List of equations in fluid mechanics
| Continuum mechanics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Laws
|
||||
This article summarizes equations in the theory of fluid mechanics.
Definitions
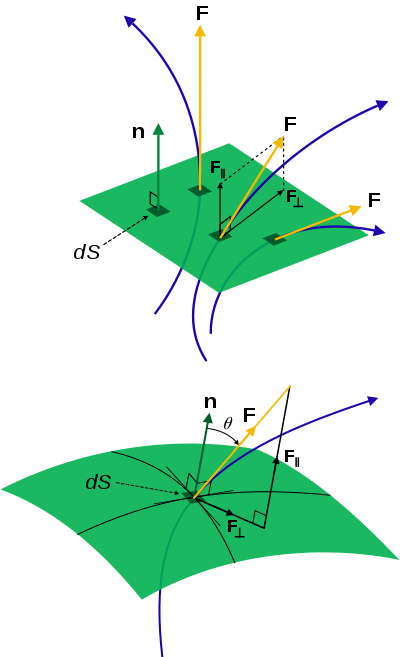
Flux F through a surface, dS is the differential vector area element, n is the unit normal to the surface. Left: No flux passes in the surface, the maximum amount flows normal to the surface. Right: The reduction in flux passing through a surface can be visualized by reduction in F or dS equivalently (resolved into components, θ is angle to normal n). F•dS is the component of flux passing though the surface, multiplied by the area of the surface (see dot product). For this reason flux represents physically a flow per unit area.
Here is a unit vector in the direction of the flow/current/flux.
Quantity (common name/s) (Common) symbol/s Defining equation SI units Dimension Flow velocity vector field u m s−1 [L][T]−1 Velocity pseudovector field ω s−1 [T]−1 Volume velocity, volume flux φV (no standard symbol) m3 s−1 [L]3 [T]−1 Mass current per unit volume s (no standard symbol) kg m−3 s−1 [M] [L]−3 [T]−1 Mass current, mass flow rate Im kg s−1 [M][T]−1 Mass current density jm kg m−2 s−1 [M][L]−2[T]−1 Momentum current Ip kg m s−2 [M][L][T]−2 Momentum current density jp kg m s−2 [M][L][T]−2
Equations
Physical situation Nomenclature Equations Fluid statics,
pressure gradient- r = Position
- ρ = ρ(r) = Fluid density at gravitational equipotential containing r
- g = g(r) = Gravitational field strength at point r
- ∇P = Pressure gradient
Buoyancy equations - ρf = Mass density of the fluid
- Vimm = Immersed volume of body in fluid
- Fb = Buoyant force
- Fg = Gravitational force
- Wapp = Apparent weight of immersed body
- W = Actual weight of immersed body
Buoyant force
Bernoulli's equation pconstant is the total pressure at a point on a streamline Euler equations - ρ = fluid mass density
- u is the flow velocity vector
- E = total volume energy density
- U = internal energy per unit mass of fluid
- p = pressure
- denotes the tensor product
Convective acceleration Navier–Stokes equations - TD = Deviatoric stress tensor
- = volume density of the body forces acting on the fluid
- here is the del operator.
See also
- Defining equation (physical chemistry)
- List of electromagnetism equations
- List of equations in classical mechanics
- List of equations in gravitation
- List of equations in nuclear and particle physics
- List of equations in quantum mechanics
- List of photonics equations
- List of relativistic equations
- Table of thermodynamic equations
Sources
- P.M. Whelan, M.J. Hodgeson (1978). Essential Principles of Physics (2nd ed.). John Murray. ISBN 0-7195-3382-1.
- G. Woan (2010). The Cambridge Handbook of Physics Formulas. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-57507-2.
- A. Halpern (1988). 3000 Solved Problems in Physics, Schaum Series. Mc Graw Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-025734-4.
- R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg (2005). Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd ed.). VHC Publishers, Hans Warlimont, Springer. pp. 12–13. ISBN 978-0-07-025734-4.
- C.B. Parker (1994). McGraw Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-07-051400-3.
- P.A. Tipler, G. Mosca (2008). Physics for Scientists and Engineers: With Modern Physics (6th ed.). W.H. Freeman and Co. ISBN 978-1-4292-0265-7.
- L.N. Hand, J.D. Finch (2008). Analytical Mechanics. Cambridge University Press,. ISBN 978-0-521-57572-0.
- T.B. Arkill, C.J. Millar (1974). Mechanics, Vibrations and Waves. John Murray,. ISBN 0-7195-2882-8.
- H.J. Pain (1983). The Physics of Vibrations and Waves (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons,. ISBN 0-471-90182-2.
Further reading
- L.H. Greenberg (1978). Physics with Modern Applications. Holt-Saunders International W.B. Saunders and Co. ISBN 0-7216-4247-0.
- J.B. Marion, W.F. Hornyak (1984). Principles of Physics. Holt-Saunders International Saunders College. ISBN 4-8337-0195-2.
- A. Beiser (1987). Concepts of Modern Physics (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill (International). ISBN 0-07-100144-1.
- H.D. Young, R.A. Freedman (2008). University Physics – With Modern Physics (12th ed.). Addison-Wesley (Pearson International). ISBN 0-321-50130-6.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.
