Logudorese dialect
| Logudorese Sardinian | |
|---|---|
|
Sardu Logudoresu Logudoresu | |
| Native to | Italy |
| Region | Sardinia |
Native speakers | 500,000 (1993)[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
src Logudorese Sardinian |
| Glottolog |
logu1236 Logudorese Sardinian[2] |
| Linguasphere |
51-AAA-sa |
|
Languages and dialects of Sardinia | |
Logudorese Sardinian[1][2] (Sardinian: Sardu Logudoresu, Italian: Sardo Logudorese) is a standardised variety of Sardinian, often considered the most conservative of all Romance languages. Its ISO 639-3 code is src. Italian-speakers do not understand Sardinian, which is a separate language.
Characteristics
Latin G and K before /i, e/ are not palatalized in it, in stark contrast with all other Romance languages. Compare Logudorese kentu with Italian cento /ˈtʃɛnto/, Spanish ciento /ˈθjento/, /ˈsjento/ and French cent /sɑ̃/.
Logudorese is intelligible to those from the southern part of Sardinia, where Campidanese Sardinian is spoken,[3] but it is not to those from the extreme north of the island, where Corsican–Sardinian dialects are spoken.
Location and distribution
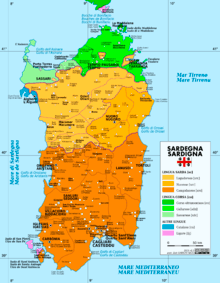
The area of Logudoro (term originated as a blend of the kingdom's name of Logu de Torres) in which it is spoken, a northern subregion of the island of Sardinia with close ties to Ozieri (Othieri) and Nuoro (Nùgoro) for culture and language, as well as history, with important particularities in the western area, where the most important town is Ittiri. It is an area of roughly 150 × 100 km with some 500,000–700,000 inhabitants.
Origins and features
The language's origins have been investigated by Eduardo Blasco Ferrer and others. The language derives from Latin and a pre-Latin, Paleo-Sardinian (Nuragic) substratum, but has been influenced by Catalan and Spanish due to the dominion of the Crown of Aragon and later the Spanish Empire over the island. Logudorese is the northern macro-dialect of the Sardinian language, the southern macro-dialect being Campidanese, spoken in the southern half of the island. The two variants share a clear common origin and history, but have experienced somewhat different developments.
Though the language is typically Romance, some words in it are not of Latin origin, and are of uncertain etymology. One such is "nura", found in "nuraghe", the main form of pre-Roman building, hence the term for the pre-Roman era as the Nuragic Period. Various place names similarly have roots that defy analysis.
Logudorese changed only very slowly from Vulgar Latin in comparison to other Romance lects, even though in terms of vocabulary it is not as close to its Latin ancestor as Italian. Campidanese, in contrast, has more archaic features than Logudorese, particularly in its verb forms, such as the retention of the 3rd-person plural in -nt(), which is reduced to -n() in Logudorese.
Subdialects
Logudorese has multiple dialects, some confined to individual villages or valleys. Though such differences can be noticeable, the dialects are mutually intelligible, and share some mutual intelligibility with the neighbouring Campidanese dialects.
Sample of text
| English | Logudorese Sardinian | Transitional Mesanìa dialect | Campidanese Sardinian |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Our Father in heaven, |
Babbu nostru chi ses in chelu, |
Babbu nostru chi ses in celu, |
Babbu nostu chi ses in celu, |
Writers
A large body of Sardinian poetry, songs and literature is composed in Logudorese.
See also
References
- 1 2 Logudorese Sardinian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- 1 2 Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "
Logudorese Sardinian". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. - ↑ Sardinian intonational phonology: Logudorese and Campidanese varieties, Maria Del Mar Vanrell, Francesc Ballone, Carlo Schirru, Pilar Prieto
External links
- Ditzionàriu online - Dizionario della lingua sarda
- Sardinian Grammar of Oliena's dialect
- A iscola de sardu - Sassari.tv
- Logudorese basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- Sardinian basic phrases