List of Storm Prediction Center high risk days

A high risk severe weather event is the greatest threat level issued by the Storm Prediction Center (SPC) for convective weather events in the United States. High risks are issued only a few times a year when forecasters at the SPC are confident that a major severe weather outbreak, namely tornadoes and occasionally derechoes, will occur on the given day. These are typically reserved for the most extreme events.[1]
Limited details are available for days before the late 1990s, and it is probable that there were additional high risk days with no online documentation, especially in the 1980s.
High Risk days
1980s–1999
Prior to 1997, data on high risk events is relatively scarce due to a lack of online documentation by the Storm Prediction Center. Most of the listed events from 1984 to 1997 are constructed from case studies on certain outbreak, namely for those in North Carolina, as well as storm chaser accounts.[2] During this time period, at least 42 high risk outlooks were issued for the United States.
| Storm Prediction Center High Risk Events – 1980s–1999[nb 1] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Year | Region | Tornadoes | Peak gust | Fatalities | Outlook | Notes |
| March 28 | 1984 | East-Central Alabama, Central Georgia, South Carolina, and eastern North Carolina[3] | 24 | 57 |  |
1984 Carolinas tornado outbreak – Twenty-four tornadoes touched down; seven were rated F4. In addition to the 57 tornadic deaths, 1,249 people were injured.[4] | |
| May 3 | 1984 | North Carolina[5] | 38 | 5 | Full extent of high risk is unknown, though likely included areas further southeast where most tornadoes occurred.[5] Thirty-eight tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[6] | ||
| May 7 | 1988 | Oklahoma[2] | 5 | 0 | Severe weather outbreak did not consolidate and event "busted."[2] Five tornadoes touched down; two were rated F2.[7] | ||
| May 16 | 1989 | Oklahoma, Texas[8] | 20 | 1 | Twenty tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[9] | ||
| November 15 | 1989 | Southern U.S.[2] | 17 | 21 |  |
November 1989 tornado outbreak – Seventeen tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[10] | |
| March 13 | 1990 | Central U.S.[2] | 59 | 2 | March 1990 Central United States tornado outbreak – Uncertainty in risk-level; assumed to have been high due to tornadic activity.[2] Fifty-nine tornadoes touched down; two were rated F5.[11] | ||
| May 15 | 1990 | Oklahoma[2] | 17 | 1 | Seventeen tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[12] | ||
| June 2 | 1990 | Ohio Valley[2] | 65 | 9 | June 1990 Lower Ohio Valley tornado outbreak – Sixty-five tornadoes touched down; seven were rated F4.[13] | ||
| March 29 | 1991 | North Carolina[5] | 21 | 0 | The extent of the high risk is unknown outside of North Carolina.[5] Twenty-one tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[14] | ||
| April 11 | 1991 | Oklahoma, Kansas, and the Texas Panhandle[15] | 7 | 0 | Severe weather outbreak did not consolidate due to a lack of moisture and instability anticipated to develop.[2] Seven tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[16] | ||
| April 12 | 1991 | Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas[2] | 24 | 0 | Twenty-four tornadoes touched down; two were rated F3.[17] | ||
| April 26 | 1991 | Central U.S.[2] | 55 | 21 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 26, 1991 – Fifty-five tornadoes touched down; one was rated F5.[18] | |
| April 28 | 1991 | Eastern Oklahoma and Kansas[2] | 13 | 0 | Thunderstorm complex early in the day prevented significant moisture from moving into the region and ultimately limited severe weather activity.[19] Thirteen tornadoes touched down; two were rated F2.[20] | ||
| June 16 | 1992 | Midwest [21] | 65 | 1 | Mid-June 1992 tornado outbreak – Sixty-five tornadoes touched down; one was rated F5.[22] | ||
| June 17 | 1992 | Great Lakes | 28 | 0 | Mid-June 1992 tornado outbreak – Twenty-eight tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[23] | ||
| June 7 | 1993 | Upper Midwest | 40 | 0 | Forty tornadoes touched down; two were rated F4.[24] | ||
| March 27 | 1994 | Southern U.S. | 29 | 40 |  |
1994 Palm Sunday tornado outbreak – Twenty-nine tornadoes touched down; two were rated F4.[25] | |
| April 25 | 1994 | Central U.S. | 28 | 3 | Numerous hail reports. Twenty-eight tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[26] | ||
| August 27 | 1994 | Upper Midwest | 12 | 4 | Only high risk ever issued in August. Twelve tornadoes touched down; two were rated F3.[27] | ||
| November 27 | 1994 | Southern U.S. | 18 | 6 | Eighteen tornadoes touched down; four were rated F3.[28] | ||
| April 17 | 1995 | Oklahoma, Texas | 21 | 0 | Primarily a derecho event | ||
| May 7 | 1995 | Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas | 33 | 6 | May 1995 tornado outbreak sequence – Day one of a 5-day event | ||
| May 12 | 1995 | Kansas | 14 | 0 | May 1995 tornado outbreak sequence | ||
| May 13 | 1995 | Ohio Valley | 25 | 3 | May 1995 tornado outbreak sequence – Included a major derecho | ||
| May 17 | 1995 | Kansas | 6 | 0 | May 1995 tornado outbreak sequence | ||
| April 19 | 1996 | Illinois, Indiana | 63 | 104 mph (167 km/h) | 1 | April 1996 tornado outbreak sequence | |
| May 26 | 1996 | Kansas, Oklahoma | 20 | 119 mph (192 km/h) | 0 | Also a derecho | |
| May 2 | 1997 | Mississippi, Alabama | 8 | 92 mph (148 km/h) | 1 | Also a derecho event | |
| July 1 | 1997 | Upper Mississippi Valley | 19 | 109 mph (175 km/h) | 0 | Moderate tornado outbreak reorganized into a progressive derecho | |
| February 10 | 1998 | Texas, Louisiana | 25 | 135 mph (217 km/h) | 0 | Rare winter serial derecho | |
| April 8 | 1998 | Alabama[29] | 14 | 92 mph (148 km/h) | 35 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 6–9, 1998 – F5 damage in suburban Birmingham |
| April 15 | 1998 | Middle Mississippi Valley | 21 | 75 mph (121 km/h) | 2 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 15–16, 1998 – Day 1 of outbreak |
| April 16 | 1998 | Tennessee | 41 | 98 mph (158 km/h) | 10 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 15–16, 1998 – Day 2 of outbreak |
| May 31 | 1998 | Northeastern U.S.[30][31][32][33] | 42 | 128 mph (206 km/h) | 7 |  |
Late-May 1998 tornado outbreak and derecho – Only high risk ever issued in the Northeast |
| June 14 | 1998 | Ohio Valley | 22 | 92 mph (148 km/h) | 0 | Followed by a progressive derecho | |
| January 21 | 1999 | Arkansas[34][35] | 82 | 8 |  |
Tornado outbreak of January 21–23, 1999; earliest high risk to be issued on record | |
| March 8 | 1999 | Arkansas, Louisiana | 10 | 0 | Few tornadoes with some scattered hail and wind | ||
| April 8 | 1999 | Iowa, Missouri, Illinois | 47 | 2 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 8–9, 1999 | |
| May 3 | 1999 | Oklahoma, Kansas[36] | 73 | 46 |  |
1999 Oklahoma tornado outbreak – Highest winds ever recorded in a tornado, 301 mph (484 km/h)[37] | |
| May 4 | 1999 | Oklahoma, Arkansas, Texas[36] | 43 | 1 | .png) |
1999 Oklahoma tornado outbreak – Day 2 of outbreak | |
| May 5 | 1999 | Southern U.S. | 15 | 3 | 1999 Oklahoma tornado outbreak – First and only occurrence of three consecutive high risk days. Major derecho event | ||
| June 5 | 1999 | South Dakota, Nebraska[38] | 8 | 0 |  |
Event failed to consolidate with only isolated tornadoes and scattered severe wind reported. A shortwave ridge maintained a capping inversion.[39] | |
2000–2009
There were no high risk days in 2000.
| Storm Prediction Center High Risk Events – 2000–2009[nb 1][nb 2] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Year | Region | Tornadoes | Peak gust | Fatalities | Outlook | Notes |
| April 6 | 2001 | Texas Panhandle, Western Oklahoma, much of Kansas, and extreme southern Nebraska[40] | 6 | 124 mph (200 km/h)† | 1 |  |
Serial derecho with widespread wind damage One person was killed by lightning in Ohio.[41] Six tornadoes touched down; two were rated F2.[42] |
| April 11 | 2001 | Eastern Iowa, Southern Wisconsin, and northwest Illinois[43] | 40 | 92 mph (148 km/h) | 3 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 10–11, 2001 – Three people were killed by tornadoes.[44] Forty tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[45] |
| June 11 | 2001 | Southern Minnesota, Northeastern Iowa, and West-Central Wisconsin[46] | 29 | 120 mph (190 km/h) | 2 |  |
Progressive derecho with widespread wind damage. Measured thunderstorm wind gust of 120 miles per hour (193 km/h) near Atwater, Minnesota.[47] Twenty-nine tornadoes touched down; one was rated F2.[48] |
| October 13 | 2001 | U.S. Gulf Coast[49] | 32 | 112 mph (180 km/h)† | 1 |  |
One person was killed by straight-line winds in Illinois.[50] Thirty-two tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[51] |
| October 24 | 2001 | Midwest[52] | 25 | 104 mph (167 km/h)† | 3 |  |
North Central Indiana-Michigan tornado outbreak – Plus a major serial derecho. One person was killed by straight-line winds in Michigan.[53] Twenty-five tornadoes touched down; two were rated F3.[54] |
| April 16 | 2002 | Upper Midwest[55] | 14 | 85 mph (137 km/h)† | 1 |  |
One person was killed by straight-line winds in Kansas.[56] Fourteen tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[57] High risk removed at 2000 UTC outlook update, prior to the initiation of the most intense severe weather. |
| July 31 | 2002 | Minnesota, Wisconsin[58] | 3 | 75 mph (121 km/h)† | 0 |  |
No fatalities took place.[59] Three weak tornadoes touched down.[60] Only the 0600 UTC outlook included a high risk, the only known time in which a high risk was issued in the early morning outlook and then removed from all subsequent outlooks. |
| November 10 | 2002 | Midwest and Southern U.S.[61] | 61 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 32 |  |
2002 Veterans Day Weekend tornado outbreak – No non-tornadic death took place.[62] Sixty-one tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4 (in Northwest Ohio, outside the high risk area - the strongest tornadoes within the high risk were rated F3). Thirty-two people were killed by the outbreak. Part of a three-day oubreak that resulted in 83 tornadoes and 36 deaths.[63] |
| December 23 | 2002 | Texas, Louisiana[64] | 15 | 70 mph (110 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Only high risk ever issued in December and latest in the year by over a month a high risk has been issued since 2000 (second latest November 17, 2013). No fatalities took place.[65] Fifteen tornadoes touched down; three were rated F1.[66] |
| April 6 | 2003 | Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi[67] | 18 | 83 mph (134 km/h) | 0 |  |
Eighteen tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[68] |
| May 4 | 2003 | Central U.S.[69] | 85 | 89 mph (143 km/h)† | 39 |  |
May 2003 tornado outbreak sequence – Eighty-five tornadoes touched down; four were rated F4.[70] |
| May 5 | 2003 | Southern U.S.[71] | 21 | 104 mph (167 km/h)† | 0 |  |
May 2003 tornado outbreak sequence – Twenty-one tornadoes touched down; one was rated F3.[72] |
| May 8 | 2003 | Kansas, Oklahoma[73] | 43 | 104 mph (167 km/h) | 0 |  |
May 2003 tornado outbreak sequence – Forty-three tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[74] |
| May 10 | 2003 | Central U.S.[75] | 52 | 92 mph (148 km/h)† | 0 |  |
May 2003 tornado outbreak sequence – Fifty-one tornadoes touched down; four were rated F3.[76] Also included 35% tornado probability area, above the 25% minimum threshold for a high risk. |
| May 15 | 2003 | Texas, Oklahoma[77] | 47 | 92 mph (148 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Forty-seven tornadoes touched down; seven were rated F2.[78] |
| March 4 | 2004 | Texas, Oklahoma[79] | 25 | 91 mph (146 km/h) | 0 |  |
Reorganized into a large serial derecho Twenty-five tornadoes touched down; two were rated F2.[80] |
| May 22 | 2004 | Nebraska, Iowa[81] | 68 | 106 mph (171 km/h) | 1 |  |
May 2004 tornado outbreak sequence – Sixty-eight tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[82] First of only two known times a high risk was not issued until 0100 UTC (the other is April 30, 2010). |
| May 24 | 2004 | Nebraska, Iowa[83] | 54 | 104 mph (167 km/h)† | 1 |  |
May 2004 tornado outbreak sequence – Also a major derecho event. Fifty-four tornadoes touched down; two were rated F2.[84] |
| May 29 | 2004 | Central U.S.[85] | 80 | 90 mph (140 km/h) | 3 | 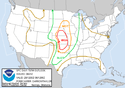 |
May 2004 tornado outbreak sequence – Eighty tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[86] |
| May 30 | 2004 | Central U.S.[87] | 86 | 120 mph (190 km/h)† | 2 |  |
May 2004 tornado outbreak sequence – Eighty-six tornadoes touched down; two were rated F3.[88] Included 35% tornado risk area above minimum threshold of 25%. |
| April 11 | 2005 | Louisiana, Mississippi[89] | 3 | 86 mph (138 km/h) | 0 |  |
Three weak tornadoes touched down.[90] |
| June 4 | 2005 | Central U.S.[91] | 44 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Forty-four tornadoes touched down; one was rated F2.[92] |
| November 15 | 2005 | Midwest and Southern U.S.[93] | 49 | 98 mph (158 km/h)† | 1 |  |
Mid-November 2005 tornado outbreak – Forty-nine tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[94] |
| March 12 | 2006 | Midwest[95] | 59 | 107 mph (172 km/h)† | 9 |  |
March 2006 tornado outbreak sequence – Fifty-nine tornadoes touched down; one was rated F4.[96] One supercell storm tracked nearly 800 miles from Oklahoma to Michigan, producing many tornadoes along its path. |
| April 6 | 2006 | Nebraska, Kansas[97] | 12 | 82 mph (132 km/h) | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 6–8, 2006 – Twelve tornadoes touched down; one was rated F2.[98] |
| April 7 | 2006 | Southern U.S.[99] | 47 | 92 mph (148 km/h)† | 10 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 6–8, 2006 – Outlook included a 60 percent probability of tornadoes, the highest level issued by the SPC.[100] Forty-seven tornadoes touched down; two were rated F3.[101] Also is the first of only two known occurrences (the other April 14, 2012) in which a Day 2 high risk outlook was issued. |
| March 1 | 2007 | Southern U.S.[102] | 36 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† | 20 |  |
February–March 2007 tornado outbreak – Thirty-six tornadoes touched down; two were rated EF4.[103] |
| April 13 | 2007 | Texas[104] | 7 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† | 1 |  |
Busted, seven tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF1.[105] |
| April 24 | 2007 | Texas[106] | 23 | 90 mph (140 km/h)† | 7 |  |
Twenty-three tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF3.[107] |
| May 5 | 2007 | Nebraska, Kansas[108] | 90 | 100 mph (160 km/h) | 1 |  |
May 2007 tornado outbreak – Ninety tornadoes touched down; two were rated EF3.[109] |
| June 7 | 2007 | Upper Midwest[110] | 12 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Reorganized into a moderate wind event Twelve tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF3.[111] |
| February 5 | 2008 | Middle Mississippi Valley[112] | 63 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 48 |  |
2008 Super Tuesday tornado outbreak – Sixty-three tornadoes touched down; three were rated EF4.[113] One EF4 tornado in Arkansas tracked over 120 miles. One of only two high risk issued in January or February since January 21, 1999 continuing to present, with the other being January 22, 2017. |
| March 15 | 2008 | Georgia, South Carolina[114] | 44 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 2 |  |
2008 Atlanta tornado outbreak – Forty-four tornadoes touched down; three were rated EF3.[115] |
| May 22 | 2008 | Kansas[116] | 28 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 1 |  |
Tornado outbreak sequence of May 22–31, 2008 – Twenty-eight tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF3.[117] |
| May 29 | 2008 | Nebraska, Iowa, South Dakota[118] | 37 | 85 mph (137 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak sequence of May 22–31, 2008 – Thirty-seven tornadoes touched down; two were rated EF3.[119] |
| June 5 | 2008 | Midwest[120] | 40 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak sequence of June 3–11, 2008 – Forty tornadoes touched down; three were rated EF2.[121] Also including a 60% significant severe wind probability which meets high risk standards. |
| April 10 | 2009 | Alabama, Georgia, Tennessee [122] | 62 | 96 mph (154 km/h)† | 2 | 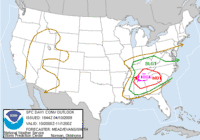 |
Tornado outbreak of April 9–11, 2009 – Sixty-two tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF4.[123] |
| April 26 | 2009 | Oklahoma, Kansas, Texas [124] | 11 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† |  |
Eleven tornadoes touched down; one was rated EF2.[125] Despite the maintenance of the high risk through the day, the outbreak busted as a whole. | |
| † – Value is estimated | |||||||
2010–present
There were no high risk days (for two consecutive years) in 2015 or 2016. The 31 months between high risk days in June 2014 and January 2017 is the longest since at least the 1980s.
| Storm Prediction Center High Risk Events – 2010–2017[nb 1] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Year | Region | Tornadoes | Peak gust | Fatalities | Outlook | Notes |
| April 24 | 2010 | Southern U.S. [126] | 39 | 120 mph (190 km/h)† | 10[127] | 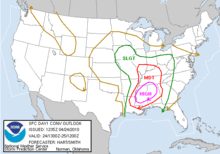 |
Tornado outbreak of April 22–25, 2010 – 39 tornadoes were confirmed; two were rated EF4. One tornado was the widest in Mississippi state history, and the fourth-longest tracked in the state. Discontinued at 01Z. |
| April 30 | 2010 | Arkansas[128] | 27 | 75 mph (121 km/h)† | 1[129] |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 30–May 2, 2010 – Day 2 of outbreak. For only the second known time a high risk was not issued until 0100 UTC (the first such occurrence was May 22, 2004) and was a slight risk for most of the day. This is the only day in which the area to eventually be in a high risk was not even in a moderate risk until 2000 UTC. 27 tornadoes touched down; two were rated EF3. |
| May 1 | 2010 | Middle Mississippi Valley[130] | 12 | 83 mph (134 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 30–May 2, 2010 – Event busted; 12 weak tornadoes were confirmed. A major flood disaster also occurred from the same storm. |
| May 10 | 2010 | Oklahoma, Kansas [131] | 70 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 3 |  |
Tornado outbreak of May 10–13, 2010 – 70 tornadoes were confirmed; two were rated EF4. |
| May 19 | 2010 | Oklahoma [132] | 13 | 70 mph (110 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak of May 10–13, 2010 Discontinued at 01Z. |
| October 26 | 2010 | Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan[133] | 43 | 85 mph (137 km/h)† | 0 |  |
October 2010 North American storm complex – Event set record for the deepest extratropical low over the continental US, major derecho event. High risk was based on 60% significant severe wind probability, with a tornado probability of 15% falling short of high risk standards. Discontinued at 2000 UTC as the main activity was in the morning and early afternoon. |
| April 16 | 2011 | North Carolina, Virginia [134] | 53 | 81 mph (130 km/h)† | 26 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 14–16, 2011 Discontinued at 01Z; storms had mostly moved off the East Coast. |
| April 26 | 2011 | South-Central U.S.[135] | 58 | 110 mph (180 km/h)† | 0 |  |
2011 Super Outbreak – Day 2 of outbreak, mostly weak and short lived tornadoes |
| April 27 | 2011 | Southern U.S.[136] | 218 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 317 |  |
2011 Super Outbreak – Day 3 of outbreak; Deadliest high risk day; event set record for most tornadoes in a 24-hour period. Included a 45% tornado area which is above the minimum thresholds for a high risk. Also produced only known watch (PDS tornado watch 235) with a >95% probability for all severe and significant severe hazards.[137] |
| May 24 | 2011 | Oklahoma, Kansas, Texas[138] | 47 | 92 mph (148 km/h)†* | 14 |  |
Tornado outbreak sequence of May 21–26, 2011 – Day 4 of outbreak. Included a 45% tornado area, above minimum high risk threshold. Discontinued at 01Z. |
| May 25 | 2011 | Midwest [139] | 94 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 4 |  |
Tornado outbreak sequence of May 21–26, 2011 – Day 5 of outbreak. Discontinued at 01Z. |
| March 2 | 2012 | Midwest and Southern U.S.[140] | 64 | 86 mph (138 km/h)† | 41 |  |
Tornado outbreak of March 2–3, 2012 – Sixty-four tornadoes touched down; two were rated EF4. Discontinued at 01Z. |
| April 14 | 2012 | Central U.S. [141] | 83 | 97 mph (156 km/h) | 6 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 13–16, 2012 – Day 2 of outbreak; Second high risk to be issued on Day 2 (the day before the event; first Day 2 high risk was for April 7, 2006) and the first/only to date ever issued on the initial (0600 UTC) Day 2 outlook.[141] Included 45% tornado probability above minimum threshold of 30%. Risk largely busted in most of Oklahoma (except far northern and western); brunt of outbreak was focused in Kansas. |
| June 12 | 2013 | Midwest [142] | 19 | 95 mph (153 km/h)† | 0 |  |
June 12–13, 2013 derecho series – High risk driven by 60% significant severe wind probability, with maximum tornado probability of 15%. Discontinued at 01Z. |
| November 17 | 2013 | Midwest [143] | 73 | 85 mph (137 km/h)† | 8[144] |  |
Tornado outbreak of November 17, 2013 – An unusually far north tornado outbreak; One of five high risk days during the month of November in recorded history.[145] Second latest date in the year a high risk has been issued since 2000 (the latest was December 23, 2002 in the Deep South), and latest date a high risk has been issued in the Midwest, surpassing previous latest of November 15, 2005. Also included a high risk level (60% significant severe) wind probability in 2000 UTC outlook. Discontinued at 01Z; storms had moved east of areas that had been in a high risk. |
| April 27 | 2014 | Southwestern Arkansas [146] | 16 | 90 mph (140 km/h)† | 19 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 27–30, 2014 – Day 1 of outbreak. Small high risk area that included the cities of Little Rock, Camden, and Danville. Only one tornado touched down in the area before the high risk was discontinued in a special outlook update at 0230 UTC.[147] |
| April 28 | 2014 | Alabama, Mississippi [148] | 50 | 70 mph (110 km/h)† | 16 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 27–30, 2014 – Day 2 of outbreak. Numerous long-tracked and strong to violent tornadoes across Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee. Largest tornado outbreak in central Alabama since April 27, 2011. Discontinued at 01Z.[149] |
| June 3 | 2014 | Nebraska, Iowa, Missouri [150] | 16 | 100 mph (160 km/h)† | 0 |  |
Issued for 60% wind probability and potential derecho; tornado probability was 10%, well short of high risk level. Extreme hail/wind and some tornadoes reported. High risk discontinued at 01Z. |
| January 22 | 2017 | Georgia, Florida[151] | 18 | 75 mph (121 km/h) | 16 |  |
Tornado outbreak of January 21–23, 2017 – Day 2 of outbreak, Issued for 30% tornado probability as well as 10% probability of EF2 or greater tornado (within 25 miles of a point) primarily in Northern FL and Southern GA. Only the second known high risk day in January; first January high risk since 1999. The first high risk for Florida since March 1, 2007 20Z outlook, and the first on record for the Florida Peninsula.[152] Also the first high risk issued under the five-category system (which began in October 2014). Eighteen tornadoes touched down during the day; two were rated EF3. Sixteen deaths resulted from the tornadoes. High risk discontinued at 01Z. |
| April 2 | 2017 | Texas, Louisiana[153] | 22 | 70 mph (110 km/h) | 2 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 2 – Issued for a 30% probability of significant tornadoes. A Particularly Dangerous Situation (PDS) Tornado Watch was issued during the event. The high risk was eventually discontinued at 01Z, however the storm yielded twenty-two tornadoes; six of which were rated EF2.[154] |
| April 5 | 2017 | Georgia, South Carolina[155] | 22 | 80 mph (130 km/h) | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak of April 5 – Issued for a 30% probability of significant tornadoes. PDS Tornado Watch #125 was issued just before 19Z for parts of Florida, Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina. A total of twenty-two tornadoes were confirmed, four of which were rated EF2. The high risk was discontinued at around 01Z.[156] |
| May 18 | 2017 | Kansas, Oklahoma[157] | 36 | 104 mph (167 km/h) | 0 |  |
Tornado outbreak of May 18 – Issued for a 30% probability of significant tornadoes. The outbreak was widely anticipated with a Moderate risk originally being issued on Day 2. PDS Tornado Watch 235 and 239 was issued for Oklahoma and Texas at 18Z and Kansas at 2030Z. A total of thirty-six tornadoes were confirmed, two of which were rated EF2. The high risk was discontinued at 01Z.[158] |
| † – Value is estimated * – Peak wind gust of 151 mph (243 km/h) measured during the EF5 El Reno tornado ** – Values are preliminary and subject to change | |||||||
See also
Notes
- 1 2 3 All values include events that took place outside the high risk area. Tornado and fatality totals only include incidents that occurred on the respective high risk days. Fatality totals encompass all storm-related events.
- ↑ Starting on February 1, 2007, the Fujita Scale was replaced with the Enhanced Fujita Scale for rating tornadoes.
References
- ↑ Chris Hayes Novy (March 25, 2010). "SPC and its Products: Convective Outlooks". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "High-Risk Days of the 1980s and 1990s". ConvectiveOutlook. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ Phillip Badgett; Barrett Smith; Jonathan Blaes; Rod Gonski & Kermit Keeter (March 18, 2009). "March 28, 1984 Carolina's Tornado Outbreak". National Weather Service Office in Raleigh, North Carolina. North Carolina State University. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "March 28, 1984 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Terry Click; Darin Figurskey; Gail Hartfield; Bradley McLamb; Jeff Orrock; Scott Sharp; Barrett Smith; Brandon Vincent; Jonathan Blaes; Rachel Wrenn & Lindsey Andersen (February 3, 2012). "April 16, 2011 North Carolina Tornado Outbreak". National Weather Service Office in Raleigh, North Carolina. North Carolina State University. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "May 3, 1984 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- ↑ "May 7, 1988 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- ↑ "The Weather Channel - May 16, 1989". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ Ziem, Andrew. "This Date in Weather History". El Gheko Neighborhood Weather Station. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ "November 15, 1989 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- ↑ "March 13, 1990 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- ↑ "May 15, 1990 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "June 2, 1990 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "March 29, 1991 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ Robert Satkus. "April 11, 1991". Fire Dispatcher. Archived from the original on February 25, 2002. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "April 11, 1991 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "April 12, 1991 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "April 26, 1991 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ Robert Satkus. "April 28, 1991". Fire Dispatcher. Archived from the original on June 10, 2007. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "April 28, 1991 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ Ostby, Frederick P. (1992). "Operations of the National Severe Storms Forecast Center" (PDF). National Severe Storms Forecast Center. Retrieved 2008-08-02.
- ↑ "June 16, 1992 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "June 17, 1992 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "June 7, 1993 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "March 27, 1994 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "April 25, 1994 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "August 27, 1994 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "November 27, 1994 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ NOAA's National Weather Service - Birmingham, Alabama
- ↑ Derecho - May 31, 1998
- ↑ The Southern Great Lakes Derecho of 1998
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 31, 1998 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 31, 1998 1500 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ http://www.targetarea.net/pic3/high21.jpg
- ↑ Front Page Display and Description-Example
- 1 2 Eric Nguyen's 1999 Chase Documents!
- ↑ "Doppler On Wheels". 3 May 1999. Retrieved 13 June 2013.
- ↑ http://www.nwas.org/ej/2007-EJ3/figure_1.htm
- ↑ Identification of Inhibiting Factors of a Null Significant Tornado Event
- ↑ Imy (April 6, 2001). "April 6, 2001 2000UTC Day 1 Outlook". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: April 6, 2001 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "April 6, 2001 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Craven (April 11, 2001). "April 11, 2001 2000UTC Day 1 Outlook". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: April 11, 2001 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "April 11, 2001 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Johns (June 11, 2001). "June 11, 2001 2000UTC Day 1 Outlook". Storm Prediction Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: June 11, 2001 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "June 11, 2001 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2001). "Severe weather outlook for October 13, 2001". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: October 13, 2001 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "October 13, 2001 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2001). "Severe weather outlook for October 24, 2001". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: October 24, 2001 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "October 24, 2001 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2002). "Severe weather outlook for April 16, 2002". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: April 16, 2002 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "April 16, 2002 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2002). "Severe weather outlook for July 31, 2002". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: July 31, 2002 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "July 31, 2002 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2002). "Severe weather outlook for November 10, 2002". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: November 10, 2002 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "November 10, 2002 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2002). "Severe weather outlook for December 23, 2002". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "Storm Events Database: December 23, 2002 All Reports". National Climatic Data Center. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ "December 23, 2002 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 15, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather outlook for April 6, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 6, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather outlook for May 4, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 4, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather outlook for May 5, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 5, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather outlook for May 8, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 8, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather outlook for May 10, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 10, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2003). "Severe weather report for May 15, 2003". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 15, 2003 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2004). "Severe weather outlook for March 4, 2004". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "March 4, 2004 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2004). "Severe weather outlook for May 22, 2004". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 22, 2004 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2004). "Severe weather outlook for May 24, 2004". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 24, 2004 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2004). "Severe weather outlook for May 29, 2004". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 29, 2004 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2004). "Severe weather outlook for May 30, 2004". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 30, 2004 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2005). "Severe weather outlook for April 11, 2005". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 11, 2005 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2005). "Severe weather outlook for June 4, 2005". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "June 4, 2005 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2005). "Severe weather outlook for November 15, 2005". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "November 15, 2005 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2006). "Severe weather outlook for March 12, 2006". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "March 12, 2006 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2006). "Severe weather outlook for April 6, 2006". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 6, 2006 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2006). "Severe weather outlook for April 7, 2006". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2006). "Severe weather outlook for April 7, 2006 (Day 2)". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 7, 2006 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2007). "Severe weather outlook for March 1, 2007". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "March 1, 2007 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2007). "Severe weather outlook for April 13, 2007". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 13, 2007 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2007). "Severe weather outlook for April 24, 2007". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "April 24, 2007 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2007). "Severe weather outlook for May 5, 2007". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "May 5, 2007 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2007). "Severe weather outlook for June 7, 2007". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "June 7, 2007 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center (2008). "Severe weather outlook for February 5, 2008". Retrieved 2008-03-12.
- ↑ "February 5, 2008 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center Mar 15, 2008 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "March 15, 2008 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 22, 2008 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "May 22, 2008 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 29, 2008 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "May 29, 2008 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center June 5, 2008 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "June 5, 2008 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 10, 2009 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "April 10, 2009 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 26, 2009 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "April 26, 2009 Tornado List". National Climatic Data Center. Tornado History Project. 2013. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 24, 2010 1200 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Storm Prediction Center Monthly and Annual Summaries". Spc.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2013-06-13.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 30, 2010 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Ark. tornadoes kill 1, injure two dozen - Weather | NBC News". MSNBC. 2010-01-05. Retrieved 2013-06-13.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 1, 2010 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 10, 2010 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 19, 2010 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center October 26, 2010 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 16, 2011 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 26, 2011 1300 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 27, 2011 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Tornado Watch 235 Watch Hazard Probabilities April 27, 2011 1846 UTC
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 24, 2011 1200 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 25, 2011 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center March 2, 2012 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- 1 2 Storm Prediction Center April 13, 2012 0600 UTC Day 2 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center June 12, 2013 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center November 17, 2013 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Coroner: 2 killed when tornado strikes farmhouse in southern Illinois as storms slam Midwest". Associated Press. The Republic. November 17, 2013. Retrieved November 17, 2013.
- ↑ Danielle Dozier (November 18, 2013). "How rare are high risk days in November?". KOCO TV. KOCO TV. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 27, 2014 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 28, 2014 0100 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 28, 2014 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Tornado Outbreak April 28-29, 2014". National Weather Service office in Birmingham, Alabama. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 2, 2014. Retrieved May 3, 2014.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center June 3, 2014 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center January 22, 2017 2000 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ Ferrell, Jesse. "Major tornado outbreak likely Sunday". Accuweather. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 2, 2017 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Storm Prediction Center". SPC Storm Reports. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center April 5, 2017 1630 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Storm Prediction Center". SPC Storm Reports. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- ↑ Storm Prediction Center May 18, 2017 0600 UTC Day 1 Convective Outlook
- ↑ "Storm Prediction Center". SPC Storm Reports. Retrieved 19 May 2017.