List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia

Map of Ancient Thrace made by Abraham Ortelius in 1585
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology.
Mythological[1]

Thracian king Rhesus slain by Odysseus
- Haemus, became a mountain Haemus Mons
- Thrax, son of Ares
- Tegyrios, mortal
- Eumolpus, inherited a kingdom from Tegyrios
- Tereus, the king that was turned into a hoopoe[2]
- Phineus, Phoenician son of Agenor, blind king and seer[3]
- Poltys, son of Poseidon[4]
- Pyreneus, died trying to harm the Muses
- Harpalykos,[5] king of the Amymnaeans
- Thoas, founder of Thoana
- Mopsus, killed Myrine, an amazon queen
- Peirous, a Thracian war leader[6] killed by Thoas the Aetolian
- Rhesus of Thrace, died in the Trojan war[7]
- Cisseus, father of Theano, the wife of Antenor
- Diomedes of Thrace, Giant that ruled over the Bistones
- Lycurgus, of the Edoni
- Oeagrus, father of Orpheus and Linus
- Orpheus[8] of the Cicones
- Polymestor of the Bistonians[9]
- Zalmoxis of the Getae "This Zalmoxis lived many years before Pythagoras (569–475 BC)" Herodotus [55]
- Charnabon of the Getae, who came into power when grain was first given to men[10] mentioned by Sophocles[11]
- Pyraechmes of the Paeonians
- Asteropaios of the Paeonians
Persian

The Persian Empire in 490 BC
- Darius I, Persian Satrapy named Skudra by 516 BC[12]
- Darius I, Thrace is resubjucated by Mardonius at 492 BC
- Xerxes I, retains Thrace from 486 BC to 479 BC
Tribal kings

Triballi habitat
- Olorus, 5th century BC[13]
- Syrmus, king of the Triballi[14] 4th century BC
- Bergaios, petty king of Pangaeum
- Dromichaetes, of the Getae 300 BC
- Langarus, of the Agrianes
- Pleuratus, a Thracian or Illyrian king that attacked Tylis 213–208 BC
- Diegylis, chieftain of the Caeni extremely bloodthirsty 145 BC
- Ziselmius, Diegylis' son
- Mostis, of the Caeni, king ~130–90 BC
- Abrupolis of the Sapaeans, 2nd century BC
- Rabocentus[15] of the Bessi mentioned by Cicero
- Cosingas,[16] chieftain and priest of Hera to the tribes of Cebrenii and Sucaeboae
- Getas, king[17][18] of the Edones
Getic and Dacian

Dacia
- Charnabon, king currently ruling over the Getae as mentioned by Sophocles in Triptolem - 5th century BC
- Cothelas,[19] father of Meda of Odessa – 4th century BC
- Rex Histrianorum, ruler in Histria, mentioned by Trogus Pompeius and Justinus - 339 BC
- Dual – 3rd century BC
- Moskon[20] – 3rd century BC
- Dromichaetes[21] – 3rd century BC
- Zalmodegicus[22] – around 200 BC[23]
- Rhemaxos – around 200 BC[24][25]
- Rubobostes[26] – around 200 BC
- Zoltes - 200 BC [27]
- Oroles[28] – 2nd century BC
- Dicomes[29] – 1st century BC
- Rholes[30] – 1st century BC
- Dapyx[31] – 1st century BC
- Zyraxes[32] – 1st century BC
- Burebista[33] – 82–44 BC
- Deceneus[34] – 44 BC - around 27 BC High Priest
- Thiamarkos - 1st century BC - 1st century AD, Dacian king (inscription "Basileys Thiamarkos epoiei")[35]
- Cotiso[36] – c. 40 BC - c.9 BC
- Comosicus[37] – 9 BC–30 AD
- Scorilo[37] – c.30–70 AD
- Coson[38]
- Duras[38] – c. 69–87
- Decebalus[39] – 87–106
- 106 AD, Dacia becomes a province of the Roman Empire conquered by Trajan.
- Pieporus, king of Dacian Costoboci – 2nd century AD (inscription)[40][41]
- Tarbus – 2nd century AD. Dio Cassius mentioned him without specifying his origin. Some authors consider a possible Dacian ethnicity[42][43]
- Regalianus - died 260 AD
Paeonian

Paeonia,tribes and Environs
Celtic
- Cerethrius[44]
- Critasirus, a Celt[45]
- Cavarus,[46] the last king of Tylis
- Bathanatos[47][48] of the Scordisci
Macedonian

Map of the territory of Philip II of Macedon
- Philip II of Macedon, annexed Thrace, 341–336 BC
- Alexander the Great retains Thrace and suppresses rebellion, 335–323 BC
- Lysimachus, one of the Diadochi, includes Thrace in his kingdom, 323–281 BC[49][50]
- Philip V of Macedon controls all cities of Thrace up to the hellespont,[51] 238–179 BC
- Perseus of Macedon continues controlling the part of Thrace his father left him, 212–166 BC
Odrysae

The Odrysian Kingdom under Sitalces

Bronze head of An Ogrysian king, most likely Seuthes III
The list below includes the known Odrysian kings of Thrace, but much of it is conjectural. Various other Thracian kings (some of them perhaps Odrysian like Pleuratus) are included as well.[52] Odrysian kings though called Kings of Thrace never exercised sovereignty over all of Thrace.[53] Control varied according to tribal relationships.[54] Odrysian kings(names are presented in Greek or Latin forms):
- Teres I, son of Odryses, (480[52]/450/430 BC[55])
- Sparatocos, brother or son of Teres I (450 /431 - 430 BC)
- Sitalces, son of Teres I (431-424 BC)
- Sadocos, son of Sitalces (425-424 BC)
- Seuthes I, nephew/son of Sparatocos (424-396 BC)
- Metokos/Amatokos I, son of Sitalkes
- Amadocus I, son of Teres or Metokos (410–[56]390 BC)
- Seuthes II, son of Maisades, Sparatokos, or grandson of Teres I, king in southern districts (405-391 BC)
- Hebryzelmis, son of Seuthes I or brother (390–384 BC)
- Maisades, father of Seuthes II (390-384 BC)
- Cotys I, son of Seuthes II (384–359 BC)
- Cersobleptes, son of Cotys I, king in eastern Thrace (359-341 BC)
- Berisades, probable brother of Cersobleptes or a grandson of Seuthes I, king in western Thrace in Strimos (359-352 BC)
- Amatokos II, brother of Cersobleptes, king in central Thrace in Chersonese and Maroneia (359-351 BC)
- Cetriporis, son of Berisades, king in western Thrace in Strimos (358-347 BC)
- Skostodokos, son of Berisades, king in western Thrace in Strimos (c. 351 BC)
- Teres II, son of Amatokos II, king in central Thrace in Chersonese and Maroneia (351-342 BC)
- Seuthes III, son of Cotys I (341–300 BC)
- Cotys II, son of Seuthes III (300–280 BC)
- Raizdos/Roigos, son of Cotys II (c. 280 BC)
- Odoroes, alternative co-ruler (c. 280-273 BC)
- Adaeus, alternative co-ruler (c. 280-273 BC)
- Scostodos, son of Berisades, alternative co-ruler (c. 275 BC)
- Orsoaltios, alternative co-ruler (c. 265 BC)
- Kersivaulos, alternative co-ruler (c. 260 BC)
- Cotys III, son of Raizdos (c. 260 BC)
- Teres III, (c. 250 BC)
- Rhescuporis I, son of Cotys III (240-215 BC)
- Adaios, alternative co-ruler (c. 235 BC)
- Seuthes IV, son of Rhescuporis I or of Teres III (213/215-190/175 BC)
- Pleuratus,[57] alternative co-ruler (213-208 BC)
- Amatokos III (until 184 BC)
- Abrupolis, Sapei king (200 - 172 BC)
- Teres IV, son of Amatokos III, or of Seuthes III (183-172 BC)
- Teres V (172-148 BC)
- Cotys IV, son of Seuthes IV (180/170 - 168/160 BC)
- Diagil / Diygyles / Diygyles / Diegylos / Dyegilos / Diagylis / Tsizelmi (168/150 - 140 BC or 180 BC)
- Biz / Byzas / Byses / Beithys / Tsizelmi (168/166 BC or 148/146 BC or 180 BC)
- Sothimes (c. 163 BC)
- Teres VI (c. 149 BC)
- Amatokos IV, rebel (80 - 90 BC)
Restored Astaean and Sapean kingdom

Temporary area of some tribes including Sapei and Astae
- Cotys I, Cotys V, son of Beithys (100 - 87 BC)
- Sadalas I, son of Cotys V (87–79 BC)
- Cotys VI, son of Sadalas I (79–45 BC)
- Cotys ? (55-48 BC)[58]
- Rhescuporis I (48-42 BC)
- Cotys ?, son of Rhescuporis (42-31 BC)
- Sadalas II, son of Cotys VI (44–42 BC)
- Raskos, co-ruler (c. 42 BC)
- Sadalas III, son of Sadalas II (c. 31 BC)
- Cotys VII, son of Sadalas II (31–18 BC)
- Rhescuporis II, son of Cotys VII, north-west Sapei king (19/18–12/11 BC)
- Cotys VIII (c. 11 BC)
- Rhoemetalces I, uncle of Roman emperor Augustus and son of Cotys (31/11 BC – AD 12)
- Cotys ? , son of Rhoemetalces, south-east Sapei king(12 - 19 AD)
- Rhoemetalces II, son of Raskouporis II (19 - 38 AD)
- Rhoemetalces III, son of Cotys (38 - 46 AD)
- Pythodoris II, co-ruling wife and cousin (38 - 46 AD)
Scythian
- Spargapeithes,[59] king of the Agathyrsi
Sapaean[52]
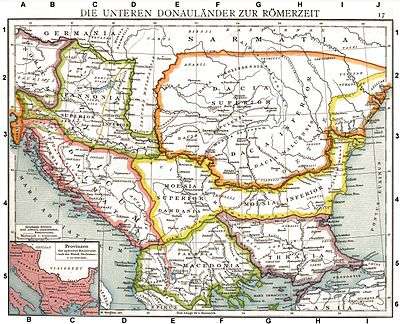
Thrace and Dacia as Roman provinces
- Cotys I, son of Rhoemetalces, ?–48 BC
- Rhescuporis I, son of Cotys I, 48 BC–41 BC
- Cotys II, son of Rhescuporis I, 42 BC–15
- Thrace becomes a client state of Rome at 11 BC[60]
- Rhoemetalces I, son of Cotys II, 15 BC–12
- Rhescuporis II, son of Cotys II, in western Thrace, deposed, 12–19
- Cotys III, son of Rhoemetalces I, in eastern Thrace, 12–19
- Rhoemetalces II, son of Cotys III and Tryphaena, 19–38
- Rhoemetalces III, son of Rhescuporis II, with his cousin-wife Pythodoris II 38–46
- 46 annexation by the Roman Empire, by Roman Emperor Claudius
See also
- Odrysian kingdom
- Sapaeans
- Paeonia
- List of ancient Cities in Thrace
- List of ancient tribes in Thrace
- List of rulers of Illyria
- List of ancient Cities in Illyria
- List of ancient tribes in Illyria
Notes
- ↑ Greek Mythology by Carlos Parada
- ↑ Tereus, "Tereus 1 is the cruel Thracian king who helped King Pandion 2 of Athens in his war against King Labdacus 1 of Thebes, and having received one of his daughters seduced the other"
- ↑ Phineus, "Phineus is the blind king and seer"
- ↑ Poltys, "Poltys. An Aenian who entertained Heracles when he came to Aenus in Thrace. He was son of Poseidon [Apd.2.5.9]."
- ↑ Harpalyce(Ἁρπαλύκη)., "1. A daughter of Harpalycus, king of the Amymnaeans in Thrace. As she lost her mother in her infancy, she was brought up by her father with the milk of cows and mares, and was trained in all manly exercises. After the death of her father, whom she had once delivered from the hand of the Myrmidons, she spent her time in the forests as a robber, being so swift in running that horses were unable to overtake her. At length, however, she was caught in a snare by shepherds, who killed her. (Serv. ad Virg. Aen. 1.321; Hyg. Fab. 193.)"
- ↑ Peiros, Peiros. Thracian leader, son of Imbrasus and father of Rhigmus. He was killed by Thoas 2, Leader of the Aetolians (Hom.Il.4.520ff., 20.484ff.).
- ↑ Rhesus Rhesus 2 is chiefly remembered because he came from Thrace to defend Troy with great pomp and circumstance, but died on the night of his arrival, without ever engaging in battle.
- ↑ Carlos Parada, "Orpheus, king of the Ciconians"
- ↑ Polymestor, "Polymestor 1 (Polymnestor). This is the king of the Bistonians in Thrace"
- ↑ Carnabon, "Carnabon. King of the Getae in Thrace who came into power when grain was first given to men [see also Lyncus, and CONSTELLATIONS] [Hyg.Ast.2.14]."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 41: "... Trixae and Sophocles (Triptolem, FR 547) mentions a local king, Charnabon, as a typical anti-hero."
- ↑ The Oxford Classical Dictionary by Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth, ISBN 0-19-860641-9, page 1515, "The Thracians were subdued by the Persians by 516"
- ↑ The Histories by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, page 373: "... 500 mercenaries, and married Hegesipyle, daughter of the Thracian King Olorus."
- ↑ Plutarch's Lives by Plutarch, 2008, ISBN 1-4404-1432-7, page 183: "... Danube, and by winning a signal victory over Syrmus, the King of the Triballi. After this, as he heard that the Thebans had revolted, ..."
- ↑ The Oxford Classical Dictionary by Simon Hornblower and Antony Spawforth, 2003, page 1515: "... *Calpurnius Piso Caesoninus, and *Cicero calls Rabocentus, chief of the Bessi, a faithful ally, although hitherto they had been troublesome ..."
- ↑ Polyaenus: Stratagems - BOOK 7 ,The generals of the Cebrenii and Sycaeboae, two Thracian tribes, were chosen from among the priests of Hera. Cosingas, according to the tradition of the country, was elected to be their priest and general; but the army took some objection to him, and refused to obey him. To suppress the rebelliousness that had taken hold of the troops, Cosingas built a number of long ladders, and fastened them one to another. He then put out a report, that he had decided to climb up to heaven, in order to inform Hera of the disobedience of the Thracians. The Thracians, who are notoriously stupid and ridiculous, were terrified by the idea of their general's intended journey, and the resulting wrath of heaven. They implored him not to carry out his plan, and they promised with an oath to obey all of his future commands.
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald, 1998, ISBN 0-19-815047-4, page 106
- ↑ Ancient Coins of Greek Cities and Kings: From Various Collections Principally in Great Britain by James Millingen, 2004, page 42: "... silver mines so renowned in history. A coin of Geta, king of the Edones, with the legend FETAI HAONEON BAIIAEYI of the same types, ..."
- ↑ Atlas of Classical History by R. Talbert, 1989, page 63, "Getae under Cothelas"
- ↑ https://revistapontica.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/pontica-3-pag-125-129.pdf Radu Ocheșeanu: Monedele basileului Moskon aflate în colecțiile Muzeului de Arheologie Constanța
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index Dromichaetes King of the Getians
- ↑ McGing B.C.: The foreign policy of Mithridates VI Eupator, King of Pontus
- ↑ Kurt W. Treptow and Ioan Bolovan in “A history of Romania - East European Monographs”, 1996, ISBN 9780880333450, page 17 "..Two inscriptions discovered at Histria indicate that Geto-Dacian rulers (Zalmodegikos and later Rhemaxos) continued to exercise control over that city-state around 200 BC ...."
- ↑ The Hellenistic Age from the Battle of Ipsos to the Death of Kleopatra VII by Stanley M. Burstein, 1985, Index Rhemaxos Getic or Scythian ruler
- ↑ Kurt W. Treptow and Ioan Bolovan in “A history of Romania - East European Monographs”, 1996, ISBN 9780880333450, page 17 "Two inscriptions discovered at Histria indicate that Geto-Dacian rulers (Zalmodegikos and later Rhemaxos) continued to exercise control over that city-state around 200 BC ...."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index Rubobostes Dacian King
- ↑ Theodossiev, Nikola (2010). "Thrace". In Gagarin, Michael. The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece and Rome. 1. Oxford University Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-19-517072-6. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 53, "Dacian King Oroles"
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 47, "Dicomes of the Getians"
- ↑ The Roman History: The Reign of Augustus by Cassius Dio, Ian Scott-Kilvert, and John Carter, 1987, page 85: "... Then he completed their destruction with the help of Roles, the king of a tribe of the Getae. When Roles visited Octavian, he was treated as a friend ..."
- ↑ Cassius Dio. Roman History, Book LI. "While he was thus engaged, Roles, who had become embroiled with Dapyx, himself also king of a tribe of the Getae, sent for him. Crassus went to his aid, and by hurling the horse of his opponents back upon their infantry he so thoroughly terrified the latter also that what followed was no longer a battle but a great slaughter of fleeing men of both arms. Next he cut off Dapyx, who had taken refuge in a fort, and besieged him. In the course of the siege someone hailed him from the walls in Greek, obtained a conference with him, and arranged to betray the place. The barbarians, thus captured, turned upon one another, and Dapyx was killed along with many others. His brother, however, Crassus took alive, and not only did him no harm but actually released him."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 146, "Zyraxes who ruled in Dobruja"
- ↑ Studies in Ancient Greek and Roman Society by Robin Osborne, 2004, page 128: "... of its citizens, named Akornion, went on an embassy to Burebista, the first and greatest of the kings in Thrace..."
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, Index (Decaeneus/Dekaineus/Dicineus) Dacian High priest"
- ↑ Berciu 1981, p. 139-140.
- ↑ Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 48, "The Dacian king Cotiso"
- 1 2 Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 72, "At least two of his successors Comosicus and Scorillo/Corilus/Scoriscus became high priests and eventually Dacian kings"
- 1 2 Dacia: Landscape, Colonization and Romanization by Ioana A Oltean, 2007, page 47, "Kings Coson (who minted his own coins) and Duras"
- ↑ De Imperatoribus Romanis . Retrieved 2007-11-08. "In the year 88, the Romans resumed the offensive. The Roman troops were now led by the general Tettius Iulianus. The battle took place again at Tapae but this time the Romans defeated the Dacians. For fear of falling into a trap, Iulianus abandoned his plans of conquering Sarmizegetuza and, at the same time, Decebalus asked for peace. At first, Domitian refused this request, but after he was defeated in a war in Pannonia against the Marcomanni (a Germanic tribe), the emperor was obliged to accept the peace."
- ↑ Wilhelm Tomachek in “Les restes de la langue dace” published in “Le Muséon By Société des lettres et des sciences, Louvain, Belgium, page 407 "Pieporus, prince des daces Costoboces..."
- ↑ Gudmund Schütte in Ptolemy's maps of northern Europe, H. Hagerup, 1917 page 82 "historical king Pieporus. The same author Schütte in “Our forefathers” published by University Press, 1929 page 74 "The North Dacian tribes of the Koistobokoi and Karpoi unlike the rest of Dacia escaped the Roman conquest of AD 105..."
- ↑ Wilhelm Tomachek (1883): “Les restes de la langue dace” published in “Le Muséon By Société des lettres et des sciences, Louvain, Belgium, page 409
- ↑ Batty, Roger (2007): Rome and the Nomads: the Pontic-Danubian realm in antiquity, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-814936-0, ISBN 978-0-19-814936-1, page 366
- ↑ The Oxford Illustrated History of Prehistoric Europe (Oxford Illustrated Histories) by Barry Cunliffe, 2001, page 380
- ↑ Strabo,Geography(7.5.2), "A part of this country was laid waste by the Dacians when they subdued the Boii and Taurisci, Celtic tribes under the rule of Critasirus"
- ↑ Celts and the Classical World by David Rankin, ISBN 0-415-15090-6, 1996, page 189: "... and destroyed it. According to Polybius, the last of the kings of Tylis, Cavarus, was a man of magnanimity and regal character (8.24). ..."
- ↑ The Ancient Celts by Barry Cunliffe, ISBN 0-14-025422-6, 2000, page 86: "... distinguished suggests that one of the returning groups, led by Bathanatos, finally settled in the Middle Danube region at the confluence ..."
- ↑ Celts - a History, The by Daithi O HOgain, ISBN 1-905172-20-6, 2006, page 60, "... those who, on their return from Greece under their leader Bathanatos, had settled at the confluence of the Danube and the ..."
- ↑ Heckel, Waldemar. Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire. Blackwell Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1-4051-1210-7, p. 155. "In 306 or 305, he assumed the title of "King", which he held until his death at Corupedium in 282/1."
- ↑ Heckel, Waldemar. Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great: Prosopography of Alexander's Empire. Blackwell Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1-4051-1210-7, p. 155. "In 323 Lysimachus was assigned control of Thrace, and was probably strategos rather than satrap. The subordinate position of strategos may account for the failure of the sources to mention Lysimachus in the settlement of Triparadeisus; his brother Autodicus was, however, named as a Somatophylax of Philip III at that time
- ↑ The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 by Christopher Webber, ISBN 1-84176-329-2, 2001, page 11, "Philip V of Macedon occupied all the cities in Thrace up to the Hellespont, "
- 1 2 3 Thracian Kings, University of Michigan
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald,1998, ISBN 0-19-815047-4, page 105
- ↑ The Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace: Orpheus Unmasked (Oxford Monographs on Classical Archaeology) by Z. H. Archibald,1998, ISBN 0-19-815047-4, page 107
- ↑ Thrace. The History Files.
- ↑ Smith, William (1867). "Amadocus (I)". In William Smith. Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology 1
- ↑ The History Of Rome by Livy, 2004, ISBN 1-4191-6629-8, page 27: "... Pleuratus and Scerdilaedus might be included in the treaty. Attalus was king of Pergamum in Asia Minor; Pleuratus, king of the Thracians;
- ↑ http://www.historyfiles.co.uk/KingListsEurope/GreeceThraceSapes.htm
- ↑ Readings in Greek History: Sources and Interpretations by D. Brendan Nagle and Stanley M. Burstein, ISBN 0-19-517825-4, 2006, page 26: "... Ariapeithes, the Scythian king, had several sons, among them, ... by Spargapeithes, king of the Agathyrsi; whereupon Scylas succeeded to the throne, and married one of ..."
- ↑ Thracian Kings, University of Michigan, "On the death of the last Astaean king in 11 BC, the emperor Augustus conferred all Thrace to his Sapaean uncle Roimētalkēs I. In 46, on the murder of Roimētalkēs III by his wife, the kingdom of Thrace was annexed to the Roman Empire by the emperor Claudius I."
References
- The Histories, translated by G. C. Macaulay, Barnes & Noble, Inc., 2004.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ancient Thrace and Ancient Thracians. |
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.