List of political parties in Malaysia
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Malaysia |
|
|
This is a list of political parties in Malaysia, including existing and historical ones.
Legislation
Under the current legislation, all political parties (termed "Political Associations") must be registered under the Societies Act.
Election expenses
The Election Offences Act (1954) regulate the maximum expenses allowed for candidates vying for parliamentary seats and for state seats during the campaign period (excluding before the nomination day and after election day). The permissible campaign expenditure set by the Election Offences Act (1954) is RM100,000 per candidate for state seats, and RM200,000 per candidate for federal seats. According to this guideline, with 505 state seats and 222 parliamentary seats in the 2013 general election, the maximum amount that Barisan Nasional was allowed to spend was only about RM95 million. Due to the lack of record and regulations, Malaysian politicians may not even know how much they spent on their campaigns or overspending the expenditure than permitted by law. Another related problem was the secrecy surrounding political funds and their use. Although many politicians, including members of newly appointed cabinets, voluntarily disclosed their personal finances, such disclosure is not compulsory and many sources of revenue remain obscure.
Election deposits
The deposit was RM10,000 to contest a parliamentary seat, or RM5,000 to contest a state assembly seat. The deposit is used to pay for infringements of election laws and is returned after polling day unless the candidate loses and fails to garner more than 12.5 percent or one-eighth of the votes cast. Additionally it is required that each candidate provide a RM5,000 deposit for cleaning up banners and posters after the election.
Political donations
Political donations are legal in Malaysia. There is no limit, and parties are not obliged to disclose the source of the funding, which makes political donations a vague subject but still entirely legal in the country. All political donations are allowed to be given into accounts of individuals and accounts of the political party. Anonymous donors and foreigners may request to not to reveal their identities.
Political parties are funded by contributions from:
- party members and individual supporters (via membership fees/dues/subscriptions and/or local/foreign small donations),
- organisations, which share their political views (e.g. by trade union affiliation fees) or which stand to benefit from their activities (e.g. by local/foreign corporate donations) or
- taxpayers respectively the general revenue fund (by grants that are called state aid, government or public funding).
Latest election results
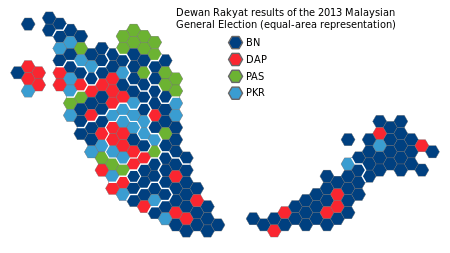

- ↑ Contested using dacing election symbol on the ballot papers.
- 1 2 3 Parties in the informal coalition, People's Pact (Pakatan Rakyat). Contested using separate election symbol on the ballot papers.
- ↑ Net seat change of component parties is –5. Sabah Progressive Party left the National Front after the 2008 election, which accounted for 2 more seats lost.
The parties
Parties represented in the Parliament and/or the state legislative assemblies
This is the list of coalitions and parties that have representation in the Parliament of Malaysia (Dewan Rakyat & Dewan Negara) and/or the state legislative assemblies, sorted by the year in which the respective parties were legalised and registered with the Registrar of Societies (ROS).
| Name | Abbr. | Leader | Ideology | Political position | International affiliation | Registered | Notes URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic Action Party Parti Tindakan Demokratik | DAP | Collective leadership | Social democracy Secularism | Centre-left | Socialist International Progressive Alliance | 1966 | [A] |
| Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party Parti Islam Se-Malaysia | PAS | Abdul Hadi Awang | Islamism Islamic democracy Pan-Islamism | Right-wing | Muslim Brotherhood (Ikhwanul Muslimin) | 1951 (established) 1955 (registered as political party) | [B] |
| National Front Barisan Nasional | BN | Najib Razak | Nationalism Conservatism | Centre-right
to Right-wing |
1973 | ||
| Malaysian Indian Muslim Congress Kongres India Muslim Malaysia | KIMMA | Syed Ibrahim Kader | Islamism Conservatism | Centre-right | N/A | 1977 | |
| Socialist Party of Malaysia Parti Sosialis Malaysia | PSM | Mohd Nasir Hashim | Socialism | Left-wing | N/A | 1998 | [D] |
| People's Justice Party Parti Keadilan Rakyat | PKR / KeADILan | Wan Azizah Wan Ismail | Social liberalism | Centre to centre-left | Liberal International (observer) | 2003 | |
| Love Sabah Party Parti Cinta Sabah | PCS | Nicholas James Guntobon | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| National Trust Party Parti Amanah Negara | AMANAH | Mohamad Sabu | Islamic socialism Islamic modernism Islamic democracy | Centre-left | N/A | 2015 | [C] |
| Malaysian Indian United Party Parti Bersatu India Malaysia | MIUP | Nallakaruppan Solaimalai | Hindu nationalism Dravidian parties | Right-wing | N/A | 2007 | |
| Malaysian United Indigenous Party Parti Pribumi Bersatu Malaysia | PPBM/BERSATU | Muhyiddin Yassin | Malay nationalism Conservative Islamism | Right-wing | N/A | 2016 | |
| Sabah Heritage Party Parti Warisan Sabah | WARISAN | Shafie Apdal | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2016 | ||
| Sabah People's Hope Party Parti Harapan Rakyat Sabah | PHRS | Lajim Ukin | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2016 | ||
|
A The term "collective leadership" is used to describe the party's Central Executive Committee since its establishment in 1966.[1][2] | |||||||
Barisan Nasional component parties
The list is sorted by the year in which the respective parties were legalised and registered with the Registrar of Societies (ROS).
| Name | Abbr. | Leader | Ideology | Political position | International affiliation | Registered | Notes URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| People's Progressive Party Parti Progresif Penduduk | myPPP | M. Kayveas | Liberalism | Centre | N/A | 1956 | |
| Sarawak United People's Party Parti Rakyat Bersatu Sarawak | SUPP | Sim Kui Hian | Nationalism Sarawak regionalism | Centre | N/A | 1959 | |
| Malaysian Indian Congress Kongres India Malaysia | MIC | Subramaniam Sathasivam | Nationalism Social conservatism Dravidian parties | Right-wing | N/A | 1963 | |
| Malaysian Chinese Association Persatuan Cina Malaysia | MCA | Liow Tiong Lai | Chinese nationalism Social conservatism | Right-wing | N/A | 1963 | |
| Malaysian People's Movement Party Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia | Gerakan/ PGRM | Mah Siew Keong | Liberalism | Centre | Liberal International Alliance of Democrats Council of Asian Liberals and Democrats | 1968 | |
| United Bumiputera Heritage Party Parti Pesaka Bumiputera Bersatu | PBB | Adenan Satem | Nationalism Sarawak regionalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1973 | |
| United Sabah Party Parti Bersatu Sabah | PBS | Joseph Pairin Kitingan | Nationalism Sabah regionalism | Centre | N/A | 1985 | [A] |
| United Malays National Organisation Pertubuhan Kebangsaan Melayu Bersatu | UMNO/ PEKEMBAR | Najib Razak | Ketuanan Melayu Social conservatism Economic liberalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1988 | [B] |
| Liberal Democratic Party Parti Liberal Demokratik | LDP | Teo Chee Kang | Liberal democracy Sabah regionalism | Centre | N/A | 1988 | |
| United Sabah People's Party Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sabah | PBRS | Joseph Kurup | Nationalism Sabah regionalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1994 | |
| United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organisation Pertubuhan Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Bersatu | UPKO | Madius Tangau | Nationalism Sabah regionalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1999 | |
| Sarawak Progressive Democratic Party Parti Demokratik Progresif Sarawak | SPDP | Tiong King Sing | Nationalism Sarawak regionalism | Right-wing | N/A | 2002 | |
| Sarawak People's Party Parti Rakyat Sarawak | PRS | James Jemut Masing | Nationalism Sarawak regionalism | Centre | N/A | 2004 | |
|
A UMNO, which was founded in 1946 was deregistered in 1988 and the Prime Minister of Malaysia formed a new party known as United Malays National Organisation (Baru) on 16 February 1988. The term "Baru" or "New" was removed by a constitutional amendment on July of the same year. | |||||||
Parties without representation in the Parliament and the state legislative assemblies
This is the list of coalitions and parties that do not have representation in the Parliament of Malaysia (Dewan Rakyat & Dewan Negara) and the state legislative assemblies, sorted by the year in which the respective parties were legalised and registered with the Registrar of Societies (ROS).
| Name | Abbr. | Leader | Ideology | Political position | International affiliation | Registered | Notes URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaysian Ceylonese Congress Kongres Ceylonese Malaysia | MCC | NKS Tharmaseelan | Hindu nationalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1970 | |
| Pan-Malaysian Islamic Front Barisan Jemaah Islamiah Se-Malaysia | BERJASA | Mohd Yusoff Haron | Islamism Islamic democracy Pan-Islamism | Centre-right | N/A | 1977 | |
| Sabah National Party Parti Kebangsaan Sabah | PKS | Thomas Anggan | Nationalism Sabah regionalism | Right-wing | N/A | 1978 | |
| Punjabi Party of Malaysia Parti Punjabi Malaysia | PPM | Gurjeet Singh Rhande | Conservatism Secularism | Centre-right | N/A | 1986 | [A] [6] |
| Community Coalition Congress Kongres Penyatuan Masyarakat | CCC | Islamism Islamic democracy Pan-Islamism | Centre-right | N/A | 1988 | ||
| Malaysian People's Party Parti Rakyat Malaysia | PRM | Rohana Ariffin | Democratic socialism Left-wing nationalism | Left-wing | N/A | 1989 | |
| All Malaysian Indian Progressive Front Barisan Kemajuan India Se-Malaysia | AMIPF | M. Sambanthan | Hindu nationalism Dravidian parties | Right-wing | N/A | 1990 | |
| Sabah Progressive Party Parti Maju Sabah | SAPP | Yong Teck Lee | Progressivism Sabah regionalism | Centre | N/A | 1994 | |
| Malaysian Democratic Party Parti Demokratik Malaysia | MDP | Wee Choo Keong | Social democracy | Centre-left | N/A | 1998 | |
| Love Malaysia Party Parti Cinta Malaysia | PCM | Tang Weng Chew | Conservatism Nationalism | Right-wing | N/A | 2009 | |
| Malaysia Makkal Sakti Party Parti Makkal Sakti Malaysia | MMSP | R. S. Thanenthiran | Hindu nationalism Dravidian parties | Right-wing | N/A | 2009 | |
| Human Rights Party Parti Hak Asasi | HRP | P. Uthayakumar | Human right | Centre | N/A | 2009 | |
| Sabah People's Front Barisan Rakyat Sabah | SPF | Berman Angkap | Social conservatism Sabah regionalism | Centre | N/A | 2010 | |
| Homeland Human's Wellbeing Party Parti Kesejahteraan Insan Tanah Air | KITA | Masrum Dayat | Secularism Social justice | Centre-left | N/A | 2010 | [B] |
| Malaysian United People's Party Parti Bersatu Rakyat Malaysia | MUPP | Shuhaidin Langkap | Nationalism Conservatism | Right-wing | N/A | 2011 | |
| Sarawak Workers Party Parti Pekerja Sarawak | SWP | Larry Sng Wei Shien | Social democracy Liberal socialism Sarawak regionalism | Centre-left | N/A | 2012 | |
| National Alliance Party Parti Ikatan Bangsa Malaysia | IKATAN | Abdul Kadir Sheikh Fadzir | Nationalism Social justice Social democracy | Right-wing | N/A | 2012 | |
| United Sabah National Organisation Party (New) Parti Pertubuhan Kebangsaan Sabah Bersatu (Baru) | USNO Baru | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| The Idea with Sabah People's Party Parti Gagasan Bersama Rakyat Sabah | Bersama | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah National People's Unity Organisation Pertubuhan Perpaduan Rakyat Kebangsaan Sabah | Perpaduan | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah Truth Party Parti Kebenaran Sabah | Kebenaran | Bentan Alamin | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| Sabahan Bugis United Party Parti Bersatu Bugis Sabah | PBBS | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah People's Economy Party Parti Ekonomi Rakyat Sabah | PERS | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah Prosperous Party of Unity Front Parti Sejahtera Angkatan Perpaduan Sabah | Sapu | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah Peace Party Parti Damai Sabah | SPP | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Sabah People's Co-operation Party Parti Kerjasama Rakyat Sabah | PAKAR | Zainal Nasiruddin | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| Sabah People's Unity Party Parti Perpaduan Rakyat Sabah | PPRS | Mohd Arshad Abd Mualap | Sabah regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| Land of the Hornbills Party Parti Bumi Kenyalang | PBK | Yu Chang Ping | Sarawak regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| New Sarawak Native People's Party Parti Bansa Dayak Sarawak Baru | PBDS Baru | Sarawak regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Economic Sarawak United People's Party Parti Ekonomi Rakyat Sarawak Bersatu | PERSB | Salleh Mahali | Conservatism Populism Sarawak regionalism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| Justice of the Peace Coalition People's Party Parti Rakyat Gabungan Jaksa Pendamai | PRGJP | Social conservatism Sarawak regionalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Malaysian Indian Justice Party Parti Keadilan India Malaysia | MIJP | V. Krishna | Hindu nationalism Dravidian parties | N/A | 2013 | ||
| New Generation Party Parti Generasi Baru | NewGen | S. Gobi Krishnan | Youth politics Elitism | N/A | 2013 | ||
| Malaysian National Party Parti Nasional Malaysia | MNP | Nationalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| Malaysian Citizen National Party Parti Nasional Penduduk Malaysia | MCNP | Nationalism | N/A | 2013 | |||
| United People's Party Parti Rakyat Bersatu | UPP | Wong Soon Koh | Sarawak regionalism | Centre | N/A | 2014 | |
| People's Alternative Party Parti Alternatif Rakyat | PAP | Zulkifli Mohd Noor | Centrism Liberal democracy | N/A | 2015 | ||
|
A The Punjabi Party of Malaysia was established in 1986[6] but only registered with the Elections Commission in 2003.[7] | |||||||
Shirt colours
The candidates and supporters of the various political parties tend to wear the following shirt colours while making their rounds in various wards or campaigning.
| Party | Shirt colour |
|---|---|
| Barisan Nasional | Blue |
| Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party | Green and white |
| Democratic Action Party | White |
| People's Justice Party | Light blue |
| National Trust Party | Orange |
Historical parties
- Communist Party of Malaya (CPM; Parti Komunis Malaya, 1930–1989), operated legally from 1945–1948. After it was banned, the party went underground as the Malayan Races Liberation Army to conduct an armed rebellion. In 1970, the former 8th Regiment of the Malayan Races Liberation Army, the armed wing of the CPM, broke away to form the Maoist Communist Party of Malaya (Revolutionary Faction). In 1974, a third split occurred among cadres who wanted the CPM to end its ideological opposition to the larger Malaysian federation and formed the Communist Party of Malaya (Marxist-Leninist).[8]
- Young Malays Union (KMM; Kesatuan Melayu Muda, 1938–1945), first nationalist political party established in British Malaya
- Malay Nationalist Party (PKMM/MNP; ms:Parti Kebangsaan Melayu Malaya, 1945–1948), first left-wing Malays party advocating socialism
- Malayan Democratic Union (MDU; ms:Kesatuan Demokratik Malaya, 1945–1948)[9]
- Conscious Youth Front (API; ms:Angkatan Pemuda Insaf, 1946–1947), left-wing Malay youth socialist party. The party became the first political party banned by the British Government.
- Conscious Women Front (AWAS; Angkatan Wanita Sedar, 1946–1948), left-wing Malay women socialist party.
- All-Malaya Council of Joint Action (AMCJA; Majlis Tindakan Bersama Se-Malaya, 1946–1948), the first all-race political action in Malaya[10]
- United Malays Organisation (UMO; ms:Pertubuhan Melayu Bersatu, 1946), right-wing Malay party
- United Malays National Organisation (UMNO/PEKEMBAR; Persatuan Kebangsaan Melayu Bersatu, 1946–1988), right-wing Malays party
- Malayan Indian Congress (MIC; Kongres India Malaya, 1946–1963), right wing Indian party
- Pan-Malayan Farmer Front (BATAS; ms:Barisan Tani Se-Malaya, 1947–1948)
- Pan-Malayan Supreme Religion Council (MATA; ms:Majlis Agama Tinggi Se-Malaya, 1947–1948)
- Malayan New Democratic Youth League (MNDYL; ms:Liga Pemuda Demokratik Baru Malaya, 1947–1948)
- Movement of Youth Corps (GERAM; ms:Gerakan Angkatan Muda, 1947–1948)
- People's United Front (PUTERA; Pusat Tenaga Rakyat, 1947–1948), left-wing multiracial party
- Hizbul Muslimin (1948)
- Malay Radical Youth (PERAM; ms:Pemuda Radikal Melayu, 1948)
- Malayan Chinese Association (MCA; Persatuan Cina Malaya, 1949–1963)
- Radical Party (ms:Parti Radikal, 1951–1952)
- Alliance (Perikatan, 1951–1973) was expanded to include other component parties beyond the original 3, UMNO, MCA and MIC, and renamed the National Front (Barisan Nasional)
- Independence of Malaya Party (IMP; Parti Kemerdekaan Malaya, 1951–1954)
- Pan-Malayan Islamic Organisation (ms:Persatuan Islam Se-Malaya, 1951–1955)
- Penang Labour Party (ms:Parti Buruh Pulau Pinang, 1951–1952)
- Malacca Labour Party (ms:Parti Buruh Melaka, 1951–1952)
- Perak Labour Party (ms:Parti Buruh Perak, 1951–1952)
- Selangor Labour Party (Parti Buruh Selangor, 1951–1952)
- Pan-Malayan Labour Party (Parti Buruh Se-Malaya, 1952–1954)
- Hizb ut-Tahrir (HT, 1953–?) is an international political movement with a branch in Malaysia.
- Perak Progressive Party (PPP; ms:Parti Progresif Perak, 1953–1956)
- National Association of Perak (NAP; ms:Parti Kebangsaan Perak, 1953–1957)
- National Party (Parti Negara, 1953–1962)
- Labour Party of Malaya (Lab/LPM; Parti Buruh Malaya, 1954–1969)
- Labour Front (1954–1960)
- Pan-Malayan Islamic Party (PMIP; Parti Islam Se-Malaya, 1955–1973)
- Malayan People's Party (Ra'ayat; Partai Ra'ayat Malaya, 1955–1970)
- Malayan Socialist Youth League (MSYL; ms:Liga Pemuda Sosialis Malaya, 1956–1958)
- Malayan Party (ms:Parti Malaya, 1956–1964)
- Malayan Peoples' Socialist Front (SF; Fron Sosialis Rakyat Malaya, 1957–1969)
- Malayan Ceylonese Congress (MCC; ms:Kongres Ceylonese Malaya, 1958–1970)
- National Party of Sarawak (PANAS; ms:Parti Negara Sarawak, 1960–1968)
- Socialist Front (BS; Barisan Sosialis, 1961)
- United National Kadazan Organisation (UNKO; Parti Kebangsaan Kadazan Bersatu, 1961–1964)
- United Sabah National Organisation (USNO; Pertubuhan Kebangsaan Sabah Bersatu, 1961–1994)
- Sarawak Native People's Front (BARJASA; ms:Barisan Rakyat Jati Sarawak, 1961–1968)
- Sarawak National Party (SNAP; Parti Kebangsaan Sarawak, 1961–2013) joined Perikatan in 1963 but was expelled in 1965, rejoined again the new Barisan Nasional coalition in 1976 but was expelled again from the coalition in 2004.[11] SNAP joined Pakatan Rakyat on 20 April 2010.[12][13][14] SNAP quits Pakatan Rakyat on 6 May 2011.[15] On 17 January 2013, the Federal Court of Malaysia declared that SNAP is no longer a registered party because the party did not furnish evidence that leadership tussle in the party has been resolved.
- North Borneo Democratic Party (ms:Parti Demokratik Borneo Utara, 1962)
- United Party (ms:Parti Bersatu, 1962–1963)
- North Borneo National Party (ms:Parti Kebangsaaan Borneo Utara, 1962)
- United Pasokmomogun Organisation (ms:Pertubuhan Pasokmomogun Bersatu, 1962–1964)
- Sarawak Chinese Association (SCA; ms:Persatuan Cina Sarawak, 1962–?)
- Sarawak Native's Heritage Party (PESAKA; ms:Parti Pesaka Anak Sarawak, 1962–1973)
- Sabah Chinese Association (SCA; ms:Persatuan Cina Sabah, 1962–1979)
- United Democratic Party (UDP; ms:Parti Demokratik Bersatu, 1962–1967)
- Sarawak Alliance (ms:Perikatan Sarawak, 1962–1973)
- Sabah Alliance (ms:Perikatan Sabah, 1962–1973)
- Sabah National Party (SANAP; ms:Parti Kebangsaan Sabah, 1963–?)
- National Convention Party (PPK; Parti Perhimpunan Kebangsaan, 1963–1965)
- MACHINDA Party (ms:Parti MACHINDA, 1964–?)
- United Pasokmomogun Kadazan Organisation (UPKO; Pertubuhan Pasokmomogun Kadazan Bersatu, 1964–1967)
- Sabah Indian Congress (SIC; ms:Kongres India Sabah, 1964–?)
- Malaysian Solidarity Convention (MSC; Konvensyen Solidariti Malaysia, 1965), was a confederation of political parties formed in 9 May until 9 August 1965 to oppose Article 153 of the Constitution of Malaysia.
- Bumiputera Party (BUMIPUTERA; ms:Parti Bumiputera, 1967–1973)
- Malaysian Marhaen Party (PMM; Parti Marhaen Malaysia, 1968–1974)
- United Malaysian Chinese Organisation (UMCO; Pertubuhan Cina Malaysia Bersatu, 1969–?)
- United Sabah Action Party (USAP; ms:Parti Tindakan Sabah Bersatu, 1970–1974)
- Communist Party of Malaya (Revolutionary Faction) (CPM-RF; Parti Komunis Malaya (Puak Revolusioner), 1970–?)
- Malaysian People's Socialist Party (PSRM; Parti Sosialis Rakyat Malaysia, 1970–1989)
- North Kalimantan Communist Party (NKCP; Parti Komunis Kalimantan Utara, 1971–1990) never operated as a legal political entity.
- Malaysian Social Justice Party (PEKEMAS; Parti Keadilan Masyarakat Malaysia, 1972–1982)
- United Sabah Action Party (USAP; Parti Tindakan Sabah Bersatu, 1972–1974)
- Communist Party of Malaya (Marxist-Leninist) (CPM-ML; Parti Komunis Malaya (Marxis-Leninis), 1974–?)
- Independent People's Progressive Party (IPPP; ms:Parti Progresif Penduduk Bebas, 1974–?)
- Homeland Consciousness Union (KITA; ms:Kesatuan Insaf Tanah Air, 1974–?)
- Sarawak People's National Party (PNRS or NEGARA; ms:Parti Negara Rakyat Sarawak, 1974–?)
- Sabah People's United Front (BERJAYA; Parti Bersatu Rakyat Jelata Sabah, 1976–1991)
- United Sabah Assembly Party (PUSAKA; ms:Parti Perhimpunan Sabah Bersatu, 1977–1978)
- Sarawak People's Organisation (SAPO; ms:Pertubuhan Rakyat Sarawak, 1978–?)
- Social Democratic Party (SDP; ms:Parti Sosial Demokratik, 1978–?)
- Sarawak Native's Party (PAJAR; ms:Parti Anak Jati Sarawak, 1978)
- Sarawak United Democratic Party (BERSATU; ms:Parti Sarawak Demokratik Bersatu, 1978–?)
- United Pasok Nunukragang National Organisation (PASOK; Pertubuhan Kebangsaan Pasok Nunukragang Bersatu, 1978–2008)
- Malaysian Workers Party (PPM; ms:Parti Pekerja-Pekerja Malaysia, 1978–2015)
- Socialist Action Party (Parti Tindakan Sosialis, 1979–?)
- Muslim People's Party of Malaysia (HAMIM; Parti Hizbul Muslimin Malaysia, 1983–?)
- Sarawak Native People's Party (PBDS; Parti Bansa Dayak Sarawak, 1983–2004), succeeded by the two offshoot parties, one is successfully registered Sarawak People's Party (PRS) while another Malaysian Dayak Congress (MDC) failed to be registered by ROS.
- Sarawak United Labour Party (ms:Parti Buruh Bersatu Sarawak, 1983–?)
- Sarawak United Bumiputera People's Party (BERSEPADU; ms:Parti Bersatu Rakyat Bumiputera Sabah, 1984–?)
- Malaysian Nationalist Party (NASMA; ms:Parti Nasionalis Malaysia, 1985–?)
- Democratic Malaysian Indian Party (DMIP; ms:Parti Demokratik India Malaysia, 1985–1997)
- Sabah Chinese Party (SCP; ms:Parti Cina Sabah, 1986–?)
- Malaysian Solidarity Party (MSP; ms:Parti Solidariti Malaysia, 1986–?)
- People's Justice Movement (HAK; ms:Harakah Keadilan Rakyat, 1986), informal coalition between PAS and PRM.[16]
- Sarawak Malaysian People's Association (PERMAS; Persatuan Rakyat Malaysia Sarawak, 1987–1991)
- Spirit of 46 Malay Party (S46; Parti Melayu Semangat 46, 1989–1996)
- Sabah People's Party (ms:Parti Rakyat Sabah, 1989–1991)
- People's Justice Front (AKAR; ms:Angkatan Keadilan Rakyat, 1989–2001)
- People's Might (GR; Gagasan Rakyat, 1989–1996), informal coalition
- Muslims Unity Movement (APU; Angkatan Perpaduan Ummah, 1989–1996), informal coalition
- Community Unity Party (PPM; ms:Parti Perpaduan Masyarakat, ?)
- Malaysian Independence Party (PMM; ms:Parti Merdeka Malaysia, ?)
- Malaysian National Momogun Party (MOMOGUN; ms:Parti Momogun Kebangsaan Malaysia, ?)
- Sarawak People's National Party (PNRS; ms:Parti Negara Rakyat Sarawak, ?)
- Sabah Chinese United Party (PCBS; ms:Parti Cina Bersatu Sabah, ?)
- United Action Party (ms:Parti Tindakan Bersatu, 1990–?)
- Muslim Community Union of Malaysia (IKATAN; Ikatan Masyarakat Islam Malaysia, 1991–1999), the constitution of the party was amended to change the name of the party to the National Justice Party (KeADILan).[17]
- United Democratic Sabah People's Power Party (SETIA; Parti Demokratik Setiahati Kuasa Rakyat Bersatu Sabah, 1994–2011) was renamed as Malaysian United People's Party (MUPP).
- Sabah Democratic Party (PDS; ms:Parti Demokratik Sabah, 1994–1999) was renamed as United Pasokmomogun Kadazandusun Murut Organisation (UPKO)
- Malaysian Human's Justice Front (AKIM; Angkatan Keadilan Insan Malaysia, 1995–2010) was later renamed as Homeland Human's Wellbeing Party (KITA) on 13 December 2010 by its new chairman, Zaid Ibrahim.
- Federated Sabah People's Front (BERSEKUTU; Barisan Rakyat Sabah Bersekutu, 1998–2010), succeeded by the establishment of Sabah People's Front (SPF)
- Alternative Front (BA; Barisan Alternatif, 1998–2004), informal coalition between PAS, KeADILan, DAP and PRM formed before 1999 general election.
- Conscious People's Movement (AIR; ms:Angkatan Insaf Rakyat, 1999), informal coalition of five PAS splinter parties in Kelantan (led by Malaysian People's Justice Movement) to contest against PAS and Barisan Nasional in the 1999 general election.
- National Justice Party (KeADILan; Parti KeADILan Nasional, 1999–2003), this entity subsequently was renamed the People's Justice Party (PKR).[18]
- Malaysian People's Reform Party (PRIM; ms:Parti Reformasi Insan Malaysia, 1999–2009), had failed to be registered by ROS.
- Malaysian Dayak Congress (MDC; Kongres Dayak Malaysia, 2005) has failed to obtain registration as a society to date.[19] Candidates of the MDC have participated in elections as Independents or on other party's tickets.[20]
- National Student Party (PMN; ms:Parti Mahasiswa Negara, 2008) was set up by a group university student but faced legal obstacle in registering for contravening the University and University College Act (UUCA).[21]
- People's Pact (PR; Pakatan Rakyat, 2008–2015), informal coalition between PKR, DAP, PAS and SNAP formed after the 2008 general election.
- Malaysian Indian Democratic Action Front (MINDRAF; ms:Barisan Bertindak Demokratik India Malaysia, 2009) has failed to be registered by ROS and been inactive since the formation of Human Right Party (HRP).[22]
- Sarawak People's Energy Party (TERAS; ms:Parti Tenaga Rakyat Sarawak, 2013–2016)
- State Reform Party (STAR; Parti Reformasi Negeri, 1996–2016)
- Sabah Heritage Development Party (PPWS; Parti Pembangunan Warisan Sabah, 2013–2016)
See also
- Politics of Malaysia
- List of political parties by country
- List of Malaysian electoral districts
- List of the winning political parties in the Malaysian general election by parliamentary constituency
References
- ↑ "Devan Nair steps down". The Straits Times. 31 July 1967. p. 8.
- ↑ Liew Chin Tong (18 October 2013). "What Utusan doesn't know about DAP". The Rocket.
- ↑ Hooker, M. B. (1983). Islam in South-East Asia. Boston: Brill Archive. pp. 203–204. ISBN 90-04-06844-9.
- ↑ Ram Anan (31 August 2015). "GHB to take over dormant Workers Party". The Malaysian Insider. Retrieved 31 August 2015.
- ↑ "Parti Bersatu Sabah (PBS)". MalaysiaToday.com. 5 June 2008. Archived from the original on 1 December 2008. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- 1 2 Patrick, Sennyah; Chow Kum Hor (10 November 2002). "Parti Punjabi willing to wait for admission into BN". New Straits Times. The New Straits Times Press (M) Berhad. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ↑ "Parti Punjabi forced to amend constitution". New Straits Times. The New Straits Times Press (M) Berhad. 3 October 2002. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ↑ Staar, Richard Phillip; M. Drachkovitch, Milorad; H. Gann, Lewis (1975). Yearbook of International Communist Affairs. Hoover Institution on War, Revolution, and Peace. Stanford: Hoover Institution Press. p. 376. ISBN 0-8179-1461-7.
- ↑ "Malayan Democratic Union is formed - Singapore History".
- ↑ "Pan-Malayan Council of Joint Action is formed - Singapore History".
- ↑ Weiner, Myron; Ergun Özbudun (1987). Competitive Elections in Developing Countries. Durham: Duke University Press. p. 129. ISBN 0-8223-0766-9.
- ↑ Sarawak party joins Pakatan, 10 January 2010, MalaysianMirror
- ↑ "Snap secara rasmi sertai Pakatan Rakyat". Malaysiakini. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- ↑ SNAP now fourth PR member, 20 April 2010, MalaysianMirror
- ↑ SNAP quits Pakatan
- ↑ "Kejayaan pilihan raya 2008 dirintis dari episod 1986:".
- ↑ "iMOL Archives - PKR抯 watershed election". Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- ↑ Malaysiakini : PKR launched, promises to be truly multi-racial
- ↑ "In Search of the Elusive Dayak Political Unity". Bernama. 3 October 2002. Retrieved 14 May 2006.
- ↑ "It's All Systems Go For Sarawak BN". Bernama. 9 February 2008. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ↑ "University Students Form New Party". People are the boss. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- ↑ "ANNOUNCEMENT OF HUMAN RIGHTS PARTY (HRP), MALAYSIA. | Human Rights Party Malaysia".
External links
- The Registry of Societies Malaysia offfical website
- Societies Act 1966
- List of political parties registered with Election Commission