List of BMP-1 operators
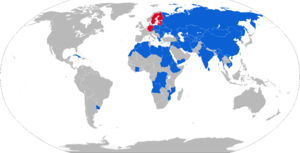
Map of BMP-1 operators in blue with former operators in red
Four Afghan BMP-1 IFVs, 2005

Chinese Type 86.

Hungarian BMP-1.

Two New Iraqi Army BMP-1s at Coalition checkpoint in Tarmiya, Iraq, 25 June 2006.

New Iraqi Army BMP-1 on the move.
BWP-1 on a military parade in Warsaw on Polish Army Day, 15 August 2007.

Romanian-made MLI-84M fitted with Israeli OWS-25R overhead mount turret armed with 25 mm Oerlikon KBA autocannon and two 9S415 ATGM launchers, Expomil exhibition, 22 October 2005.

Slovak BVP-1, 26 March 2007.

BMP-1 at the Great Patriotic War museum in Kiev, Ukraine, 1 October 2006.
The BMP-1 is a Soviet amphibious tracked Infantry fighting vehicle used by many different nations around the world. This is a list of nations that operate it.
-
 Abkhazia – 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the Abkhaziyan Army.[1]
Abkhazia – 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the Abkhaziyan Army.[1] -
 Afghanistan – 350 BMP-1s ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1990 (some of the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet service).[2] 550 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1992.[3] Between 60 and 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were delivered from Russia after 2002.[4]
Afghanistan – 350 BMP-1s ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1990 (some of the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet service).[2] 550 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1992.[3] Between 60 and 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were delivered from Russia after 2002.[4] -
 Albania – More than 17 BMP-1s acquired from East German stock in 1995.
Albania – More than 17 BMP-1s acquired from East German stock in 1995. -
 Algeria – Between 690 and 800 BMP-1s ordered in 1978 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1984. There were 684 BMP-1s in service in 1996.[5] Algeria signed a contract with Russia for modernization of 400 BMP-1s in 2006.
Algeria – Between 690 and 800 BMP-1s ordered in 1978 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1984. There were 684 BMP-1s in service in 1996.[5] Algeria signed a contract with Russia for modernization of 400 BMP-1s in 2006. -
 Angola – 21 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Belarus and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service and were sold through a Bulgarian company). 29 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service). 35 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Russia and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Russian service). 183 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Russia and delivered between 1993 and 1994.[2] 65 BMP-1s were delivered from Russia in 1998. 7 BMP-1s were delivered from Belarus in 1999.[6][7] 150 are currently in service.[8]
Angola – 21 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Belarus and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service and were sold through a Bulgarian company). 29 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service). 35 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Russia and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Russian service). 183 BMP-1s ordered in 1993 from Russia and delivered between 1993 and 1994.[2] 65 BMP-1s were delivered from Russia in 1998. 7 BMP-1s were delivered from Belarus in 1999.[6][7] 150 are currently in service.[8] -
 Armenia – 150 BMP vehicles in service with the armed forces in 1993. 212 BMP-1s in service with the armed forces in 1994, 159 in 1995 and 1996, 125 in 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 80 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006. 8 BMP-1Ks in service with the armed forces in 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 7 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006. 20 BRM-1s in service with the armed forces in 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 12 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006.[9]
Armenia – 150 BMP vehicles in service with the armed forces in 1993. 212 BMP-1s in service with the armed forces in 1994, 159 in 1995 and 1996, 125 in 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 80 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006. 8 BMP-1Ks in service with the armed forces in 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 7 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006. 20 BRM-1s in service with the armed forces in 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000, 12 in 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006.[9] -
 Azerbaijan – 102 BMP-1s in service with the armed forces in 1992, 172 in 1993, 104 in 1994, 135 in 1995, 119 in 1996, 114 in 1997 and 1998, 95 in 1999, 44 in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003 and 2004 and 6 in 2006 including 2 ordered in 2004 from Ukraine and delivered in 2005.[2] 13 BRM-1s in service with the armed forces in 1992, 12 in 1993, 34 in 1994, 33 in 1995, 1996, 1997 and 1998, 23 in 1999 and 21 in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006.[9]
Azerbaijan – 102 BMP-1s in service with the armed forces in 1992, 172 in 1993, 104 in 1994, 135 in 1995, 119 in 1996, 114 in 1997 and 1998, 95 in 1999, 44 in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003 and 2004 and 6 in 2006 including 2 ordered in 2004 from Ukraine and delivered in 2005.[2] 13 BRM-1s in service with the armed forces in 1992, 12 in 1993, 34 in 1994, 33 in 1995, 1996, 1997 and 1998, 23 in 1999 and 21 in 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 and 2006.[9] -
 Belarus – Originally 938 BMP-1s were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 461 BMP-1s in service in 1995, 98 in 2000 and 109 in 2003 and 2005.[10] There were also 161 BRM-1s in service in 1995, 2000, 2003 and 2005.[10]
Belarus – Originally 938 BMP-1s were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 461 BMP-1s in service in 1995, 98 in 2000 and 109 in 2003 and 2005.[10] There were also 161 BRM-1s in service in 1995, 2000, 2003 and 2005.[10] -
 Brunei –[5]
Brunei –[5] -
 Bulgaria – 560 bought including 100 ordered in 1995 from Russia and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Russian service).[2] 100 BMP-1Ps are currently in service.[11]
Bulgaria – 560 bought including 100 ordered in 1995 from Russia and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Russian service).[2] 100 BMP-1Ps are currently in service.[11] -
 Cambodia – 70[12]
Cambodia – 70[12] -
 China – Produced more than 3,000 Type 86s and vehicles based on it.[13] 1,000 Type 86s were in service in 2003 and 2005.[14] Around 1,000 are currently in service.[15]
China – Produced more than 3,000 Type 86s and vehicles based on it.[13] 1,000 Type 86s were in service in 2003 and 2005.[14] Around 1,000 are currently in service.[15] -
 Ivory Coast – 13 ordered in 2002 from Belarus and delivered between 2002 and 2003.[2][13]
Ivory Coast – 13 ordered in 2002 from Belarus and delivered between 2002 and 2003.[2][13] -
 Cuba – 200 ordered in 1978 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1981 and 1988. 200 more were ordered in 1989 and delivered in 1990. They are now modernized to the BMP-1P variant with new ATGMs and improved night vision equipment.[2]
Cuba – 200 ordered in 1978 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1981 and 1988. 200 more were ordered in 1989 and delivered in 1990. They are now modernized to the BMP-1P variant with new ATGMs and improved night vision equipment.[2] -
 Czech Republic – 623 BVP-1s, 145 BPzV "Svatava"s and 413 OT-90s were inherited from former Czechoslovakia in 1992.[16] There were 605 in service as 1995, 600 BVP-1s as 1996.[5] On 1 January 2008 there were 207 BVP-1s (most in reserve – getting replaced by APCs), 76 BPzV "Svatava"s and 29 OT-90s (in the process of being withdrawn from service and replaced by more modern vehicles).[17] There are also 15 BRM-1Ks in service.[18]
Czech Republic – 623 BVP-1s, 145 BPzV "Svatava"s and 413 OT-90s were inherited from former Czechoslovakia in 1992.[16] There were 605 in service as 1995, 600 BVP-1s as 1996.[5] On 1 January 2008 there were 207 BVP-1s (most in reserve – getting replaced by APCs), 76 BPzV "Svatava"s and 29 OT-90s (in the process of being withdrawn from service and replaced by more modern vehicles).[17] There are also 15 BRM-1Ks in service.[18] -
 Democratic Republic of the Congo – 20 ordered in 2005 from Ukraine and delivered in 2006.[2][13]
Democratic Republic of the Congo – 20 ordered in 2005 from Ukraine and delivered in 2006.[2][13] -
 Egypt – 80 were delivered between July and August 1973, 150 between August and September 1973. After the war Egypt received between 30 and 50. There were 200 in service in 1996. Those 200 were fitted with French diesel engines and received the designation BMP-1S (See Egypt section in BMP-1 variants article for details).[5]
Egypt – 80 were delivered between July and August 1973, 150 between August and September 1973. After the war Egypt received between 30 and 50. There were 200 in service in 1996. Those 200 were fitted with French diesel engines and received the designation BMP-1S (See Egypt section in BMP-1 variants article for details).[5] -
 Equatorial Guinea – 20 ordered in 2006 from Czech Republic and delivered in 2007.[2][13]
Equatorial Guinea – 20 ordered in 2006 from Czech Republic and delivered in 2007.[2][13] -
 Eritrea – Received a number from Ethiopia.[16]
Eritrea – Received a number from Ethiopia.[16] -
 Ethiopia – 70 along with 1000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1977 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978.[2] 20 were in service in 1995.
Ethiopia – 70 along with 1000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1977 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978.[2] 20 were in service in 1995. -
 Georgia – Originally 667 were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 15 were ordered in 2007 from Ukraine and delivered in 2008.[2] 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the Abkhaziyan Army and the same amount by the South Ossetian Army.[1] 51 were in service in 1992 and 1995, 67 in 2000, 68 in 2002, 65 in 2005, 40 in 2007,[16] 149 in 2008[19] and 79 BMP-1P and BMP-1Us in 2011. 11 BRM-1Ks were in service in 2000, 2002 and 2005 and 1 in 2008.[19]
Georgia – Originally 667 were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 15 were ordered in 2007 from Ukraine and delivered in 2008.[2] 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the Abkhaziyan Army and the same amount by the South Ossetian Army.[1] 51 were in service in 1992 and 1995, 67 in 2000, 68 in 2002, 65 in 2005, 40 in 2007,[16] 149 in 2008[19] and 79 BMP-1P and BMP-1Us in 2011. 11 BRM-1Ks were in service in 2000, 2002 and 2005 and 1 in 2008.[19] -
 Greece – Originally 501 BMP-1A1 Osts were order from Germany in 1991 and delivered between 1992 and 1994.[2] Greece offered 500 as aid to Iraq but only 100 were accepted in 2005 with 36 being delivered in 2005 and 64 in 2006.[13] There were 377 BMP-1A1 Osts in service in 2006.[13] In late 2014, a number of BMP-1A1 Ost were fitted with the ZU-23-2 anti-aircraft gun in place of the standard tower. After successful acceptance tests, the conversion of more vehicles is planned.[20]
Greece – Originally 501 BMP-1A1 Osts were order from Germany in 1991 and delivered between 1992 and 1994.[2] Greece offered 500 as aid to Iraq but only 100 were accepted in 2005 with 36 being delivered in 2005 and 64 in 2006.[13] There were 377 BMP-1A1 Osts in service in 2006.[13] In late 2014, a number of BMP-1A1 Ost were fitted with the ZU-23-2 anti-aircraft gun in place of the standard tower. After successful acceptance tests, the conversion of more vehicles is planned.[20] -
 Hungary – 500 BMP-1s and BRM-1Ks ordered in 1972 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1978. 2 BMP-1s ordered in 1994 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1995.[2][21] At peak there were 502 BMP-1s in service.[22] There were 502 BMP-1s and BRM-1Ks in 1995 and 500 in 1996.[5] There were 487 BMP-1s and 12 BRM-1Ks in 2006 and 2007[13] (mostly in stock).
Hungary – 500 BMP-1s and BRM-1Ks ordered in 1972 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1978. 2 BMP-1s ordered in 1994 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1995.[2][21] At peak there were 502 BMP-1s in service.[22] There were 502 BMP-1s and BRM-1Ks in 1995 and 500 in 1996.[5] There were 487 BMP-1s and 12 BRM-1Ks in 2006 and 2007[13] (mostly in stock). -
 India – Between 350 and 700 ordered in 1982 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1989.[2] Between 450 and 100 produced. 800 were in service in 1990, around 600 in 1995, more than 350 in 2000 and 2002 around 600 in 2005 and 700 in 2008.[23] Currently 700 are in active service.[24]
India – Between 350 and 700 ordered in 1982 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1989.[2] Between 450 and 100 produced. 800 were in service in 1990, around 600 in 1995, more than 350 in 2000 and 2002 around 600 in 2005 and 700 in 2008.[23] Currently 700 are in active service.[24] -
 Iran – 200 along with 2000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1981 from Syria and delivered between 1982 and 1983. 400 along with 4000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1986 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1986 and 1989 (the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2] A number of Type 86s were also bought from PRC.[15] More than 150 BMP-1s and Type 86s in service in 1990, 300 in 1995, 300 in 2000, 350 in 2002 and about 210 in 2005 and 2008.[25] There 200 BMP-1s in service in 1996.[5] Iran also produced 80 Boragh-based IFVs between 2001 and 2008[2] (note the entire production started in 1997). There were 40 Boragh APCs in service in 2000 and 2002 and 140 Boragh APCs in 2005 and 2008.[25]
Iran – 200 along with 2000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1981 from Syria and delivered between 1982 and 1983. 400 along with 4000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1986 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1986 and 1989 (the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2] A number of Type 86s were also bought from PRC.[15] More than 150 BMP-1s and Type 86s in service in 1990, 300 in 1995, 300 in 2000, 350 in 2002 and about 210 in 2005 and 2008.[25] There 200 BMP-1s in service in 1996.[5] Iran also produced 80 Boragh-based IFVs between 2001 and 2008[2] (note the entire production started in 1997). There were 40 Boragh APCs in service in 2000 and 2002 and 140 Boragh APCs in 2005 and 2008.[25] -
 Iraq – 200 ordered in 1973 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975. 750 ordered in 1981 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1981 and 1987 (the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2] A number of Type 86s were bought from PRC. 1,500 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1990, about 900 in 1995, about 1000 in 2000 and about 900 in 2002.[26] 100 BMP-1A1 Osts ordered in 2005 from Greece with 36 being delivered in 2005 and 64 in 2006 (Greece offered 500 of these vehicles as aid but Iraq accepted only 100) and 110 ordered in 2006 from Ukraine and delivered in 2007.[2][13] Currently the New Iraqi Army operates 434 BMP-1s[27] (including BMP-1A1 Osts).
Iraq – 200 ordered in 1973 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975. 750 ordered in 1981 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1981 and 1987 (the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2] A number of Type 86s were bought from PRC. 1,500 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1990, about 900 in 1995, about 1000 in 2000 and about 900 in 2002.[26] 100 BMP-1A1 Osts ordered in 2005 from Greece with 36 being delivered in 2005 and 64 in 2006 (Greece offered 500 of these vehicles as aid but Iraq accepted only 100) and 110 ordered in 2006 from Ukraine and delivered in 2007.[2][13] Currently the New Iraqi Army operates 434 BMP-1s[27] (including BMP-1A1 Osts). -
 Israel – Captured some BMP-1s during the Yom Kippur War. Some of the captured vehicles have been converted into mortar carriers (See Israel section for details).
Israel – Captured some BMP-1s during the Yom Kippur War. Some of the captured vehicles have been converted into mortar carriers (See Israel section for details). -
 Kazakhstan – There were 300 in 1995 and 2000, 350 in 2002 and about 210 in 2005. There were also 40 Boragh APCs in service in 2000 and 2002 and about 140 Boragh APCs in 2005.[28]
Kazakhstan – There were 300 in 1995 and 2000, 350 in 2002 and about 210 in 2005. There were also 40 Boragh APCs in service in 2000 and 2002 and about 140 Boragh APCs in 2005.[28] -
 Kyrgyzstan – There were 349 in service in 1995 and 274 in 2000 and 2005. There were also 28 BRM-1s in service in 1995 and 113 in 2000 and 2005.[29]
Kyrgyzstan – There were 349 in service in 1995 and 274 in 2000 and 2005. There were also 28 BRM-1s in service in 1995 and 113 in 2000 and 2005.[29] -
 Libya – 800 ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1982.[2] 800 in service in 1986, 750 in 1996.[5][30] Currently 740 are in service.[31]
Libya – 800 ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1982.[2] 800 in service in 1986, 750 in 1996.[5][30] Currently 740 are in service.[31] -
 Mongolia – 400 along with 3000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1981 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1982 and 1985.[2] 400 in service in 1996,[5] 310 in 2003[32]
Mongolia – 400 along with 3000 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1981 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1982 and 1985.[2] 400 in service in 1996,[5] 310 in 2003[32] -
 Morocco – 50.
Morocco – 50. -
 Moldova – There were 210 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1994.
Moldova – There were 210 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1994. -
 Mozambique – 40 in 2003.
Mozambique – 40 in 2003. -
 Myanmar – More than 50 bought from PRC.[15]
Myanmar – More than 50 bought from PRC.[15] -
 Republic of Artsakh –
Republic of Artsakh – -
 North Korea – 100 ordered in 1972 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1972 and 1973. 122 ordered in 1984 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1985 and 1991.[2] There were 1110 Korshuns (North Korean designation for BMP-1[2]), VTT-323s, Type 63s (YW-531), BTR-40s, BTR-50s, BTR-60s and BTR-152s in service in 1985.[33] 200 Korshuns in service in 1996.[5]
North Korea – 100 ordered in 1972 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1972 and 1973. 122 ordered in 1984 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1985 and 1991.[2] There were 1110 Korshuns (North Korean designation for BMP-1[2]), VTT-323s, Type 63s (YW-531), BTR-40s, BTR-50s, BTR-60s and BTR-152s in service in 1985.[33] 200 Korshuns in service in 1996.[5] -
 Poland – 1,409 BWP-1s ordered in 1969 from USSR and delivered between 1972 and 1979.[2] Poland also bought 22 BWR-1D (BRM-1K) reconnaissance vehicles in 1987 from USSR[34] and 16 BWR-1S (modernized BPzV) reconnaissance vehicles from Czech Republic in the early 1990s. The number of BWR-1D and BWR-1S has not changed. There were 1,409 BWP-1s in service in 1994,[16] 1,367 on 1 January 1998,[35] 1,366 on 1 January 1999 and 1 January 2000,[36][37] 1,332 on 1 January 2002,[38] 1,328 BWP-1 IFVs on 1 January 2003,[39] 1,321 in 2004[40] and 1,307 at the beginning of 2006[41] (Polish Ministry of Defence states that on 8 January 2006 there were 1,298 BWP-1s[42]). 1,306 BWP-1s, 33 BWP-1Ds, 5 MP-31s and 6 ZWDSz-2s in service in the first half of 2008.[43]
Poland – 1,409 BWP-1s ordered in 1969 from USSR and delivered between 1972 and 1979.[2] Poland also bought 22 BWR-1D (BRM-1K) reconnaissance vehicles in 1987 from USSR[34] and 16 BWR-1S (modernized BPzV) reconnaissance vehicles from Czech Republic in the early 1990s. The number of BWR-1D and BWR-1S has not changed. There were 1,409 BWP-1s in service in 1994,[16] 1,367 on 1 January 1998,[35] 1,366 on 1 January 1999 and 1 January 2000,[36][37] 1,332 on 1 January 2002,[38] 1,328 BWP-1 IFVs on 1 January 2003,[39] 1,321 in 2004[40] and 1,307 at the beginning of 2006[41] (Polish Ministry of Defence states that on 8 January 2006 there were 1,298 BWP-1s[42]). 1,306 BWP-1s, 33 BWP-1Ds, 5 MP-31s and 6 ZWDSz-2s in service in the first half of 2008.[43] -
 Romania – Apart from their own variant of BMP-1, MLI-84, Romania also operates Soviet-made PRP-4 "Nard"s.[44] There were 156 MLI-84s in service in 1994 and 177 in 2002.[16]
Romania – Apart from their own variant of BMP-1, MLI-84, Romania also operates Soviet-made PRP-4 "Nard"s.[44] There were 156 MLI-84s in service in 1994 and 177 in 2002.[16] -
 Rwanda –[45]
Rwanda –[45] -
 Russia – 12,200 BMP-1s, BMP-2s and BMP-3s in 1995 and 12,700 in 2000, 2002 and 2009.[46] 1,543 in active service and more than 9,057 in reserve in 2008.[47][48] Currently there are around 750 in active service and more than 10,000 in reserve in 2009.[47]
Russia – 12,200 BMP-1s, BMP-2s and BMP-3s in 1995 and 12,700 in 2000, 2002 and 2009.[46] 1,543 in active service and more than 9,057 in reserve in 2008.[47][48] Currently there are around 750 in active service and more than 10,000 in reserve in 2009.[47] -
 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic – More than 50.
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic – More than 50. -
 Slovakia – Originally 383 BVP-1s, 120 BPzV "Svatava"s and 207 OT-90s were inherited from former Czechoslovakia in 1992.[16] There were 311 BVP-1s in service in 1995 and 300 in 1996.[5] Currently there are 308 BVP-1s, 71 BPzV "Svatava"s and 205 OT-90s. There are also BRM-1Ks in service.[49]
Slovakia – Originally 383 BVP-1s, 120 BPzV "Svatava"s and 207 OT-90s were inherited from former Czechoslovakia in 1992.[16] There were 311 BVP-1s in service in 1995 and 300 in 1996.[5] Currently there are 308 BVP-1s, 71 BPzV "Svatava"s and 205 OT-90s. There are also BRM-1Ks in service.[49] -
 Sri Lanka – 12 ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1994.[2] Currently there are 13 inservice.[50]
Sri Lanka – 12 ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1994.[2] Currently there are 13 inservice.[50] -
 South Ossetia – 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the South Ossetian Army and they were in service in 2007.[1]
South Ossetia – 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were claimed by the South Ossetian Army and they were in service in 2007.[1] -
 Sudan – 24 including 1 delivered by Belarus in 2004.[13]
Sudan – 24 including 1 delivered by Belarus in 2004.[13] -
 Syria – Syria received between 150 and 170 BMP-1s before the October 1973 Yom Kippur War. 2,300 ordered in 1977 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1989.[2] There were 2,250 in service in 1990 and 1995, 2,300 in 1996,[5] 2,250 in 2000 and 2001, 2,600 in 2003 and 2,100 in 2005.[51]
Syria – Syria received between 150 and 170 BMP-1s before the October 1973 Yom Kippur War. 2,300 ordered in 1977 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1989.[2] There were 2,250 in service in 1990 and 1995, 2,300 in 1996,[5] 2,250 in 2000 and 2001, 2,600 in 2003 and 2,100 in 2005.[51] -
 Tajikistan – 40 were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 9 in service in 2000 and 2005.[52] There are 11 now in service.
Tajikistan – 40 were inherited from former USSR in 1991. 9 in service in 2000 and 2005.[52] There are 11 now in service. -
 Turkmenistan – 538 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1995, 930 in 2000 and 2005. 51 BRM-1s in service in 1995 and 12 in 2000 and 2005.[53] Currently 156 BMP-1s are in service.
Turkmenistan – 538 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1995, 930 in 2000 and 2005. 51 BRM-1s in service in 1995 and 12 in 2000 and 2005.[53] Currently 156 BMP-1s are in service. -
 Ukraine – Around 2,525 in service in 1994,[16] 1,325 in 1995, 1,011 in 2000 and 1,008 in 2005. Also there were 490 BRM-1Ks in service in 1995 and 458 in 2000 and 2005.[54] A number of BMP-1s was modernized to BMP-1U standard while some were converted into ARVes.[55]
Ukraine – Around 2,525 in service in 1994,[16] 1,325 in 1995, 1,011 in 2000 and 1,008 in 2005. Also there were 490 BRM-1Ks in service in 1995 and 458 in 2000 and 2005.[54] A number of BMP-1s was modernized to BMP-1U standard while some were converted into ARVes.[55] -
 Uruguay – 10 ordered in 1995 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Czech service).[2][21] 5 ordered in 1996 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1998.[2] Between 3 and 5 ordered in 1996 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Czech service).[21]
Uruguay – 10 ordered in 1995 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Czech service).[2][21] 5 ordered in 1996 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1998.[2] Between 3 and 5 ordered in 1996 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Czech service).[21] -
 Uzbekistan – 180 BMP-1s are currently in service. 6 BRM-1s in service in 2000 and 2005.[56]
Uzbekistan – 180 BMP-1s are currently in service. 6 BRM-1s in service in 2000 and 2005.[56] -
 Vietnam – 150 along with 1500 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1981.600 BMP-1s and 600 BMP-2s are in service .[2]
Vietnam – 150 along with 1500 9M14M Malyutka ATGMs ordered in 1979 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1981.600 BMP-1s and 600 BMP-2s are in service .[2] -
 Yemen – 150 in service in 1996.[5]
Yemen – 150 in service in 1996.[5]
Former operators

East German BMP-1s on a parade in East Berlin, 7 October 1988.

Swedish Pbv 501A displayed at the museum Arsenalen in Sweden
-
 Chechen Republic of Ichkeria – 36 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in 1991–1992.
Chechen Republic of Ichkeria – 36 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in 1991–1992. -
 Czechoslovakia – 2,252 ordered in 1973 and delivered between 1973 and 1989 (most produced in Czechoslovakia while the rest was imported from the Soviet Union).[2] 1,006 BVP-1 and BVP-1KS, 265 BPzV "Svatava" reconnaissance vehicles and 620 OT-90 APCs right before the breakup of Czechoslovakia, passed on to successor states.[16] Czechoslovakia also produced 151 BMP-1P/c for East Germany.
Czechoslovakia – 2,252 ordered in 1973 and delivered between 1973 and 1989 (most produced in Czechoslovakia while the rest was imported from the Soviet Union).[2] 1,006 BVP-1 and BVP-1KS, 265 BPzV "Svatava" reconnaissance vehicles and 620 OT-90 APCs right before the breakup of Czechoslovakia, passed on to successor states.[16] Czechoslovakia also produced 151 BMP-1P/c for East Germany. -
 Finland – 195, bought in three batches. The first one which consisted of BMP-1 IFVs was delivered in June 1981 by the Soviet Union. The second one which consisted of BMP-1 and BMP-1K IFVs was delivered in summer of 1982 by the Soviet Union. A total of 85 BMP-1 and BMP-1K IFVs was delivered by the USSR. The third one which consisted of 110 units, was made out different variants of BMP-1/BMP-1P vehicles and was delivered in 1990 by Germany from ex-East German stocks (all were modernized in 1994–1997 by Patria Vammas Oy). There were 40 BMP-1 (+ native produced BMP-1TJ "Tuija" artillery reconnaissance vehicles) in service with the Finnish Army in 1995 and 1996.[5] The BMP-1 IFVs were withdrawn from Finnish Army service in 2004 but around 50 were saved and converted to command and artillery observing vehicles.
Finland – 195, bought in three batches. The first one which consisted of BMP-1 IFVs was delivered in June 1981 by the Soviet Union. The second one which consisted of BMP-1 and BMP-1K IFVs was delivered in summer of 1982 by the Soviet Union. A total of 85 BMP-1 and BMP-1K IFVs was delivered by the USSR. The third one which consisted of 110 units, was made out different variants of BMP-1/BMP-1P vehicles and was delivered in 1990 by Germany from ex-East German stocks (all were modernized in 1994–1997 by Patria Vammas Oy). There were 40 BMP-1 (+ native produced BMP-1TJ "Tuija" artillery reconnaissance vehicles) in service with the Finnish Army in 1995 and 1996.[5] The BMP-1 IFVs were withdrawn from Finnish Army service in 2004 but around 50 were saved and converted to command and artillery observing vehicles. -
 East Germany – 1,133 ordered in 1974 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1982 (some of the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2]
East Germany – 1,133 ordered in 1974 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1982 (some of the vehicles were produced in Czechoslovakia).[2] -
 West Germany/
West Germany/ Germany – Taken from East Germany's Army. After the reunification, the West-German Bundeswehr modified more than 851 vehicles (mainly BMP-1P model) and brought them to NATO safety standards and gave them the designation BMP-1A1 Ost. There were 764 BMP-1A1 Ost vehicles in 1994 and 450 in 1996.[5][57] Eventually all were scrapped or sold to other countries. 110 different variants of BMP-1/BMP-1P were sold to Finland in 1990 (these weren't modified). 501 BMP-1A1 Ost IFVs were sold to Greece in 1993–1994 and 350 BMP-1A1 Ost IFVs were sold to Sweden in the beginning of the 1990s.[58]
Germany – Taken from East Germany's Army. After the reunification, the West-German Bundeswehr modified more than 851 vehicles (mainly BMP-1P model) and brought them to NATO safety standards and gave them the designation BMP-1A1 Ost. There were 764 BMP-1A1 Ost vehicles in 1994 and 450 in 1996.[5][57] Eventually all were scrapped or sold to other countries. 110 different variants of BMP-1/BMP-1P were sold to Finland in 1990 (these weren't modified). 501 BMP-1A1 Ost IFVs were sold to Greece in 1993–1994 and 350 BMP-1A1 Ost IFVs were sold to Sweden in the beginning of the 1990s.[58] -
 Sweden – 12 ordered from Germany in 1993 and delivered between 1995 and 1997 for trials. 360 ordered from Germany in 1994 and delivered between 1998 and 2001 (the vehicles were modernized in Poland before being delivered).[2] All upgraded to Pbv 501A standard. 340 in service in 2006. In the same year they were withdrawn from service and later were sold.[58]
Sweden – 12 ordered from Germany in 1993 and delivered between 1995 and 1997 for trials. 360 ordered from Germany in 1994 and delivered between 1998 and 2001 (the vehicles were modernized in Poland before being delivered).[2] All upgraded to Pbv 501A standard. 340 in service in 2006. In the same year they were withdrawn from service and later were sold.[58] -
 Soviet Union – More than 20,000 BMP-1s and vehicles based on it produced. 5,100 BMP-1s ordered in 1972 from Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1972 and 1988.[2] More than 14,473 BMP-1s before the Soviet War in Afghanistan. 24,000 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1985.[46] About 14,353 BMP-1s and vehicles based on it right before the breakup of USSR, passed on to successor states.
Soviet Union – More than 20,000 BMP-1s and vehicles based on it produced. 5,100 BMP-1s ordered in 1972 from Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1972 and 1988.[2] More than 14,473 BMP-1s before the Soviet War in Afghanistan. 24,000 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1985.[46] About 14,353 BMP-1s and vehicles based on it right before the breakup of USSR, passed on to successor states. -
 North Yemen – 150
North Yemen – 150 -
 South Yemen – 100 ordered in 1983 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1984. 40 ordered in 1986 from Soviet Union and delivered in 1986.[2]
South Yemen – 100 ordered in 1983 from Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1984. 40 ordered in 1986 from Soviet Union and delivered in 1986.[2] -
 Lebanon – A few BMP-1s were captured from the Syrian Army by the Lebanese Arab Army (LAA) in 1976.[59][60] An unknown number was provided on loan between 1983 and 1990 to the Druze People’s Liberation Army (PLA) militia by Syria and the Soviet Union.
Lebanon – A few BMP-1s were captured from the Syrian Army by the Lebanese Arab Army (LAA) in 1976.[59][60] An unknown number was provided on loan between 1983 and 1990 to the Druze People’s Liberation Army (PLA) militia by Syria and the Soviet Union.
Evaluation only operators
-
 Chad – Captured 36 BMP-1s during the Chadian–Libyan conflict, transferred in 1987 to USA for technical evaluation.[2]
Chad – Captured 36 BMP-1s during the Chadian–Libyan conflict, transferred in 1987 to USA for technical evaluation.[2] -
 South Africa – Captured 6 BMP-1s during the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale. One experimentally fitted with IST Dynamics Unmanned Multi-Weapon Platform.[44]
South Africa – Captured 6 BMP-1s during the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale. One experimentally fitted with IST Dynamics Unmanned Multi-Weapon Platform.[44] -
 United States – Captured 4 BMP-1s during a number of conflicts.[16] Received 36 ex-Libyan BMP-1s in 1987 from Chad for technical evaluation. Received 19 BMP-1s from Germany in 1991 and 3 in 1993.[2] The captured and received vehicles were evaluated and used in the OPFOR role. They later found their way to museums.
United States – Captured 4 BMP-1s during a number of conflicts.[16] Received 36 ex-Libyan BMP-1s in 1987 from Chad for technical evaluation. Received 19 BMP-1s from Germany in 1991 and 3 in 1993.[2] The captured and received vehicles were evaluated and used in the OPFOR role. They later found their way to museums.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to BMP-1. |
- 1 2 3 АБХАЗИЯ.ORG :: Статьи : Почему Грузия проиграет будущую войну. Abkhaziya.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 SIPRI Arms Transfers Database. Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ История России. Всемирная, мировая история – Афганистан в конце XX в. Istorya.ru. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Defence Express News – РОССИЯ И АФГАНИСТАН ВЫПОЛНЯЮТ ДОГОВОРЕННОСТИ, ЗАКЛЮЧЕННЫЕ МЕЖДУ ВОЕННЫМИ ВЕДОМСТВАМИ ДВУХ СТРАН В КАБУЛЕ В 2002 Г. Defense-ua.com (2003-01-29). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Pancerni.net 2. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Россия и Ангола подписали документ о военно-техническом сотрудничестве Archived 4 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑
- ↑ Angolan army armyrecognition.com
- 1 2 Международный Контроль Над Обычными Вооружениями И Неконтролируемое Оружие. (PDF) . Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 Belarus Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Bulgarian army Archived 13 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine. armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Cambodian army armyrecognition.com
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BMP-1. Deagel.com. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ People's Liberation Army. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 3 Sino Defense. Sinodefence.com (2009-02-20). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 World Defence Almanac
- ↑ Czech Ministry of Defense. Army.cz. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Czech army armyrecognition.com
- 1 2 Georgia Army. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Theodore L Valmas (11 December 2014). "Greece trials ZU-23-2 armed BMP-1P infantry fighting vehicle". IHS Jane's Defence Weekly. Retrieved 13 December 2014.
- 1 2 3 Czech/web Archived 2 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Hungarian army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Indian Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Land Forces Site – BMP-1. Bharat Rakshak. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 Iranian Ground Forces Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Iraqi Ground Forces Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Shapir, Yiftah S., Middle East Military Balance, Tel Aviv University, 6, 7 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2008. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ↑ Kazak Ground Forces Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Kyrgyz-Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Libyan Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Libyan army Archived 9 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine. armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Армии стран мира : Вооруженные силы иностранных государств на 2001 год : М. Soldiering.ru. Retrieved on 2012-12-18.
- ↑ Equipment Holdings – Korean People's Army globalsecurity.org
- ↑ MON Archived 1 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine.. Wp.mil.pl. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ disarmament.un.org
- ↑ disarmament.un.org 2
- ↑ disarmament.un.org 3
- ↑ disarmament.un.org 4
- ↑ disarmament.un.org 5
- ↑ Wojsko Polskie AD 2004 Archived 6 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine.. Militarium (2008-09-04). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Wojsko Polskie AD 2006 Archived 6 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine.. Militarium (2008-09-06). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Ministerstwo Obrony Narodowej Archived 18 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine.. Mon.gov.pl (2006-01-08). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Uzbrojenie Wojska Polskiego w 2008 r Archived 9 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine.. Militarium (2008-08-18). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 JED The Military Equipment Directory
- ↑ Ruandan army armyrecognition.com
- 1 2 Russian Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- 1 2 Warfare.ru. Warfare.ru (2010-09-05). Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ A Brief Guide to Russian Armored Fighting Vehicles
- ↑ Slovak army Archived 3 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine. armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Sri Lankan army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Syria – Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Tajik-Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Turkmen-Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Ground Forces Equipment – Ukraine. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Ukrainian army Archived 24 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine. armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Uzbek-Army Equipment. Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Malyshev S. (2002). Tanks in Russia. Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty BMP-1 (1964–2000). Russian Motor Books. ISBN 5-09-873406-4.
- 1 2 Swedish Defence Materiel Administration. Fmv.se. Retrieved on 6 January 2012.
- ↑ Samer Kassis, 30 Years of Military Vehicles in Lebanon, Beirut: Elite Group, 2003. ISBN 9953-0-0705-5, p. 72.
- ↑ Samer Kassis, Véhicules Militaires au Liban/Military Vehicles in Lebanon 1975-1981, Trebia Publishing, Chyah 2012, ISBN 978-9953-0-2372-4, p. 66.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.