Municipalities of Estonia
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Estonia |
|
Legislature
|
|
Judiciary |
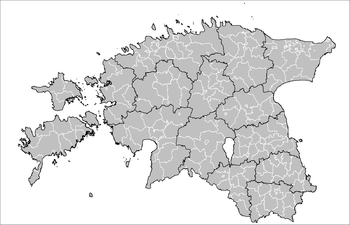

A municipality (Estonian: omavalitsus, plural omavalitsused) is the smallest administrative subdivision of Estonia. Each municipality is a unit of self-government with its representative and executive bodies. The municipalities in Estonia cover the entire territory of the country.
Municipalities in Estonia are of two types: urban municipalities or towns (linnad, singular linn) and rural municipalities or parishes (vallad, singular vald). There is no other status distinction between them.
Municipality may contain one or several settlements. All urban municipalities plus 6 rural municipalities contain only one settlement. Of the latter six, 5 are so-called "borough-parishes", consisting of one borough, while Ruhnu Parish consists of one village.
Some municipalities are divided into districts. The 8 urban districts (linnaosad, singular linnaosa) of Tallinn have limited self-government, while other urban districts are formed for administrative purposes. Some rural districts (osavallad) have limited self-government, while other types of rural districts do not.
Municipalities range in population from Tallinn with 427,500 inhabitants to Ruhnu with 68.[1] As over two-thirds of the municipalities have a population of under 3,000, many of them have found it advantageous to co-operate in providing services and carrying out administrative functions.
Currently, since 12 December 2014,[2] there are total of 213 municipalities, 30 of which are urban and 183 rural. By county, these are:
Harju County
23 municipalities (6 urban, 17 rural)

Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Aegviidu (borough)
- Anija Parish (includes the town of Kehra)
- Harku Parish
- Jõelähtme Parish
- Keila Parish
- Kernu Parish (will form Saue Parish in 2017)
- Kiili Parish (includes the borough of Kiili)
- Kose Parish
- Kuusalu Parish
- Nissi Parish (will form Saue Parish in 2017)
- Padise Parish
- Raasiku Parish
- Rae Parish
- Saku Parish
- Saue Parish (will form Saue Parish in 2017)
- Vasalemma Parish
- Viimsi Parish
Hiiu County
4 rural municipalities

Rural municipalities:
- Emmaste Parish
- Hiiu Parish (includes the town of Kärdla)
- Käina Parish
- Pühalepa Parish
Ida-Viru County
20 municipalities (5 urban, 15 rural)
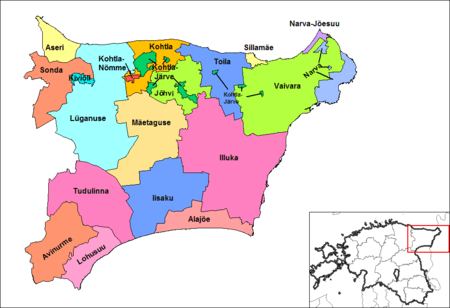
Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Alajõe Parish
- Aseri Parish
- Avinurme Parish
- Iisaku Parish
- Illuka Parish
- Jõhvi Parish (includes the town of Jõhvi)
- Kohtla Parish
- Kohtla-Nõmme (borough)
- Lohusuu Parish
- Lüganuse Parish (includes the town of Püssi)
- Mäetaguse Parish
- Sonda Parish
- Toila Parish
- Tudulinna Parish
- Vaivara Parish
Järva County
12 municipalities (1 urban, 11 rural)

Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Albu Parish
- Ambla Parish
- Imavere Parish
- Järva-Jaani Parish (includes the borough of Järva-Jaani)
- Kareda Parish
- Koeru Parish
- Koigi Parish
- Paide Parish
- Roosna-Alliku Parish
- Türi Parish (includes the town of Türi)
- Väätsa Parish
Jõgeva County
13 municipalities (3 urban, 10 rural)
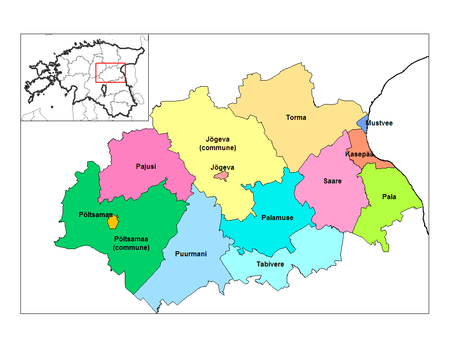
Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Jõgeva Parish
- Kasepää Parish
- Pajusi Parish
- Pala Parish
- Palamuse Parish
- Puurmani Parish
- Põltsamaa Parish
- Saare Parish
- Tabivere Parish
- Torma Parish
Lääne County
10 municipalities (1 urban, 9 rural)
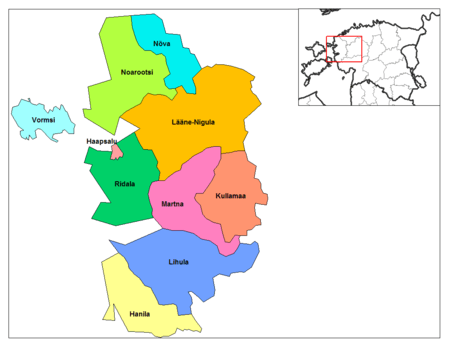
Urban municipality:
Rural municipalities:
- Hanila Parish
- Kullamaa Parish
- Lääne-Nigula Parish
- Lihula Parish (includes the town of Lihula)
- Martna Parish
- Noarootsi Parish
- Nõva Parish
- Ridala Parish
- Vormsi Parish
Lääne-Viru County
15 municipalities (2 urban, 13 rural)
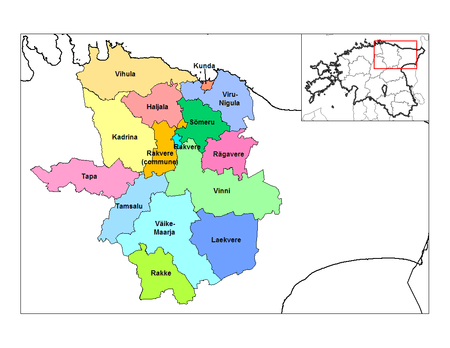
Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Haljala Parish
- Kadrina Parish
- Laekvere Parish
- Rakke Parish
- Rakvere Parish
- Rägavere Parish
- Sõmeru Parish
- Tamsalu Parish (includes the town of Tamsalu)
- Tapa Parish (includes the town of Tapa)
- Vihula Parish
- Vinni Parish
- Viru-Nigula Parish
- Väike-Maarja Parish
Pärnu County
19 municipalities (2 urban, 17 rural)

Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Are Parish
- Audru Parish (includes the borough of Lavassaare)
- Halinga Parish (includes the borough of Pärnu-Jaagupi)
- Häädemeeste Parish
- Kihnu Parish
- Koonga Parish
- Paikuse Parish (includes the borough of Paikuse)
- Saarde Parish (includes the town of Kilingi-Nõmme)
- Sauga Parish
- Surju Parish
- Tahkuranna Parish
- Tootsi (borough)
- Tori Parish
- Tõstamaa Parish
- Varbla Parish
- Vändra Parish
- Vändra (borough)
Põlva County
13 rural municipalities

Rural municipalities:
- Ahja Parish
- Kanepi Parish
- Kõlleste Parish
- Laheda Parish
- Mikitamäe Parish
- Mooste Parish
- Orava Parish
- Põlva Parish (includes the town of Põlva)
- Räpina Parish (includes the town of Räpina)
- Valgjärve Parish
- Vastse-Kuuste Parish
- Veriora Parish
- Värska Parish
Rapla County
10 rural municipalities

Rural municipalities:
- Juuru Parish
- Järvakandi (borough)
- Kaiu Parish
- Kehtna Parish
- Kohila Parish (includes the borough of Kohila)
- Käru Parish
- Märjamaa Parish (includes the borough of Märjamaa)
- Raikküla Parish
- Rapla Parish (includes the town of Rapla)
- Vigala Parish
Saare County
14 municipalities (1 urban, 13 rural)

Urban municipality:
Rural municipalities:
- Kihelkonna Parish
- Lääne-Saare Parish
- Laimjala Parish
- Leisi Parish
- Muhu Parish
- Mustjala Parish
- Orissaare Parish
- Pihtla Parish
- Pöide Parish
- Ruhnu Parish
- Salme Parish
- Torgu Parish
- Valjala Parish
Tartu County
22 municipalities (3 urban, 19 rural)

Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Alatskivi Parish
- Haaslava Parish
- Kambja Parish
- Konguta Parish
- Laeva Parish
- Luunja Parish
- Meeksi Parish
- Mäksa Parish
- Nõo Parish
- Peipsiääre Parish
- Piirissaare Parish
- Puhja Parish
- Rannu Parish
- Rõngu Parish
- Tartu Parish
- Tähtvere Parish
- Vara Parish
- Võnnu Parish
- Ülenurme Parish
Valga County
13 municipalities (2 urban, 11 rural)
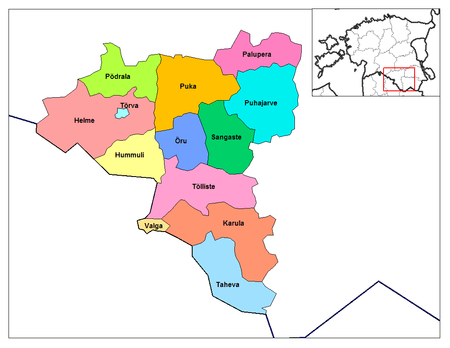
Urban municipalities:
- Tõrva (will form Tõrva Parish in 2017)
- Valga
Rural municipalities:
- Helme Parish (will form Tõrva Parish in 2017)
- Hummuli Parish (will form Tõrva Parish in 2017)
- Karula Parish
- Otepää Parish (includes the town of Otepää)
- Palupera Parish
- Puka Parish
- Põdrala Parish (will form Tõrva Parish in 2017)
- Sangaste Parish
- Taheva Parish
- Tõlliste Parish
- Õru Parish
Viljandi County
12 municipalities (3 urban, 9 rural)

Urban municipalities:
Rural municipalities:
- Abja Parish (includes the town of Abja-Paluoja)
- Halliste Parish
- Karksi Parish (includes the town of Karksi-Nuia)
- Kolga-Jaani Parish
- Kõo Parish
- Kõpu Parish
- Suure-Jaani Parish (includes the town of Suure-Jaani)
- Tarvastu Parish
- Viljandi Parish
Võru County
13 municipalities (1 urban, 12 rural)

Urban municipality:
Rural municipalities:
- Antsla Parish (includes the town of Antsla)
- Haanja Parish
- Lasva Parish
- Meremäe Parish
- Misso Parish
- Mõniste Parish
- Rõuge Parish
- Sõmerpalu Parish
- Urvaste Parish
- Varstu Parish
- Vastseliina Parish
- Võru Parish
Structure of local authorities
In each municipality there is a local government as well as a council.
The council (volikogu) is a representative body elected by the residents of a municipality for a term of three years. The members of the council elect a chairman (volikogu esimees), who organises the council’s work and represents the municipality.
The government (valitsus) is an executive body formed by the council. It is headed by a mayor (linnapea in towns, vallavanem in parishes), who is appointed for a four-year term. The mayor cannot be the chairman of the council. Other members of the government are chosen by the mayor with the approval of the council.
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.einst.ee/factsheets/factsheets_uus_kuju/local_government_reform.htm
- ↑ "Täna tõmmati esmakordselt lehvima uue Lääne-Saare valla lipp" (in Estonian). ERR. 2014-12-31. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
External links
- Local Government Reform by the Estonian Institute.
- Local Government Reform by the Institute of Baltic Studies.
- Administrative Division of Estonia at the Institute of the Estonian Language website.