue them along a face. We therefore define the sum of maps f, g : [0,1]n → X by the formula (f + g)(t1, t2, ... tn) = f(2t1, t2, ... tn) for t1 in [0,1/2] and (f + g)(t1, t2, ... tn) = g(2t1 − 1, t2, ... tn) for t1 in [1/2,1]. For the corresponding definition in terms of spheres, define the sum f + g of maps f, g : Sn → X to be Ψ composed with h, where Ψ is the map from Sn to the wedge sum of two n-spheres that collapses the equator and h is the map from the wedge sum of two n-spheres to X that is defined to be f on the first sphere and g on the second.
If n ≥ 2, then πn is abelian. (For a proof of this, note that in two dimensions or greater, two homotopies can be "rotated" around each other. See Eckmann–Hilton argument). Further, similar to the fundamental group, for a path connected space any two basepoint choices gives rise to isomorphic πn (see Allen Hatcher#Books section 4.1).
It is tempting to try to simplify the definition of homotopy groups by omitting the base points, but this does not usually work for spaces that are not simply connected, even for path connected spaces. The set of homotopy classes of maps from a sphere to a path connected space is not the homotopy group, but is essentially the set of orbits of the fundamental group on the homotopy group, and in general has no natural group structure.
A way out of these difficulties has been found by defining higher homotopy groupoids of filtered spaces and of n-cubes of spaces. These are related to relative homotopy groups and to n-adic homotopy groups respectively. A higher homotopy van Kampen theorem then enables one to derive some new information on homotopy groups and even on homotopy types. For more background and references, see "Higher dimensional group theory" and the references below.
Long exact sequence of a fibration
Let p: E → B be a basepoint-preserving Serre fibration with fiber F, that is, a map possessing the homotopy lifting property with respect to CW complexes. Suppose that B is path-connected. Then there is a long exact sequence of homotopy groups
- ... → πn(F) → πn(E) → πn(B) → πn−1(F) →... → π0(E) → 0.
Here the maps involving π0 are not group homomorphisms because the π0 are not groups, but they are exact in the sense that the image equals the kernel.
Example: the Hopf fibration. Let B equal S2 and E equal S3. Let p be the Hopf fibration, which has fiber S1. From the long exact sequence
- ⋯ → πn(S1) → πn(S3) → πn(S2) → πn−1(S1) → ⋯
and the fact that πn(S1) = 0 for n ≥ 2, we find that πn(S3) = πn(S2) for n ≥ 3. In particular, π3(S2) = π3(S3) = Z.
In the case of a cover space, when the fiber is discrete, we have that πn(E) is isomorphic to πn(B) for all n greater than 1, that πn(E) embeds injectively into πn(B) for all positive n, and that the subgroup of π1(B) that corresponds to the embedding of π1(E) has cosets in bijection with the elements of the fiber.
When the fibration is the mapping fibre, or dually, the cofibration is the mapping cone, then the resulting exact (or dually, coexact) sequence is given by the Puppe sequence.
Methods of calculation
Calculation of homotopy groups is in general much more difficult than some of the other homotopy invariants learned in algebraic topology. Unlike the Seifert–van Kampen theorem for the fundamental group and the Excision theorem for singular homology and cohomology, there is no simple known way to calculate the homotopy groups of a space by breaking it up into smaller spaces. However, methods developed in the 1980s involving a van Kampen type theorem for higher homotopy groupoids have allowed new calculations on homotopy types and so on homotopy groups. See for a sample result the 2008 paper by Ellis and Mikhailov listed below.
For some spaces, such as tori, all higher homotopy groups (that is, second and higher homotopy groups) are trivial. These are the so-called aspherical spaces. However, despite intense research in calculating the homotopy groups of spheres, even in two dimensions a complete list is not known. To calculate even the fourth homotopy group of S2 one needs much more advanced techniques than the definitions might suggest. In particular the Serre spectral sequence was constructed for just this purpose.
Certain Homotopy groups of n-connected spaces can be calculated by comparison with homology groups via the Hurewicz theorem.
A list of methods for calculating homotopy groups
- The long exact sequence of homotopy groups of a fibration.
- Hurewicz theorem, which has several versions.
- Blakers–Massey theorem, also known as excision for homotopy groups.
- Freudenthal suspension theorem, a corollary of excision for homotopy groups.
Relative homotopy groups
There are also relative homotopy groups πn(X,A) for a pair (X,A), where A is a subspace of X. The elements of such a group are homotopy classes of based maps Dn → X which carry the boundary Sn−1 into A. Two maps f, g are called homotopic relative to A if they are homotopic by a basepoint-preserving homotopy F : Dn × [0,1] → X such that, for each p in Sn−1 and t in [0,1], the element F(p,t) is in A. The ordinary homotopy groups are the special case in which A is the base point.
These groups are abelian for n ≥ 3 but for n = 2 form the top group of a crossed module with bottom group π1(A).
There is a long exact sequence of relative homotopy groups, it can be obtained via the Puppe sequence.
Related notions
The homotopy groups are fundamental to homotopy theory, which in turn stimulated the development of model categories. It is possible to define abstract homotopy groups for simplicial sets.
See also
- Fibration
- Knot theory
- Homotopy class
- Homotopy groups of spheres
- Topological invariant
- Homotopy group with coefficients
- Pointed set
Notes
References
- Hatcher, Allen (2002), Algebraic topology, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-79540-1
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001) [1994], "Homotopy group", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Ronald Brown, `Groupoids and crossed objects in algebraic topology', Homology, homotopy and applications, 1 (1999) 1–78.
- G.J. Ellis and R. Mikhailov, `A colimit of classifying spaces', arXiv:0804.3581 [math.GR]
- R. Brown, P.J. Higgins, R. Sivera, Nonabelian algebraic topology: filtered spaces, crossed complexes, cubical homotopy groupoids, EMS Tracts in Mathematics Vol. 15, 703 pages. (August 2011).
- H. Kamps and T.Porter, T. Abstract homotopy and simple homotopy theory., World Scientific Publishing Co. Inc., River Edge, NJ (1997).
